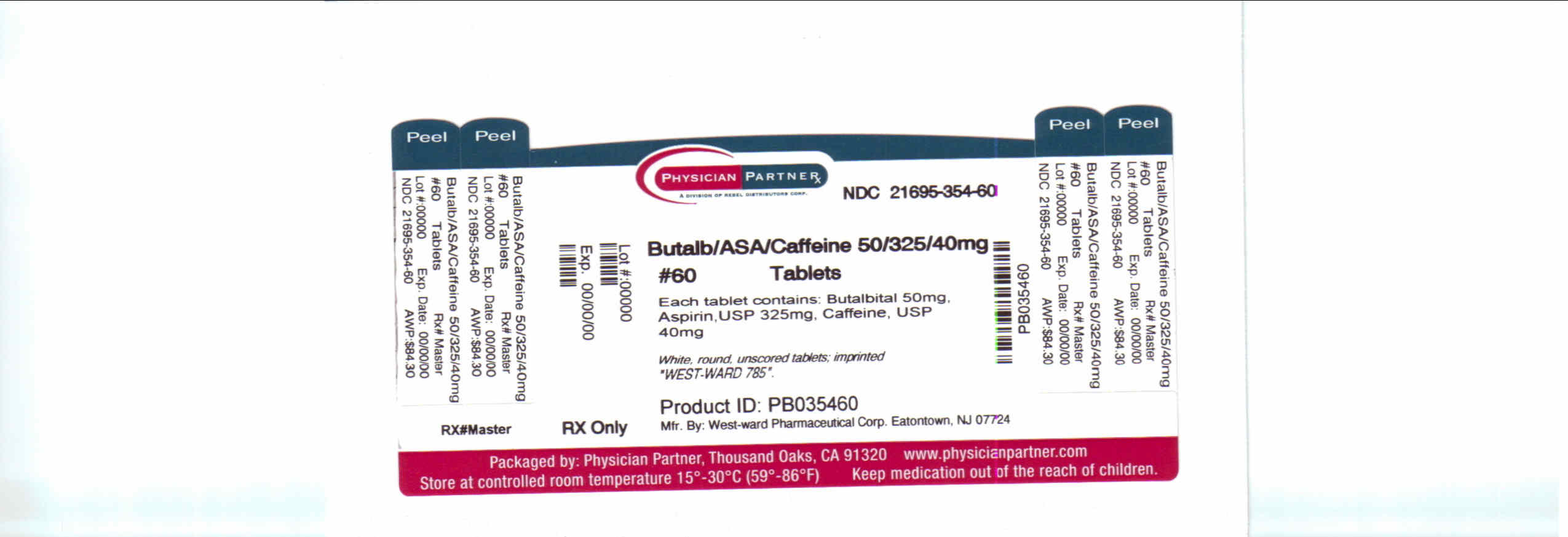
Butalbital, Aspirin and Caffeine (butalbital 50 mg aspirin 325 mg caffeine 40 mg) Dailymed
Generic: butalbital, aspirin and caffeine is used for the treatment of Arthritis, Rheumatoid Blood Coagulation Disorders Blood Platelet Disorders Cerebral Infarction Ischemic Attack, Transient Chickenpox Child, Preschool Fever Gout Hematemesis Hemorrhagic Disorders Infant Inflammation Melena Myocardial Infarction Nasal Polyps Osteoarthritis Pain Pre-Eclampsia Pregnancy Trimester, Third Rheumatic Fever Apnea Fatigue Headache Porphyrias Pregnancy
Go PRO for all pill images
Description:
Each Butalbital, Aspirin, and Caffeine Tablet for oral administration contains:
Butalbital, USP.....................50 mg
Aspirin, USP.......................325 mg
Caffeine, USP.......................40 mg
Butalbital, 5-allyl-5-isobutylbarbituric acid, a white, odorless, crystalline powder having a slightly bitter taste, is a short to intermediate-acting barbiturate. It has the following structural formula:

C11H16N2O3 M.W. 224.26
Aspirin, salicylic acid acetate, is a non-opiate analgesic, anti-inflammatory and antipyretic agent. It occurs as a white, crystalline tabular or needle-like powder and is odorless or has a faint odor. It has the following structural formula:

C9H8O4 M.W. 180.16
Caffeine, 1,3,7,-trimethylxanthine, is a central nervous system stimulant which occurs as a white powder or white gulening needles. It also has a bitter taste. Its structure is as follows:

C8H10N4O2 M.W. 194.19
Inactive Ingredients: Corn Starch, Hydrogenated Vegetable Oil, Microcrystalline Cellulose, Pregelatinized Starch, Sodium Starch Glycolate and Talc.
Clinical Pharmacology:
Pharmacologically, Butalbital, Aspirin, and Caffeine Tablets combine the analgesic properties of aspirin with the anxiolytic and muscle relaxant properties of butalbital.
The clinical effectiveness of a product containing butalbital, aspirin, and caffeine in tension headache has been established in double-blind, placebo-controlled, multiclinic trials. A factorial design study compared the combination product with each of its major components. This study demonstrated that each component contributes to the efficacy of the combination product in the treatment of the target symptoms of tension headache (headache pain, psychic tension, and muscle contraction in the head, neck, and shoulder region). For each symptom and the symptom complex as a whole, the product containing butalbital, aspirin, and caffeine was shown to have significantly superior clinical effects to either of the major components alone.
Indications And Usage:
Butalbital, Aspirin and Caffeine Tablets are indicated for the relief of the symptom complex of tension (or muscle contraction) headache.
Contraindications:
Hypersensitivity to aspirin, caffeine or barbiturates. Patients with porphyria.
Precautions:
1. General:
Butalbital, Aspirin, and Caffeine Tablets should be used with caution in patients with certain medical problems, including those with a history of asthma, allergies and nasal polyps. Also, the drug must be prescribed carefully for patients with hemophilia or other bleeding problems, peptic ulcer, renal impairment, or a history of drug abuse or dependence.
2. Information for Patients:
Butalbital, Aspirin, and Caffeine Tablets may impair the mental and/or physical abilities required for the performance of potentially hazardous tasks, such as driving a car or operating machinery. The patient should be cautioned accordingly.
3. Drug Interactions:
Patients receiving narcotic analgesics, antipsychotics, antianxiety agents, or other CNS depressants (including alcohol) concomitantly with Butalbital, Aspirin, and Caffeine Tablets may exhibit additive CNS depressant effects. When combined therapy is contemplated, the dose of one or both agents should be reduced.
DRUGS EFFECT Aspirin w/anti-inflammatory agents
Increasedulcerogenic effects.
Butalbital w/coumarin anticoagulants
Decreased effect ofanticoagulant because ofincreasedmetabolismresulting fromenzyme induction.
Butalbital w/tricyclic antidepressants
Decreased bloodlevels of theantidepressant.
4. Usage in Pregnancy:
Adequate studies have not been performed in animals to determine whether this drug affects fertility in males or females, has teratogenic potential or has other adverse effects on the fetus. While there are no well-controlled studies in pregnant women, over twenty years of marketing and clinical experience does not include any positive evidence of adverse effects on the fetus. Although there is no clearly defined risk, such experience cannot exclude the possibility of infrequent or subtle damage to the human fetus. Butalbital, Aspirin, and Caffeine Tablets should be used in pregnant women only when clearly needed.
5. Nursing Mothers:
The effects of Butalbital, Aspirin, and Caffeine Tablets on infants of nursing mothers are not known. Salicylates and barbiturates are excreted in the breast milk of nursing mothers. The serum levels in infants are believed to be insignificant with therapeutic doses.
6. Pediatric Use:
Safety and effectiveness in children below the age of 12 have not been established.
Adverse Reactions:
The most frequent adverse reactions are drowsiness and dizziness. Less frequent adverse reactions are lightheadedness and gastrointestinal disturbances including nausea, vomiting, and flatulence. Mental confusion or depression can occur due to intolerance or overdosage of butalbital.
Several cases of dermatological reactions including toxic epidermal necrolysis and erythema multiforme have been reported.
Drug Abuse And Dependence:
Butalbital, Aspirin, and Caffeine Tablets are classified as a Schedule III controlled substance.
Prolonged use of barbiturates can produce drug dependence, characterized by psychic dependence, and less frequently, physical dependence and tolerance. The abuse liability of Butalbital, Aspirin, and Caffeine Tablets are similar to that of other barbiturate-containing drug combinations. Caution should be exercised when prescribing medication for patients with a known propensity for taking excessive quantities of drugs, which is not uncommon in patients with chronic tension headache.
Overdosage:
Symptoms: The toxic effects of acute overdosage of Butalbital, Aspirin, and Caffeine Tablets are attributable mainly to its barbiturate component, and, to a lesser extent, aspirin. Because toxic effects of caffeine occur in very high dosages only, the possibility of significant caffeine toxicity from Butalbital, Aspirin, and Caffeine Tablet overdosage in unlikely. Symptoms attributable to acute barbiturate poisoning include drowsiness, confusion, and coma; respiratory depression; hypotension; shock. Symptoms attributable to acute aspirin poisoning include hyperpnea; acid-base disturbances with development of metabolic acidosis; vomiting and abdominal pain; tinnitus; hyperthermia; hypoprothrombinemia; restlessness; delirium; convulsions. Acute caffeine poisoning may cause insomnia, restlessness, tremor, and delirium; tachycardia and extrasystoles.
Treatment: Treatment consists primarily of management of barbiturate intoxication and the correction of the acid-base imbalance due to salicylism. Vomiting should be induced mechanically or with emetics in the conscious patient. Gastric lavage may be used if the pharyngeal and laryngeal reflexes are present and if less than four hours have elapsed since ingestion. A cuffed endotracheal tube should be inserted before gastric lavage of the unconscious patient and when necessary to provide assisted respiration. Diuresis, alkalinization of the urine, and correction of electrolyte disturbances should be accomplished through administration of intravenous fluids such as 1% sodium bicarbonate in 5% dextrose injection. Meticulous attention should be given to maintaining adequate pulmonary ventilation. Correction of hypotension may require the administration of norepinephrine bitartrate of phenylephrine hydrochloride by intravenous infusion. In severe cases of intoxication, peritoneal dialysis, hemodialysis, or exchange transfusion may be lifesaving. Hypoprothrombinemia should be treated with Vitamin K, intravenously.
Dosage And Administration:
Oral: One or two tablets every four hours as needed. Do not exceed 6 tablets per day.
Medication should be taken with food or a full glass of water or milk to lessen gastric irritation caused by aspirin.
How Supplied:
Butalbital, Aspirin and Caffeine Tablets, USP 50 mg/325 mg/40 mg: White, round, unscored tablets; imprinted “West-ward 785”.
Bottles of 60 tablets, NDC 21695-354-60.
Store at 20-25°C (68-77°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Protect from light and moisture.
Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container as defined in the USP using a child-resistant closure.
Manufactured By: West-ward Pharmaceutical Corp. Eatontown, NJ 07724Revised April 2003
Repackaged by:
Rebel Distributors Corp
Thousand Oaks, CA 91320
Principal Display Panel
DISCLAIMER:
"This tool does not provide medical advice, and is for informational and educational purposes only, and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, treatment or diagnosis. Call your doctor to receive medical advice. If you think you may have a medical emergency, please dial 911."
"Do not rely on openFDA to make decisions regarding medical care. While we make every effort to ensure that data is accurate, you should assume all results are unvalidated. We may limit or otherwise restrict your access to the API in line with our Terms of Service."
"This product uses publicly available data from the U.S. National Library of Medicine (NLM), National Institutes of Health, Department of Health and Human Services; NLM is not responsible for the product and does not endorse or recommend this or any other product."
PillSync may earn a commission via links on our site