Cephalexin (cephalexin 500 mg) Dailymed
Generic: cephalexin is used for the treatment of Bites, Human Bone Diseases, Infectious Endocarditis, Bacterial Escherichia coli Infections Haemophilus Infections Klebsiella Infections Otitis Media Pharyngitis Proteus Infections Staphylococcal Infections Streptococcal Infections Surgical Wound Infection Urinary Tract Infections Skin Diseases, Bacterial Pneumonia, Bacterial Soft Tissue Infections Moraxellaceae Infections
Go PRO for all pill images
1 Indications And Usage
Cephalexin is a cephalosporin antibacterial drug indicated for the treatment of the following infections caused by susceptible isolates of designated bacteria:
- Respiratory tract infection (
1.1 )- Otitis media (
1.2 )- Skin and skin structure infections (
1.3 )- Bone infections (
1.4 )- Genitourinary tract infections (
1.5 )
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of cephalexin capsules, and cephalexin for oral suspension and other antibacterial drugs, cephalexin capsules, and cephalexin for oral suspension should be used only to treat infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by bacteria. (1.6 )
1.1 Respiratory Tract Infections
Cephalexin is indicated for the treatment of respiratory tract infections caused by susceptible isolates of Streptococcus pneumoniae and Streptococcus pyogenes.
1.2 Otitis Media
Cephalexin is indicated for the treatment of otitis media caused by susceptible isolates of Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pyogenes, and Moraxella catarrhalis.
1.3 Skin and Skin Structure Infections
Cephalexin is indicated for the treatment of skin and skin structure infections caused by susceptible isolates of the following Gram-positive bacteria: Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes.
1.4 Bone Infections
Cephalexin is indicated for the treatment of bone infections caused by susceptible isolates of Staphylococcus aureus and Proteus mirabilis.
1.5 Genitourinary Tract Infections
Cephalexin is indicated for the treatment of genitourinary tract infections, including acute prostatitis, caused by susceptible isolates of Escherichia coli, Proteus mirabilis, and Klebsiella pneumoniae.
1.6 Usage
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of cephalexin capsules, and cephalexin for oral suspension and other antibacterial drugs, cephalexin capsules, and cephalexin for oral suspension should be used only to treat infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible bacteria. When culture and susceptibility information is available, this information should be considered in selecting or modifying antibacterial therapy. In the absence of such data, local epidemiology and susceptibility patterns may contribute to the empiric selection of therapy.
2 Dosage And Administration
Adults and patients at least 15 years of age
The usual dose is 250 mg every 6 hours, but a dose of 500 mg every 12 hours may be administered (2.1 )
Pediatric patients (over 1 year of age)
- Otitis media: 75 to 100 mg/kg in equally divided doses every 6 hours (
2.2 )- All other indications: 25 to 50 mg/kg given in equally divided doses (
2.2 )- In severe infections: 50 to 100 mg/kg may be administered in equally divided doses (
2.2 )
- Duration of therapy ranges from 7 to 14 days depending on the infection type and severity. (
2 )- Dosage adjustment is required in patients with severe and end stage renal disease (ESRD) defined as creatinine clearance below 30 mL/min. (
2.3 )2.1 Adults and Pediatric Patients at Least 15 Years of Age
The usual dose of oral cephalexin is 250 mg every 6 hours, but a dose of 500 mg every 12 hours may be administered. Treatment is administered for 7 to 14 days.
For more severe infections larger doses of oral cephalexin may be needed, up to 4 grams daily in two to four equally divided doses.
2.2 Pediatric Patients (over 1 year of age)
The recommended total daily dose of oral cephalexin for pediatric patients is 25 to 50 mg/kg given in equally divided doses for 7 to 14 days. In the treatment of β-hemolytic streptococcal infections, duration of at least 10 days is recommended. In severe infections, a total daily dose of 50 to 100 mg/kg may be administered in equally divided doses.
For the treatment of otitis media, the recommended daily dose is 75 to 100 mg/kg given in equally divided doses.
Cephalexin Suspension
Weight
125 mg/5 mL
250 mg/5 mL
10 kg (22 lb)
1/2 to 1 tsp q.i.d.
1/4 to 1/2 tsp q.i.d.
20 kg (44 lb)
1 to 2 tsp q.i.d.
1/2 to 1 tsp q.i.d.
40 kg (88 lb)
2 to 4 tsp q.i.d.
1 to 2 tsp q.i.d.
or
Weight
125 mg/5 mL
250 mg/5 mL
10 kg (22 lb)
1 to 2 tsp b.i.d.
1/2 to 1 tsp b.i.d
20 kg (44 lb)
2 to 4 tsp b.i.d.
1 to 2 tsp b.i.d.
40 kg (88 lb)
4 to 8 tsp b.i.d.
2 to 4 tsp b.i.d.
Directions for Mixing
125 mg per 5 mL (100 mL when mixed): Prepare suspension at time of dispensing. Add to the bottle a total of 71 mL of water. For ease in preparation, tap bottle to loosen powder, add the water in 2 portions, shaking well after each addition. The resulting suspension will contain cephalexin monohydrate equivalent to 125 mg cephalexin in each 5 mL (teaspoonful).
125 mg per 5 mL (200 mL when mixed): Prepare suspension at time of dispensing. Add to the bottle a total of 140 mL of water. For ease in preparation, tap bottle to loosen powder, add the water in 2 portions, shaking well after each addition. The resulting suspension will contain cephalexin monohydrate equivalent to 125 mg cephalexin in each 5 mL (teaspoonful).
250 mg per 5 mL (100 mL when mixed): Prepare suspension at time of dispensing. Add to the bottle a total of 71 mL of water. For ease in preparation, tap bottle to loosen powder, add the water in 2 portions, shaking well after each addition. The resulting suspension will contain cephalexin monohydrate equivalent to 250 mg cephalexin in each 5 mL (teaspoonful).
250 mg per 5 mL (200 mL when mixed): Prepare suspension at time of dispensing. Add to the bottle a total of 140 mL of water. For ease in preparation, tap bottle to loosen powder, add the water in 2 portions, shaking well after each addition. The resulting suspension will contain cephalexin monohydrate equivalent to 250 mg cephalexin in each 5 mL (teaspoonful).
* After mixing, store in refrigerator. May be kept for 14 days without significant loss of potency.
2.3 Dosage Adjustments in Adult and Pediatric Patients at Least 15 Years of Age with Renal Impairment
Administer the following dosing regimens for cephalexin to patients with impaired renal function [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.4) and Use in Specific Populations ( 8.6) ].
Table 1. Recommended Dose Regimen for Patients with Renal Impairment
Renal function
Dose regimen recommendation
Creatinine clearance > 60 mL/min
No dose adjustment
Creatinine clearance 30 to 59 mL/min
No dose adjustment; maximum daily dose should not exceed 1 g
Creatinine clearance 15 to 29 mL/min
250 mg, every 8 hours or every 12 hours
Creatinine clearance 5 to 14 mL/min not yet on dialysis*
250 mg, every 24 hours
Creatinine clearance 1 to 4 mL/min not yet on dialysis*
250 mg, every 48 hours or every 60 hours
 *There is insufficient information to make dose adjustment recommendations in patients on hemodialysis.
3 Dosage Forms And Strengths
Cephalexin Capsules USP
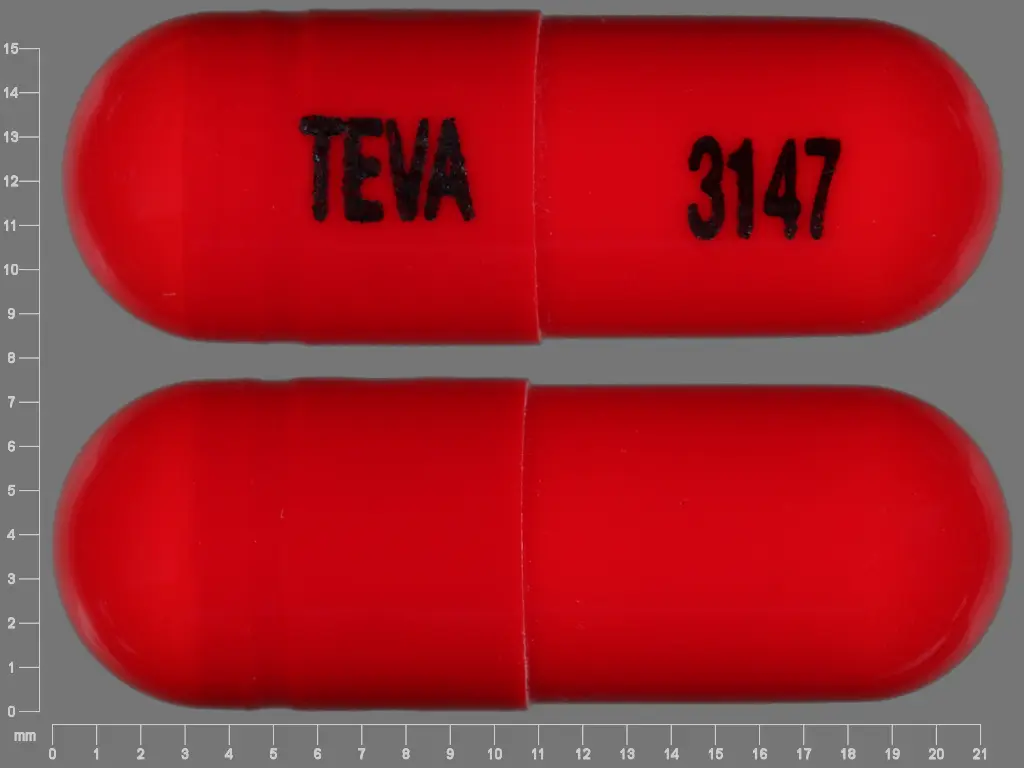
250 mg: Swedish orange body and gray cap imprinted “TEVA” on the cap and “3145” on the body
500 mg: Swedish orange body and Swedish orange cap imprinted “TEVA” on the cap and “3147” on the body
Cephalexin for Oral Suspension USP
A cherry mixed fruit flavored formula - 125 mg/5 mL and 250 mg/5 mL
Capsules: 250 mg and 500 mg (3 )
For oral suspension: 125 mg/5 mL and 250 mg/5 mL
4 Contraindications
Cephalexin is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to cephalexin or other members of the cephalosporin class of antibacterial drugs.
Patients with known hypersensitivity to cephalexin or other members of the cephalosporin class of antibacterial drugs. (4 )
5 Warnings And Precautions
- Serious hypersensitivity (anaphylactic) reactions: Prior to use, inquire regarding history of hypersensitivity to beta-lactam antibacterial drugs. Discontinue the drug if signs or symptoms of an allergic reaction occur and institute supportive measures. (
5.1 )- Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea (CDAD) : Evaluate if diarrhea occurs. (
5.2 )- Direct Coombs’ Test Seroconversion: If anemia develops during or after cephalexin therapy, evaluate for drug-induced hemolytic anemia. (
5.3 )- Seizure Potential: Use lower dose in patients with renal impairment. (
5.4 )5.1 Hypersensitivity Reactions
Allergic reactions in the form of rash, urticaria, angioedema, anaphylaxis, erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, or toxic epidermal necrolysis have been reported with the use of cephalexin. Before therapy with cephalexin is instituted, inquire whether the patient has a history of hypersensitivity reactions to cephalexin, cephalosporins, penicillins, or other drugs. Cross-hypersensitivity among beta-lactam antibacterial drugs may occur in up to 10% of patients with a history of penicillin allergy.
If an allergic reaction to cephalexin occurs, discontinue the drug and institute appropriate treatment.
5.2 -Associated Diarrhea
Clostridium difficile - associated diarrhea (CDAD) has been reported with use of nearly all antibacterial agents, including cephalexin, and may range in severity from mild diarrhea to fatal colitis. Treatment with antibacterial agents alters the normal flora of the colon leading to overgrowth of C. difficile.
C. difficile produces toxins A and B, which contribute to the development of CDAD. Hypertoxin-producing strains of C. difficile cause increased morbidity and mortality, as these infections can be refractory to antimicrobial therapy and may require colectomy. CDAD must be considered in all patients who present with diarrhea following antibiotic use. Careful medical history is necessary since CDAD has been reported to occur over two months after the administration of antibacterial agents.
If CDAD is suspected or confirmed, ongoing antibiotic use not directed against C. difficile may need to be discontinued. Appropriate fluid and electrolyte management, protein supplementation, antibiotic treatment of C. difficile, and surgical evaluation should be instituted as clinically indicated.
5.3 Direct Coombs Test Seroconversion
Positive direct Coombs’ tests have been reported during treatment with the cephalosporin antibacterial drugs including cephalexin. Acute intravascular hemolysis induced by cephalexin therapy has been reported. If anemia develops during or after cephalexin therapy, perform a diagnostic work-up for drug-induced hemolytic anemia, discontinue cephalexin and institute appropriate therapy.
5.4 Seizure Potential
Several cephalosporins have been implicated in triggering seizures, particularly in patients with renal impairment when the dosage was not reduced. If seizures occur, discontinue cephalexin. Anticonvulsant therapy can be given if clinically indicated.
5.5 Prolonged Prothrombin Time
Cephalosporins may be associated with prolonged prothrombin time. Those at risk include patients with renal or hepatic impairment, or poor nutritional state, as well as patients receiving a protracted course of antibacterial therapy, and patients receiving anticoagulant therapy. Monitor prothrombin time in patients at risk and manage as indicated.
5.6 Development of Drug-Resistant Bacteria
Prescribing cephalexin in the absence of a proven or strongly suspected bacterial infection is unlikely to provide benefit to the patient and increases the risk of the development of drug-resistant bacteria.
Prolonged use of cephalexin may result in the overgrowth of nonsusceptible organisms. Careful observation of the patient is essential. If superinfection occurs during therapy, appropriate measures should be taken.
6 Adverse Reactions
The following serious events are described in greater detail in the Warning and Precautions section:
- Hypersensitivity reactions [ see Warning and Precautions ( 5.1) ]
- Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea [ see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.2) ]
- Direct Coombs’ Test Seroconversion [ see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.3) ]
- Seizure Potential [ see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.4) ]
- Effect on Prothrombin Activity [ see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.5) ]
- Development of Drug-Resistant Bacteria [ see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.6) ]
The most common adverse reactions associated with cephalexin include diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, dyspepsia and abdominal pain. (6 )
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Teva Pharmaceuticals USA, Inc. at 1-888-838-2872 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
In clinical trials, the most frequent adverse reaction was diarrhea. Nausea and vomiting, dyspepsia, gastritis, and abdominal pain have also occurred. As with penicillins and other cephalosporins, transient hepatitis and cholestatic jaundice have been reported.
Other reactions have included hypersensitivity reactions, genital and anal pruritus, genital candidiasis, vaginitis and vaginal discharge, dizziness, fatigue, headache, agitation, confusion, hallucinations, arthralgia, arthritis, and joint disorder. Reversible interstitial nephritis has been reported. Eosinophilia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, hemolytic anemia, and slight elevations in aspartate transaminase (AST) and alanine transaminase (ALT) have been reported.
In addition to the adverse reactions uled above that have been observed in patients treated with cephalexin, the following adverse reactions and other altered laboratory tests have been reported for cephalosporin class antibacterial drugs:
Other Adverse Reactions: Fever, colitis, aplastic anemia, hemorrhage, renal dysfunction, and toxic nephropathy.
Altered Laboratory Tests: Prolonged prothrombin time, increased blood urea nitrogen (BUN), increased creatinine, elevated alkaline phosphatase, elevated bilirubin, elevated lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), pancytopenia, leukopenia, and agranulocytosis.
7 Drug Interactions
- Metformin: increased metformin concentrations. Monitor for hypoglycemia. (
7.1 )- Probenecid - The renal excretion of cephalexin is inhibited by probenecid. Co-administration of probenecid with cephalexin is not recommended. (
7.2 )- Administration of cephalexin may result in a false-positive reaction for glucose in the urine. (
7.3 )7.1 Metformin
Administration of cephalexin with metformin results in increased plasma metformin concentrations and decreased renal clearance of metformin.
Careful patient monitoring and dose adjustment of metformin is recommended in patients concomitantly taking cephalexin and metformin [ see Clinical Pharmacology ( 12.3 )].
7.2 Probenecid
The renal excretion of cephalexin is inhibited by probenecid. Co-administration of probenecid with cephalexin is not recommended.
7.3 Interaction with Laboratory or Diagnostic Testing
A false-positive reaction may occur when testing for the presence of glucose in the urine using Benedict’s solution or Fehling’s solution.
8 Use In Specific Populations
- Renal Impairment: Monitor patients longer for toxicity and drug interactions due to delayed clearance. (
8.6 )8.1 Pregnancy
 Risk Summary
Available data from published epidemiologic studies and pharmacovigilance case reports over several decades with cephalosporin use, including Cephalexin use in pregnant women have not established drug-associated risks of major birth defects, miscarriage, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes (see Data).
Animal reproduction studies with mice and rats using oral doses of cephalexin that are 0.6- and 1.2-times the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) based on body surface area during organogenesis revealed no evidence of harm to the fetus (see Data).
Â
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown.
All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Data
Human Data
Â
While available studies cannot definitively establish the absence of risk, published data from epidemiologic studies and postmarketing case reports over several decades have not identified a consistent association with
cephalosporin use, including Cephalexin, during pregnancy, and major birth defects, miscarriage, or other adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. Available studies have methodologic limitations, including small sample size, retrospective data collection, and inconsistent comparator groups.
Animal Data
Â
In animal reproduction studies, pregnant mice and rats administered oral cephalexin doses of 250 or 500 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.6 and 1.2 times the MRHD) based on body surface area, respectively during the period of organogenesis showed no adverse effects on embryofetal development.
In a pre-and post-natal developmental toxicity study, pregnant rats that received oral doses of 250 or 500 mg/kg/day of cephalexin from Day 15 of pregnancy to litter Day 21 showed no adverse effects on parturition, litter size, or growth of offspring.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
Data from a published clinical lactation study reports that cephalexin is present in human milk. The Relative Infant Dose (RID) is considered to be <1% of the maternal weight adjusted dose. There are no data on the effects of cephalexin on the breastfed child or on milk production.
The development of health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for cephalexin and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from cephalexin or from the underlying maternal condition.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of cephalexin in pediatric patients was established in clinical trials for the dosages described in the dosage and administration section [ see Dosage and Administration ( 2.2) ] .
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the 701 subjects in 3 published clinical studies of cephalexin, 433 (62%) were 65 and over. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these subjects and younger subjects, and other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients.
This drug is substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of toxic reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection [ see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.4) ].
8.6 Renal Impairment
Cephalexin should be administered with careful monitoring in the presence of renal impairment (creatinine clearance < 30 mL/min, with or without dialysis). Under such conditions, careful clinical observation and laboratory studies renal function monitoring should be conducted because safe dosage may be lower than that usually recommended [see Dosage and Administration ( 2.3)] . Monitor patients longer for toxicity and drug interactions due to delayed clearance.
10 Overdosage
Symptoms of oral overdose may include nausea, vomiting, epigastric distress, diarrhea, and hematuria. In the event of an overdose, institute general supportive measures.
Forced diuresis, peritoneal dialysis, hemodialysis, or charcoal hemoperfusion have not been established as beneficial for an overdose of cephalexin.
11 Description
Cephalexin, USP is a semisynthetic cephalosporin antibiotic intended for oral administration. It is 7-(D-α-amino-α-phenylacetamido)-3-methyl-3-cephem-4-carboxylic acid, monohydrate.
Cephalexin, USP has the following structural formula:
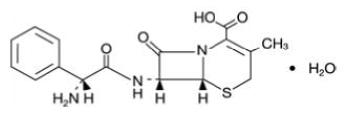
C 16H 17N 3O 4S•H 2O          M.W. 365.41
The nucleus of cephalexin, USP is related to that of other cephalosporin antibiotics. The compound is a zwitterion; i.e., the molecule contains both a basic and an acidic group. The isoelectric point of cephalexin, USP in water is approximately 4.5 to 5.
The crystalline form of cephalexin, USP which is available is a monohydrate. It is a white crystalline solid having a bitter taste. Solubility in water is low at room temperature; 1 or 2 mg/mL may be dissolved readily, but higher concentrations are obtained with increasing difficulty.
The cephalosporins differ from penicillins in the structure of the bicyclic ring system. Cephalexin, USP has a D-phenylglycyl group as substituent at the 7-amino position and an unsubstituted methyl group at the 3-position.
Each capsule contains cephalexin monohydrate, USP equivalent to 250 mg (720 ÎĽmol) or 500 mg (1,439 ÎĽmol) of cephalexin.
Inactive Ingredients: CAPSULES: magnesium stearate, silicon dioxide, and sodium starch glycolate.
Capsule Shell and Print Constituents: black iron oxide, D&C Yellow #10 Aluminum Lake, FD&C Blue #1 Aluminum Lake, FD&C Blue #2 Aluminum Lake, FD&C Red #40 Aluminum Lake, gelatin, pharmaceutical glaze modified in SD-45, silicon dioxide or carboxymethylcellulose sodium, sodium lauryl sulfate, titanium dioxide and may contain propylene glycol. In addition, the 250 mg capsule shell contains yellow iron oxide.
After mixing, each 5 mL of cephalexin for oral suspension USP will contain cephalexin monohydrate, USP equivalent to 125 mg (360 ÎĽmol) or 250 mg (720 ÎĽmol) of cephalexin.
Inactive Ingredients: SUSPENSION: FD&C Red #40, cherry mixed fruit flavor (artificial flavors, benzyl alcohol, maltodextrin, and modified corn starch), silicon dioxide, sodium benzoate, sugar (fruit granulated), and xanthan gum.
12 Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Cephalexin is a cephalosporin antibacterial drug [see Microbiology ( 12.4)] .
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption: Cephalexin is acid stable and may be given without regard to meals. Following doses of 250 mg, 500 mg, and 1 g, average peak serum levels of approximately 9, 18, and 32 mcg/mL, respectively, were obtained at 1 hour. Serum levels were detectable 6 hours after administration (at a level of detection of 0.2 mcg/mL).
Distribution: Cephalexin is approximately 10% to 15% bound to plasma proteins.
Excretion: Cephalexin is excreted in the urine by glomerular filtration and tubular secretion. Studies showed that over 90% of the drug was excreted unchanged in the urine within 8 hours. During this period, peak urine concentrations following the 250 mg, 500 mg, and 1 g doses were approximately 1000, 2200, and 5000 mcg/mL respectively.
Drug Interactions In healthy subjects given single 500 mg doses of cephalexin and metformin, plasma metformin mean Cmax and AUC increased by an average of 34% and 24%, respectively, and metformin mean renal clearance decreased by 14%. No information is available about the interaction of cephalexin and metformin following multiple doses of either drug.
12.4 Microbiology
Mechanism of Action
Cephalexin is a bactericidal agent that acts by the inhibition of bacterial cell-wall synthesis.
Resistance
Methicillin-resistant staphylococci and most isolates of enterococci are resistant to cephalexin. Cephalexin is not active against most isolates of Enterobacter spp., Morganella morganii, and Proteus vulgaris. Cephalexin has no activity against Pseudomonas spp., or Acinetobacter calcoaceticus. Penicillin-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae is usually cross-resistant to beta-lactam antibacterial drugs.
Antimicrobial Activity
Cephalexin has been shown to be active against most isolates of the following bacteria both in vitro and in clinical infections [ see Indications and Usage ( 1) ].
Gram-positive bacteria
Staphylococcus aureus (methicillin-susceptible isolates only) Streptococcus pneumoniae (penicillin-susceptible isolates)
Gram-negative bacteria
Escherichia coli
Haemophilus influenzae
Klebsiella pneumoniae
Moraxella catarrhalis
Proteus mirabilis
Susceptibility Testing
For specific information regarding susceptibility test interpretive criteria and associated test methods and quality control standards recognized by FDA for this drug, please see:Â https://www.fda.gov/STIC .
13 Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Lifetime studies in animals have not been performed to evaluate the carcinogenic potential of cephalexin. Tests to determine the mutagenic potential of cephalexin have not been performed. In male and female rats, fertility and reproductive performance were not affected by cephalexin oral doses up to 1.5 times the highest recommended human dose based upon body surface area.
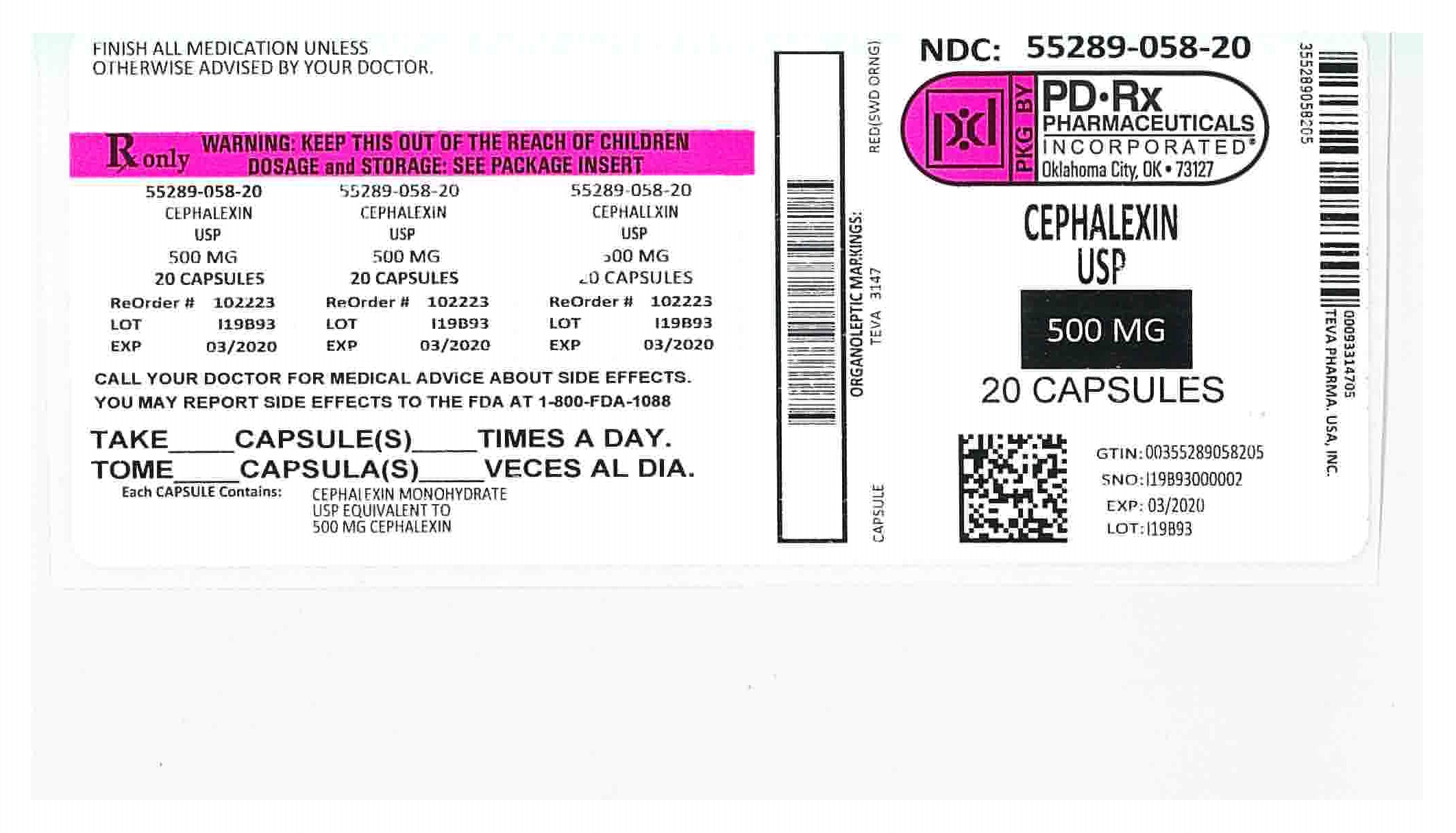
16 How Supplied/storage And Handling
Cephalexin Capsules USP
500 mg: Swedish orange body and Swedish orange cap imprinted “TEVA” on the cap and “3147” on the body.
NDC 55289-058-04 Bottles of 4
NDC 55289-058-08 Bottles of 8
NDC 55289-058-10 Bottles of 10
NDC 55289-058-14 Bottles of 14
NDC 55289-058-20 Bottles of 20
NDC 55289-058-21 Bottles of 21
NDC 55289-058-24 Bottles of 24
NDC 55289-058-28 Bottles of 28
NDC 55289-058-30 Bottles of 30
NDC 55289-058-40 Bottles of 40
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container.
17 Patient Counseling Information
Allergic Reactions
Advise patients that allergic reactions, including serious allergic reactions, could occur and that serious reactions require immediate treatment. Ask the patient about any previous hypersensitivity reactions to cephalexin, other beta-lactams (including cephalosporins) or other allergens (5.1)
Diarrhea
Advise patients that diarrhea is a common problem caused by antibacterial drugs and usually resolves when the drug is discontinued. Sometimes, frequent watery or bloody diarrhea may occur and may be a sign of a more serious intestinal infection. If severe watery or bloody diarrhea develops, advise patients to contact their healthcare provider.
Antibacterial Resistance
Counsel patients that antibacterial drugs including cephalexin capsules, and cephalexin for oral suspension, should only be used to treat bacterial infections. They do not treat viral infections (e.g., the common cold). When cephalexin capsules, and cephalexin for oral suspension are prescribed to treat a bacterial infection, tell patients that although it is common to feel better early in the course of therapy, the medication should be taken exactly as directed. Skipping doses or not completing the full course of therapy may (1) decrease the effectiveness of the immediate treatment and (2) increase the likelihood that bacteria will develop resistance and will not be treatable by cephalexin capsules, and cephalexin for oral suspension or other antibacterial drugs in the future.
Teva Pharmaceuticals USA, Inc.
North Wales, PA 19454
Rev. V 12/2020
Package/label Display Panel
Cephalexin
Capsules USP
500 mg
Rx only
DISCLAIMER:
"This tool does not provide medical advice, and is for informational and educational purposes only, and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, treatment or diagnosis. Call your doctor to receive medical advice. If you think you may have a medical emergency, please dial 911."
"Do not rely on openFDA to make decisions regarding medical care. While we make every effort to ensure that data is accurate, you should assume all results are unvalidated. We may limit or otherwise restrict your access to the API in line with our Terms of Service."
"This product uses publicly available data from the U.S. National Library of Medicine (NLM), National Institutes of Health, Department of Health and Human Services; NLM is not responsible for the product and does not endorse or recommend this or any other product."
PillSync may earn a commission via links on our site