Hydrocodone Bitartrate and Acetaminophen (hydrocodone bitartrate 5 mg acetaminophen 500 mg) Dailymed
Generic: hydrocodone bitartrate
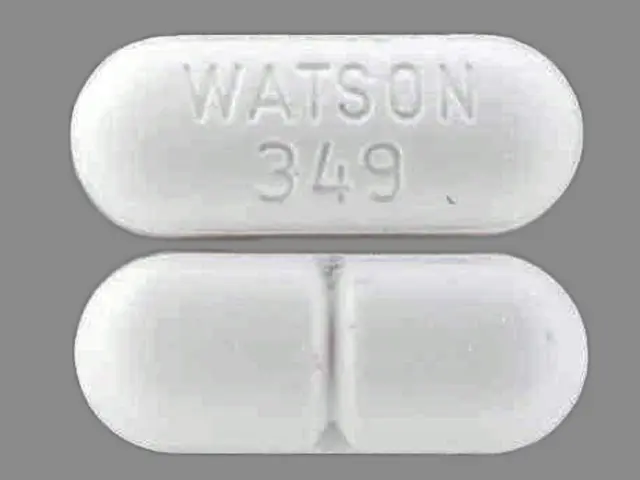
IMPRINT: WATSON 349
SHAPE: oval
COLOR: white SCORE: 2
All Imprints
hydrocodone bitartrate 5 mgacetaminophen 500 mg - watson 349 oval white
hydrocodone bitartrate 7.5 mgacetaminophen 750 mg - watson 387 oval white
hydrocodone bitartrate 7.5 mgacetaminophen 325 mg - watson 3203 oval orange
hydrocodone bitartrate 10 mgacetaminophen 500 mg - watson 540 oval blue
hydrocodone bitartrate 10 mgacetaminophen 325 mg - watson 853 oval yellow
hydrocodone bitartrate 7.5 mgacetaminophen 650 mg - watson 502 oval pink
hydrocodone bitartrate 10 mgacetaminophen 650 mg - watson 503 oval green
hydrocodone bitartrate 2.5 mgacetaminophen 500 mg - watson 388 oval white
hydrocodone bitartrate 7.5 mgacetaminophen 500 mg - watson 385 oval white
Boxed Warning
Boxed Warning
Go PRO for all pill images
Boxed Warning
Hepatotoxicity Acetaminophen has been associated with cases of acute liver failure, at times resulting in liver transplant and death. Most of the cases of liver injury are associated with the use of acetaminophen at doses that exceed 4000 milligrams per day, and often involve more than one acetaminophen containing product.
Description
Hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen is supplied in tablet form for oral administration.Hydrocodone bitartrate is an opioid analgesic and antitussive and occurs as fine, white crystals or as a crystalline powder. It is affected by light. The chemical name is 4,5tartrate (1:1) hydrate (2:5). It has the following structural formula: Acetaminophen, 4a slightly bitter, white, odorless, crystalline powder, is a non-opiate, non-salicylate analgesic and antipyretic. It has the following structural formula:
Hydrocodone Bitartrate and Acetaminophen Tablets USP for oral administration are available in a variety of strengths as described in the following table. StrengthHydrocodone BitartrateAcetaminophen2.5 mg/500 mg2.5 mg500 mg5 mg/500 mg5 mg500 mg7.5 mg/325 mg7.5 mg325 mg7.5 mg/500 mg7.5 mg500 mg7.5 mg/650 mg7.5 mg650 mg7.5 mg/750 mg7.5 mg750 mg10 mg/325 mg10 mg325 mg10 mg/500 mg10 mg500 mg10 mg/650 mg10 mg650 mg10 mg/660 mg10 mg660 mg10 mg/750 mg10 mg750 mg
Clinical Pharmacology
Hydrocodone is a semisynthetic narcotic analgesic and antitussive with multiple actions qualitatively similar to those of codeine. Most of these involve the central nervous system and smooth muscle. The precise mechanism of action of hydrocodone and other opiates is not known, although it is believed to relate to the existence of opiate receptors in the central nervous system. In addition to analgesia, narcotics may produce drowsiness, changes in mood and mental clouding. Pharmacokinetics: The behavior of the individual components is described below. Hydrocodone: Following a 10 mg oral dose of hydrocodone administered to five adult male subjects, the mean peak concentration was 23.65.2 ng/mL. Maximum serum levels were achieved at 1.30.3 hours and the half-life was determined to be 3.80.3 hours. Hydrocodone exhibits a complex pattern of metabolism including O-demethylation, N-demethylation and 6-keto reduction to the corresponding 6-and 6-hydroxy-metabolites. See OVERDOSAGEfor toxicity information. Acetaminophen: Acetaminophen is rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and is distributed throughout most body tissues. The plasma half-life is 1.25 to 3 hours, but may be increased by liver damage and following overdosage. Elimination of acetaminophen is principally by liver metabolism (conjugation) and subsequent renal excretion of metabolites. Approximately 85% of an oral dose appears in the urine within 24 hours of administration, most as the glucuronide conjugate, with small amounts of other conjugates and unchanged drug. See OVERDOSAGEfor toxicity information.
Indications & Usage
Hydrocodone and acetaminophen tablets are indicated for the relief of moderate to moderately severe pain.
Contraindications
This product should not be administered to patients who have previously exhibited hypersensitivity to hydrocodone or acetaminophen.Patients known to be hypersensitive to other opioids may exhibit cross-sensitivity to hydrocodone.
Warnings
Hepatotoxicity Acetaminophen has been associated with cases of acute liver failure, at times resulting in liver transplant and death. Most of the cases of liver injury are associated with the use of acetaminophen at doses that exceed 4000 milligrams per day, and often involve more than one acetaminophen containing product. The excessive intake of acetaminophen may be intentional to cause self-harm or unintentional as patients attempt to obtain more pain relief or unknowingly take other acetaminophen-containing products. The risk of acute liver failure is higher in individuals with underlying liver disease and in individuals who ingest alcohol while taking acetaminophen. Instruct patients to look for acetaminophen or APAP on package labels and not to use more than one product that contains acetaminophen. Instruct patients to seek medical attention immediately upon ingestion of more than 4000 milligrams of acetaminophen per day, even if they feel well. Hypersensitivity/anaphylaxis There have been post-marketing reports of hypersensitivity and anaphylaxis associated with use of acetaminophen. Clinical signs included swelling of the face, mouth, and throat, respiratory distress, urticaria, rash, pruritus, and vomiting. There were infrequent reports of life-threatening anaphylaxis requiring emergency medical attention. Instruct patients to discontinue Hydrocodone Bitartrate and Acetaminophen Tablets, USP immediately and seek medical care if they experience these symptoms. Do not prescribe Hydrocodone Bitartrate and Acetaminophen Tablets, USP for patients with acetaminophen allergy. Respiratory Depression:At high doses or in sensitive patients, hydrocodone may produce dose-related respiratory depression by acting directly on the brain stem respiratory center. Hydrocodone also affects the center that controls respiratory rhythm, and may produce irregular and periodic breathing. Head Injury and Increased Intracranial Pressure:The respiratory depressant effects of narcotics and their capacity to elevate cerebrospinal fluid pressure may be markedly exaggerated in the presence of head injury, other intracranial lesions or a pre-existing increase in intracranial pressure. Furthermore, narcotics produce adverse reactions which may obscure the clinical course of patients with head injuries. Acute Abdominal Conditions:The administration of narcotics may obscure the diagnosis or clinical course of patients with acute abdominal conditions.
Precautions
General: Special Risk Patients:As with any narcotic analgesic agent, hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen tablets should be used with caution in elderly or debilitated patients, and those with severe impairment of hepatic or renal function, hypothyroidism, Addison's disease, prostatic hypertrophy or urethral stricture. The usual precautions should be observed and the possibility of respiratory depression should be kept in mind. Cough Reflex:
Information For Owners/caregivers
Information for Patients/Caregivers      Do not take Hydrocodone Bitartrate and Acetaminophen Tablets, USP if you are allergic to any of its ingredients.      If you develop signs of allergy such as a rash or difficulty breathing stop taking Hydrocodone Bitartrate and Acetaminophen Tablets, USP and contact your healthcare provider immediately.      Do not take more than 4000 milligrams of acetaminophen per day. Call your doctor if you took more than the recommended dose. Alcohol and other CNS depressants may produce an additive CNS depression, when taken with this combination product, and should be avoided. Hydrocodone may be habit-forming. Patients should take the drug only for as long as it is prescribed, in the amounts prescribed, and no more frequently than prescribed.
Laboratory Tests
In patients with severe hepatic or renal disease, effects of therapy should be monitored with serial liver and/or renal function tests.
Drug Interactions
Patients receiving narcotics, antihistamines, antipsychotics, antianxiety agents, or other CNS depressants (including alcohol) concomitantly with hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen tablets may exhibit an additive CNS depression. When combined therapy is contemplated, the dose of one or both agents should be reduced. The use of MAO inhibitors or tricyclic antidepressants with hydrocodone preparations may increase the effect of either the antidepressant or hydrocodone.
Drug & Or Laboratory Test Interactions
Acetaminophen may produce false-positive test results for urinary 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid.
Carcinogenesis & Mutagenesis & Impairment Of Fertility
No adequate studies have been conducted in animals to determine whether hydrocodone or acetaminophen have a potential for carcinogenesis, mutagenesis, or impairment of fertility.
Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects: Pregnancy Category C: There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen tablets should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus. Nonteratogenic Effects: Babies born to mothers who have been taking opioids regularly prior to delivery will be physically dependent. The withdrawal signs include irritability and excessive crying, tremors, hyperactive reflexes, increased respiratory rate, increased stools, sneezing, yawning, vomiting, and fever. The intensity of the syndrome does not always correlate with the duration of maternal opioid use or dose. There is no consensus on the best method of managing withdrawal.
Labor & Delivery
As with all narcotics, administration of this product to the mother shortly before delivery may result in some degree of respiratory depression in the newborn, especially if higher doses are used.
Nursing Mothers
Acetaminophen is excreted in breast milk in small amounts, but the significance of its effects on nursing infants is not known. It is not known whether hydrocodone is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk and because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from hydrocodone and acetaminophen, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established.
Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of hydrocodone bitartrate 5 mg and acetaminophen 500 mg did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy. Hydrocodone and the major metabolites of acetaminophen are known to be substantially excreted by the kidney. Thus the risk of toxic reactions may be greater in patients with impaired renal function due to the accumulation of the parent compound and/or metabolites in the plasma. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection, and it may be useful to monitor renal function. Hydrocodone may cause confusion and over-sedation in the elderly; elderly patients generally should be started on low doses of hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen tablets and observed closely.
Adverse Reactions
The most frequently reported adverse reactions are lightheadedness, dizziness, sedation, nausea, and vomiting. These effects seem to be more prominent in ambulatory than in nonambulatory patients, and some of these adverse reactions may be alleviated if the patient lies down. Other adverse reactions include: Central Nervous System:Drowsiness, mental clouding, lethargy, impairment of mental and physical performance, anxiety, fear, dysphoria, psychic dependence, and mood changes. Gastrointestinal System:Prolonged administration of hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen tablets may produce constipation. Genitourinary System:Ureteral spasm, spasm of vesical sphincters, and urinary retention have been reported with opiates. Respiratory Depression:Hydrocodone bitartrate may produce dose-related respiratory depression by acting directly on the brain stem respiratory center (see OVERDOSAGE). Special Senses:Cases of hearing impairment or permanent loss have been reported predominantly in patients with chronic overdose. Dermatological:Skin rash, pruritus. The following adverse drug events may be borne in mind as potential effects of acetaminophen: allergic reactions, rash, thrombocytopenia, agranulocytosis.Potential effects of high dosage are uled in the OVERDOSAGEsection.
Drug Abuse And Dependence
Controlled Substance:Hydrocodone Bitartrate and Acetaminophen Tablets are classified as a Schedule III controlled substance. Abuse and Dependence: Physical dependence, the condition in which continued administration of the drug is required to prevent the appearance of a withdrawal syndrome, assumes clinically significant proportions only after several weeks of continued narcotic use, although some mild degree of physical dependence may develop after a few days of narcotic therapy. Tolerance, in which increasingly large doses are required in order to produce the same degree of analgesia, is manifested initially by a shortened duration of analgesic effect, and subsequently by decreases in the intensity of analgesia. The rate of development of tolerance varies among patients.
Overdosage
Following an acute overdosage, toxicity may result from hydrocodone or acetaminophen. Signs and Symptoms Hydrocodone:Serious overdose with hydrocodone is characterized by respiratory depression (a decrease in respiratory rate and/or tidal volume, Cheyne-Stokes respiration, cyanosis), extreme somnolence progressing to stupor or coma, skeletal muscle flaccidity, cold and clammy skin, and sometimes bradycardia and hypotension. In severe overdosage, apnea, circulatory collapse, cardiac arrest and death may occur. Acetaminophen:In acetaminophen overdosage: dose-dependent, potentially fatal hepatic necrosis is the most serious adverse effect. Renal tubular necrosis, hypoglycemic coma, and coagulation defects may also occur. Early symptoms following a potentially hepatotoxic overdose may include: nausea, vomiting, diaphoresis and general malaise. Clinical and laboratory evidence of hepatic toxicity may not be apparent until 48 to 72 hours post-ingestion. Treatment:A single or multiple drug overdose with hydrocodone and acetaminophen is a potentially lethal polydrug overdose, and consultation with a regional poison control center is recommended. Immediate treatment includes support of cardiorespiratory function and measures to reduce drug absorption. Oxygen, intravenous fluids, vasopressors, and other supportive measures should be employed as indicated. Assisted or controlled ventilation should also be considered. For hydrocodone overdose, primary attention should be given to the reestablishment of adequate respiratory exchange through provision of a patent airway and the institution of assisted or controlled ventilation. The narcotic antagonist naloxone hydrochloride is a specific antidote against respiratory depression which may result from overdosage or unusual sensitivity to narcotics, including hydrocodone. Since the duration of action of hydrocodone may exceed that of the antagonist, the patient should be kept under continued surveillance, and repeated doses of the antagonist should be administered as needed to maintain adequate respiration. A narcotic antagonist should not be administered in the absence of clinically significant respiratory or cardiovascular depression. Vigorous supportive therapy is required in severe intoxication. Procedures to limit the continuing absorption of the drug must be readily performed since the hepatic injury is dose dependent and occurs early in the course of intoxication.
Dosage & Administration
Dosage should be adjusted according to the severity of the pain and the response of the patient. However, it should be kept in mind that tolerance to hydrocodone can develop with continued use and that the incidence of untoward effects is dose related. 2.5 mg/500 mg 5 mg/500 mg The usual adult dosage is one or two tablets every four to six hours as needed for pain. The total daily dosage should not exceed 8 tablets. 7.5 mg/325 mg 7.5 mg/500 mg 7.5 mg/650 mg The usual adult dosage is one tablet every four to six hours as needed for pain. The total daily dosage should not exceed 6 tablets. 7.5 mg/750 mg The usual adult dosage is one tablet every four to six hours as needed for pain. The total daily dosage should not exceed 5 tablets. 10 mg/325 mg 10 mg/500 mg 10 mg/650 mg 10 mg/660 mg The usual adult dosage is one tablet every four to six hours as needed for pain. The total daily dosage should not exceed 6 tablets. 10 mg/750 mg The usual adult dosage is one tablet every four to six hours as needed for pain. The total daily dosage should not exceed 5 tablets.
How Supplied
Hydrocodone Bitartrate and Acetaminophen Tablets USP are available in the following strengths: 2.5 mg/500 mg 2.5 mg hydrocodone bitartrate and 500 mg acetaminophen, oblong, white tablets bisected on one side and debossed with WATSON 388on the other side, supplied in bottles of 100. 5 mg/500 mg 5 mg hydrocodone bitartrate and 500 mg acetaminophen, capsule-shaped, white tablets bisected on one side and debossed with WATSON 349on the other side, supplied in bottles of 100 and 500. 7.5 mg/325 mg 7.5 mg hydrocodone bitartrate and 325 mg acetaminophen, capsule- shaped, light orange tablets bisected on one side and debossed with WATSON 3203on the other side, supplied in bottles of 100. 7.5 mg/500 mg 7.5 mg hydrocodone bitartrate and 500 mg acetaminophen, capsule- shaped, white tablets bisected on one side and debossed with WATSON 385on the other side, supplied in bottles of 100 and 500. 7.5 mg/650 mg 7.5 mg hydrocodone bitartrate and 650 mg acetaminophen, capsule- shaped, pink tablets bisected on one side and debossed with WATSON 502on the other side, supplied in bottles of 100 and 500. 7.5 mg/750 mg 7.5 mg hydrocodone bitartrate and 750 mg acetaminophen, oblong, white tablets bisected on one side and debossed with WATSON 387on the other side, supplied in bottles of 100 and 500. 10 mg/325 mg 10 mg hydrocodone bitartrate and 325 mg acetaminophen, capsule-shaped, yellow tablets bisected on one side and debossed with WATSON 853on the other side, supplied in bottles of 100 and 500. 10 mg/500 mg 10 mg hydrocodone bitartrate and 500 mg acetaminophen, capsule-shaped, blue tablets bisected on one side and debossed with WATSON 540on the other side, supplied in bottles of 100 and 500. 10 mg/650 mg 10 mg hydrocodone bitartrate and 650 mg acetaminophen, capsule-shaped, light green tablets bisected on one side and debossed with WATSON 503on the other side, supplied in bottles of 100 and 500. 10 mg/660 mg 10 mg hydrocodone bitartrate and 660 mg acetaminophen, oval-shaped, white tablets bisected on one side and debossed with WATSON 517on the other side, supplied in bottles of 100 and 500. 10 mg/750 mg 10 mg hydrocodone bitartrate and 750 mg acetaminophen, capsule-shaped, yellow tablets bisected on one side and debossed with WATSON 3228on the other side, supplied in bottles of 100.
Storage And Handling
Store at 20(68[See USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container with a child-resistant closure.
Package Label.principal Display Panel Section
DRUG: Hydrocodone Bitartrate and Acetaminophen GENERIC: HYDROCODONE BITARTRATE DOSAGE: TABLET ADMINSTRATION: ORAL NDC: 24236-432-07 STRENGTH:5 mg COLOR: white SHAPE: OVAL SCORE: Two even pieces SIZE: 18 mm IMPRINT: 12 QTY: 12 ![]()
![]()
DISCLAIMER:
"This tool does not provide medical advice, and is for informational and educational purposes only, and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, treatment or diagnosis. Call your doctor to receive medical advice. If you think you may have a medical emergency, please dial 911."
"Do not rely on openFDA to make decisions regarding medical care. While we make every effort to ensure that data is accurate, you should assume all results are unvalidated. We may limit or otherwise restrict your access to the API in line with our Terms of Service."
"This product uses publicly available data from the U.S. National Library of Medicine (NLM), National Institutes of Health, Department of Health and Human Services; NLM is not responsible for the product and does not endorse or recommend this or any other product."
PillSync may earn a commission via links on our site