Aviane (levonorgestrel 0.1 mg ethinyl estradiol 0.02 mg) Dailymed
Generic: levonorgestrel and ethinyl estradiol is used for the treatment of Breast Neoplasms Cerebral Arterial Diseases Coronary Artery Disease Hypertension Hypogonadism Liver Diseases Menopause, Premature Menorrhagia Neoplasms, Hormone-Dependent Pregnancy Prostatic Neoplasms Thromboembolism Thrombophlebitis Osteoporosis, Postmenopausal Primary Ovarian Insufficiency Endometrial Neoplasms Hot Flashes Tobacco Use Abortion, Spontaneous Cerebrovascular Disorders Coronary Disease Diabetes Mellitus Heart Valve Diseases Jaundice Kidney Diseases Liver Neoplasms Tobacco Use Disorder Uterine Hemorrhage Adenoma, Liver Cell Headache Disorders
IMPRINT: DP 016
SHAPE: round
COLOR: orange
All Imprints
- dp 519 round green
levonorgestrel 0.1 mgethinyl estradiol 0.02 mg - dp 016 round orange
Go PRO for all pill images
Patients should be counseled that oral contraceptives do not protect against transmission of HIV (AIDS) and other sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) such as chlamydia, genital herpes, genital warts (human papillomavirus), gonorrhea, hepatitis B, and syphilis.
Description
21 orange active tablets each containing 0.10 mg of levonorgestrel, USP (-)-13-Ethyl-17-hydroxy-18,19-dinor-17α-pregn-4-en-20-yn-3-one, a totally synthetic progestogen, and 0.02 mg of ethinyl estradiol, USP, (19-Nor-17α-pregna-1,3,5(10)-trien-20-yne-3,17-diol). The inactive ingredients present are: FD&C yellow no. 6 aluminum lake, hypromellose, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, polyethylene glycol, pregelatinized corn starch, sodium starch glycolate and titanium dioxide.
7 light-green, inert tablets each containing: D&C yellow no. 10 aluminum lake, FD&C blue no. 1 aluminum lake, FD&C yellow no. 6 aluminum lake, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose and pregelatinized corn starch.
Levonorgestrel, USP
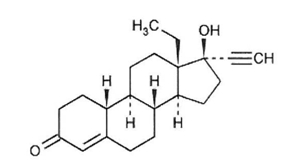
C21H28O2 M.W. 312.45
Ethinyl Estradiol, USP
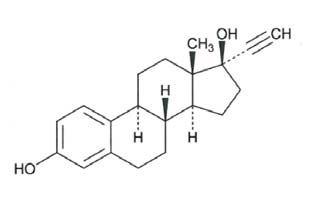
C20H24O2 M.W. 296.40
Clinical Pharmacology
Mode of Action
Combination oral contraceptives prevent pregnancy primarily by suppressing ovulation.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
No specific investigation of the absolute bioavailability of Aviane in humans has been conducted. However, literature indicates that levonorgestrel is rapidly and completely absorbed after oral administration (bioavailability about 100%) and is not subject to first-pass metabolism. Ethinyl estradiol is rapidly and almost completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract but, due to first-pass metabolism in gut mucosa and liver, the bioavailability of ethinyl estradiol is between 38% and 48%.
After a single dose of Aviane to 22 women under fasting conditions, maximum serum concentrations of levonorgestrel are 2.8 ± 0.9 ng/mL (mean ± SD) at 1.6 ± 0.9 hours. At steady state, attained from day 19 onwards, maximum levonorgestrel concentrations of 6.0 ± 2.7 ng/mL are reached at 1.5 ± 0.5 hours after the daily dose. The minimum serum levels of levonorgestrel at steady state are 1.9 ± 1.0 ng/mL. Observed levonorgestrel concentrations increased from day 1 (single dose) to days 6 and 21 (multiple doses) by 34% and 96%, respectively (Figure 1). Unbound levonorgestrel concentrations increased from day 1 to days 6 and 21 by 25% and 83%, respectively. The kinetics of total levonorgestrel are non-linear due to an increase in binding of levonorgestrel to sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG), which is attributed to increased SHBG levels that are induced by the daily administration of ethinyl estradiol.
Following a single dose, maximum serum concentrations of ethinyl estradiol of 62 ± 21 pg/mL are reached at 1.5 ± 0.5 hours. At steady state, attained from at least day 6 onwards, maximum concentrations of ethinyl estradiol were 77 ± 30 pg/mL and were reached at 1.3 ± 0.7 hours after the daily dose. The minimum serum levels of ethinyl estradiol at steady state are 10.5 ± 5.1 pg/mL. Ethinyl estradiol concentrations did not increase from days 1 to 6, but did increase by 19% from days 1 to 21 (Figure 1).
FIGURE 1: Mean (SE) levonorgestrel and ethinyl estradiol serum concentrations in 22 subjects receiving 100 mcg levonorgestrel and 20 mcg ethinyl estradiol
TABLE 1 provides a summary of levonorgestrel and ethinyl estradiol pharmacokinetic parameters.
TABLE 1: Mean (SD) Pharmacokinetic Parameters of Aviane Over a 21-Day Dosing Period
Levonorgestrel
Cmax
Tmax
AUC
CL/F
Vλz/F
SHBG
Day
ng/mL
h
ng•h/mL
mL/h/kg
L/kg
nmol/L
1
2.75 (0.88)
1.6 (0.9)
35.2 (12.8)
53.7 (20.8)
2.66 (1.09)
57 (18)
6
4.52 (1.79)
1.5 (0.7)
46.0 (18.8)
40.8 (14.5)
2.05 (0.86)
81 (25)
21
6.00 (2.65)
1.5 (0.5)
68.3 (32.5)
28.4 (10.3)
1.43 (0.62)
93 (40)
Unbound Levonorgestrel
pg/mL
h
pg•h/mL
L/h/kg
L/kg
fu%
1
51.2 (12.9)
1.6 (0.9)
654 (201)
2.79 (0.97)
135.9 (41.8)
1.92 (0.30)
6
77.9 (22.0)
1.5 (0.7)
794 (240)
2.24 (0.59)
112.4 (40.5)
1.80 (0.24)
21
103.6 (36.9)
1.5 (0.5)
1177 (452)
1.57 (0.49)
78.6 (29.7)
1.78 (0.19)
Ethinyl Estradiol
pg/mL
h
pg•h/mL
mL/h/kg
L/kg
1
62.0 (20.5)
1.5 (0.5)
653 (227)
567 (204)
14.3 (3.7)
6
76.7 (29.9)
1.3 (0.7)
604 (231)
610 (196)
15.5 (4.0)
21
82.3 (33.2)
1.4 (0.6)
776 (308)
486 (179)
12.4 (4.1)
Distribution
Levonorgestrel in serum is primarily bound to SHBG. Ethinyl estradiol is about 97% bound to plasma albumin. Ethinyl estradiol does not bind to SHBG, but induces SHBG synthesis.
Metabolism
Levonorgestrel:
The most important metabolic pathway occurs in the reduction of the Δ4-3-oxo group and hydroxylation at positions 2α, 1β, and 16β, followed by conjugation. Most of the metabolites that circulate in the blood are sulfates of 3α,5β-tetrahydro-levonorgestrel, while excretion occurs predominantly in the form of glucuronides. Some of the parent levonorgestrel also circulates as 17β-sulfate. Metabolic clearance rates may differ among individuals by several-fold, and this may account in part for the wide variation observed in levonorgestrel concentrations among users.
Ethinyl estradiol:
Cytochrome P450 enzymes (CYP3A4) in the liver are responsible for the 2-hydroxylation that is the major oxidative reaction. The 2-hydroxy metabolite is further transformed by methylation and glucuronidation prior to urinary and fecal excretion. Levels of Cytochrome P450 (CYP3A) vary widely among individuals and can explain the variation in rates of ethinyl estradiol 2-hydroxylation. Ethinyl estradiol is excreted in the urine and feces as glucuronide and sulfate conjugates, and undergoes enterohepatic circulation.
Excretion
The elimination half-life for levonorgestrel is approximately 36 ± 13 hours at steady state. Levonorgestrel and its metabolites are primarily excreted in the urine (40% to 68%) and about 16% to 48% are excreted in feces. The elimination half-life of ethinyl estradiol is 18 ± 4.7 hours at steady state.
Special Populations
Race
Based on the pharmacokinetic study with Aviane, there are no apparent differences in pharmacokinetic parameters among women of different races.
Hepatic Insufficiency
No formal studies have evaluated the effect of hepatic disease on the disposition of Aviane. However, steroid hormones may be poorly metabolized in patients with impaired liver function.
Renal Insufficiency
No formal studies have evaluated the effect of renal disease on the disposition of Aviane.
Drug-Drug Interactions
See PRECAUTIONS - Drug Interactions
Indications And Usage
Aviane (levonorgestrel and ethinyl estradiol tablets) is indicated for use by females of reproductive potential to prevent pregnancy.
Limitations of use: The efficacy of Aviane (levonorgestrel and ethinyl estradiol tablets) in women with a body mass index (BMI) of > 35 kg/m2 has not been adequately evaluated.
In a clinical trial with Aviane (levonorgestrel and ethinyl estradiol tablets), 1,477 subjects had 7,720 cycles of use and a total of 5 pregnancies were reported. This represents an overall pregnancy rate of 0.84 per 100 woman-years. This rate includes patients who did not take the drug correctly. One or more pills were missed during 1,479 (18.8%) of the 7,870 cycles; thus all tablets were taken during 6,391 (81.2%) of the 7,870 cycles. Of the total 7,870 cycles, a total of 150 cycles were excluded from the calculation of the Pearl index due to the use of backup contraception and/or missing 3 or more consecutive pills.
The mean BMI of the study population was 24 kg/m2. Females with a BMI greater than 30 kg/m2 accounted for 12.1% (n=179) of the study population. Females with a BMI over 35 kg/m2 accounted for 4.3% (n=63) of the study population.
Contraindications
Combination oral contraceptives should not be used in women with any of the following conditions:
- Thrombophlebitis or thromboembolic disorders
- A history of deep-vein thrombophlebitis or thromboembolic disorders
- Cerebrovascular or coronary artery disease (current or past history)
- Valvular heart disease with thrombogenic complications
- Thrombogenic rhythm disorders
- Hereditary or acquired thrombophilias
- Prolonged immobilization (especially with major surgery)
- Diabetes with vascular involvement
- Headaches with focal neurological symptoms or migraine with aura
- Women with migraine who are 35 years or older
- Uncontrolled hypertension
- Known or suspected carcinoma of the breast or personal history of breast cancer
- Known or suspected estrogen- or progesterone sensitive malignancy
- Undiagnosed abnormal vaginal bleeding
- Cholestatic jaundice of pregnancy or jaundice with prior pill use
- Hepatic adenomas or carcinomas, or active liver disease
Women who are receiving Hepatitis C drug combinations containing ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir, with or without dasabuvir, due to the potential for alanine aminotransferase (ALT) elevations (see WARNINGS, Risk of Liver Enzyme Elevations with Concomitant Hepatitis C Treatment ).
Warnings
BOXED WARNING SECTION
WARNING: CIGARETTE SMOKING AND SERIOUS CARDIOVASCULAR EVENTS Cigarette smoking increases the risk of serious cardiovascular events from combined oral-contraceptives (COC) use. This risk increases with age, particularly in women over 35 years of age, and with the number of cigarettes smoked. For this reason, COCs, including Aviane (levonorgestrel and ethinyl estradiol tablets), are contraindicated in women who are over 35 years of age and smoke.
The use of oral contraceptives is associated with increased risks of several serious conditions including venous and arterial thrombotic and thromboembolic events (such as myocardial infarction, thromboembolism, and stroke), hepatic neoplasia, gallbladder disease, and hypertension, although the risk of serious morbidity or mortality is very small in healthy women without underlying risk factors. The risk of morbidity and mortality increases significantly in the presence of other underlying risk factors such as certain inherited or acquired thrombophilias, hypertension, hyperlipidemias, obesity, diabetes, and surgery or trauma with increased risk of thrombosis (see CONTRAINDICATIONS).
Practitioners prescribing oral contraceptives should be familiar with the following information relating to these risks.
The information contained in this package insert is principally based on studies carried out in patients who used oral contraceptives with higher doses of estrogens and progestogens than those in common use today. The effect of long-term use of the oral contraceptives with lower doses of both estrogens and progestogens remains to be determined.
Throughout this labeling, epidemiological studies reported are of two types: retrospective or case control studies and prospective or cohort studies. Case control studies provide a measure of the relative risk of disease, namely, a ratio of the incidence of a disease among oral-contraceptive users to that among nonusers. The relative risk does not provide information on the actual clinical occurrence of a disease. Cohort studies provide a measure of attributable risk, which is the difference in the incidence of disease between oral-contraceptive users and nonusers. The attributable risk does provide information about the actual occurrence of a disease in the population. For further information, the reader is referred to a text on epidemiological methods.
1. Thromboembolic Disorders and Other Vascular Problems
Cardiovascular and Cerebrovascular Events
Use of CHCs increases the risk of cardiovascular events and cerebrovascular events, such as myocardial infarction and stroke. The risk of these events with CHC use is greater in females with concomitant risk factors: age 35 years and older, smoking, hypertension, dyslipidemia, diabetes, or obesity. The risk increases with increasing age and with increasing number of cigarettes smoked.
Venous Thromboembolism
Use of CHCs also increases the risk of VTE, such as deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. The rate of VTE in females using COCs has been estimated to be 3 to 9 cases per 10,000 woman-years. The VTE risk should be considered in the context of relevant subpopulations of females of reproductive potential who are not taking CHCs ( ADVERSE REACTIONS ).
Risk factors for VTE with CHC use include smoking, obesity, family history of VTE, and prolonged immobilization, in addition to other factors that contraindicate use of CHCs (see CONTRAINDICATIONS ). The presence of multiple risk factors for VTE with CHC use may further increase the risk. The risk of VTE is highest during the first year of CHC use and when restarting hormonal contraception after a break of four weeks or longer. The risk of VTE returns to baseline approximately 3 months after CHC use is discontinued.
Postpartum Venous Thromboembolism
The risk of VTE is increased during the first six weeks postpartum. The risk is highest up to four weeks postpartum but remains higher than baseline until at least six weeks postpartum. The presence of multiple risk factors for VTE may further increase the risk. Obstetric complications may extend the elevated risk up to 12 weeks postpartum.
2. Malignant Neoplasms
Breast Cancer Aviane is contraindicated in females who currently have or have had breast cancer because breast cancer may be hormonally sensitive (see CONTRAINDICATIONS ). Epidemiology studies have not found a consistent association between use of combined oral contraceptives (COCs) and breast cancer risk. Studies do not show an association between ever (current or past) use of COCs and risk of breast cancer. However, some studies report a small increase in the risk of breast cancer among current or recent users (<6 months since last use) and current users with longer duration of COC use (see ADVERSE REACTIONS ).
Cervical Cancer Some studies suggest that oral contraceptive use has been associated with an increase in the risk of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia or invasive cervical cancer in some populations of women. However, there continues to be controversy about the extent to which such findings may be due to differences in sexual behavior and other factors.
3. Hepatic Neoplasia
Benign hepatic adenomas are associated with oral-contraceptive use, although the incidence of these benign tumors is rare in the United States. Indirect calculations have estimated the attributable risk to be in the range of 3.3 cases/100,000 for users, a risk that increases after four or more years of use. Rupture of rare, benign, hepatic adenomas may cause death through intra-abdominal hemorrhage.
Studies from Britain have shown an increased risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma in long-term (>8 years) oral-contraceptive users. However, these cancers are extremely rare in the U.S. and the attributable risk (the excess incidence) of liver cancers in oral-contraceptive users approaches less than one per million users.
4. Risk of Liver Enzyme Elevations with Concomitant Hepatitis C Treatment
During clinical trials with the Hepatitis C combination drug regimen that contains ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir, with or without dasabuvir, ALT elevations greater than 5 times the upper limit of normal (ULN), including some cases greater than 20 times the ULN, were significantly more frequent in women using ethinyl estradiol-containing medications such as COCs. Discontinue Aviane prior to starting therapy with the combination drug regimen ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir, with or without dasabuvir (see CONTRAINDICATIONS). Aviane can be restarted approximately 2 weeks following completion of treatment with the combination drug regimen.
5. Ocular Lesions
There have been clinical case reports of retinal thrombosis associated with the use of oral contraceptives that may lead to partial or complete loss of vision. Oral contraceptives should be discontinued if there is unexplained partial or complete loss of vision; onset of proptosis or diplopia; papilledema; or retinal vascular lesions. Appropriate diagnostic and therapeutic measures should be undertaken immediately.
6. Oral-Contraceptive Use Before or During Early Pregnancy
Extensive epidemiological studies have revealed no increased risk of birth defects in infants born to women who have used oral contraceptives prior to pregnancy. Studies also do not suggest a teratogenic effect, particularly insofar as cardiac anomalies and limb-reduction defects are concerned, when taken inadvertently during early pregnancy (see CONTRAINDICATIONS).
It is recommended that for any patient who has missed two consecutive periods, pregnancy should be ruled out. If the patient has not adhered to the prescribed schedule, the possibility of pregnancy should be considered at the time of the first missed period. Oral-contraceptive use should be discontinued if pregnancy is confirmed.
7. Gallbladder Disease
Combination oral contraceptives may worsen existing gallbladder disease and may accelerate the development of this disease in previously asymptomatic women. Earlier studies have reported an increased lifetime relative risk of gallbladder surgery in users of oral contraceptives and estrogens. More recent studies, however, have shown that the relative risk of developing gallbladder disease among oral-contraceptive users may be minimal. The recent findings of minimal risk may be related to the use of oral-contraceptive formulations containing lower hormonal doses of estrogens and progestogens. A past history of COC-related cholestasis predicts an increased risk with subsequent COC use. Women with a history of pregnancy-related cholestasis may be at an increased risk for COC related cholestasis.
8. Carbohydrate and Lipid Metabolic Effects
Oral contraceptives have been shown to cause glucose intolerance in a significant percentage of users. Carefully monitor females with prediabetes and diabetes who are using Aviane. Aviane may decrease glucose tolerance.
A small proportion of women will have persistent hypertriglyceridemia while on COCs. As discussed earlier (see WARNINGS and PRECAUTIONS ), changes in serum triglycerides and lipoprotein levels have been reported in oral-contraceptive users.
9. Elevated Blood Pressure
Aviane is contraindicated in women with uncontrolled hypertension or hypertension with vascular disease (see CONTRAINDICATIONS ). For all females, including those with well-controlled hypertension, monitor blood pressure at routine visits and stop Aviane if blood pressure rises significantly.
An increase in blood pressure has been reported in females using CHCs, and this increase is more likely in older women with extended duration of use. The effect of CHCs on blood pressure may vary according to the progestin in the CHC.
10. Headache
Aviane is contraindicated in females who have headaches with focal neurological symptoms or have migraine headaches with aura, and in women over age 35 years who have migraine head aches with or without aura.
The onset or exacerbation of migraine or development of headache with a new pattern that is recurrent, persistent, or severe requires discontinuation of oral contraceptives and evaluation of the cause. Consider discontinuation of Aviane if there is an increased frequency or severity of migraines during CHC use (which may be prodromal of a cerebrovascular event; see WARNINGS and CONTRAINDICATIONS).
11. Bleeding Irregularities
Unscheduled bleeding and spotting are sometimes encountered in patients on oral contraceptives, especially during the first three months of use. The type and dose of progestogen may be important. If bleeding persists or recurs, nonhormonal causes should be considered and adequate diagnostic measures taken to rule out malignancy or pregnancy in the event of unscheduled bleeding, as in the case of any abnormal vaginal bleeding. If pathology has been excluded, time or a change to another formulation may solve the problem. In the event of amenorrhea, pregnancy should be ruled out.
Some women may encounter post-pill amenorrhea or oligomenorrhea (possibly with anovulation), especially when such a condition was preexistent.
In the clinical trial with levonorgestrel 0.1 mg and ethinyl estradiol 0.02 mg tablets, unscheduled bleeding was defined as bleeding or spotting that occurred:
- During cycle 1 on pill-pack Days 4 to 21, inclusive of a 28-day cycle.
- In subsequent cycles, on Days 5 to 21 inclusive or on pill-pack Days 1 to 4 inclusive if preceded by 2 consecutive days without bleeding or spotting.
Based on subject diaries, the proportion of subjects reporting unscheduled bleeding or spotting per 28-day cycle decreased over time: 30.5% at Cycle 1 versus 18.2% at Cycle 12.
12.Hereditary Angioedema
In women with hereditary angioedema, exogenous estrogens may induce or exacerbate symptoms of angioedema.
13.Chloasma
Chloasma may occur, especially in women with a history of chloasma gravidarum. Advise women with a history of chloasma to avoid exposure to the sun or ultraviolet radiation while taking Aviane.
14.Effect on Binding Globulins
The estrogen component of COCs may raise the serum concentrations of thyroxine-binding globulin, sex hormone-binding globulin, and cortisol-binding globulin. Monitor thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) levels for females receiving Aviane and thyroid hormone replacement therapy concomitantly. Follow the recommendation for the thyroid hormone in accordance with its Prescribing Information.
Precautions
1. General
Patients should be counseled that oral contraceptives do not protect against transmission of HIV (AIDS) and other sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) such as chlamydia, genital herpes, genital warts, gonorrhea, hepatitis B, and syphilis.
2. Physical Examination and Follow-Up
A periodic personal and family medical history and complete physical examination are appropriate for all women, including women using oral contraceptives. The physical examination, however, may be deferred until after initiation of oral contraceptives if requested by the woman and judged appropriate by the clinician. The physical examination should include special reference to blood pressure, breasts, abdomen, pelvic organs, and relevant laboratory tests. In case of undiagnosed, persistent, or recurrent abnormal vaginal bleeding, appropriate diagnostic measures should be conducted to rule out malignancy. Women with a strong family history of breast cancer or who have breast nodules should be monitored with particular care.
3. Lipid Disorders
Women who are being treated for hyperlipidemias should be followed closely if they elect to use oral contraceptives. Some progestogens may elevate LDL levels and may render the control of hyperlipidemias more difficult (see WARNINGS ).
A small proportion of women will have adverse lipid changes while taking oral contraceptives. Nonhormonal contraception should be considered in women with uncontrolled dyslipidemias. Persistent hypertriglyceridemia may occur in a small population of combination oral contraceptive users. Elevations of plasma triglycerides may lead to pancreatitis and other complications.
4. Liver Function
If jaundice develops in any woman receiving such drugs, the medication should be discontinued. Steroid hormones may be poorly metabolized in patients with impaired liver function.
5. Fluid Retention
Oral contraceptives may cause some degree of fluid retention. They should be prescribed with caution, and only with careful monitoring, in patients with conditions which might be aggravated by fluid retention.
6.Depression
Monitor females with a history of depression and discontinue Aviane if depression recurs to a serious degree. Data on the association of CHCs with onset of depression or exacerbation of existing depression are limited.
7. Contact Lenses
Contact-lens wearers who develop visual changes or changes in lens tolerance should be assessed by an ophthalmologist.
8. Gastrointestinal
Diarrhea and/or vomiting may reduce hormone absorption resulting in decreased serum concentrations. If a patient vomits or has diarrhea after taking an active tablet, instruct the patient to not take an additional active tablet on that day and to continue the regimen the next day as prescribed. In case of vomiting or diarrhea that continues for 48 hours or greater, instruct the patient to contact the health care provider and use back-up or alternative contraception until active tablets have been taken for 7 consecutive days after vomiting and diarrhea have resolved.
9. Drug Interactions
Concomitant Use with HCV Combination Therapy – Liver Enzyme Elevation
Do not coadminister Aviane with HCV drug combinations containing ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir, with or without dasabuvir, due to potential for ALT elevations (see WARNINGS , Risk of Liver Enzyme Elevations with Concomitant Hepatitis C Treatmen t).
Changes in Contraceptive Effectiveness Associated with Coadministration of Other Products:
Contraceptive effectiveness may be reduced when hormonal contraceptives are coadministered with antibiotics, anticonvulsants, and other drugs that increase the metabolism of contraceptive steroids. This could result in unintended pregnancy or breakthrough bleeding. Examples include rifampin, rifabutin, barbiturates, primidone, phenylbutazone, phenytoin, dexamethasone, carbamazepine, felbamate, oxcarbazepine, topiramate, griseofulvin, and modafinil. In such cases a back-up nonhormonal method of birth control should be considered.
Several of the anti-HIV protease inhibitors have been studied with coadministration of oral combination hormonal contraceptives; significant changes (increase and decrease) in the plasma levels of the estrogen and progestin have been noted in some cases. The safety and efficacy of oral contraceptive products may be affected with coadministration of anti-HIV protease inhibitors. Healthcare providers should refer to the label of the individual anti-HIV protease inhibitors for further drug-drug interaction information.
Herbal products containing St. John's Wort (Hypericum perforatum) may induce hepatic enzymes (cytochrome P 450) and p-glycoprotein transporter and may reduce the effectiveness of contraceptive steroids. This may also result in breakthrough bleeding.
Increase in Plasma Levels Associated with Coadministered Drugs:
Coadministration of atorvastatin and certain oral contraceptives containing ethinyl estradiol increases AUC values for ethinyl estradiol by approximately 20%. Ascorbic acid and acetaminophen increase the bioavailability of ethinyl estradiol since these drugs act as competitive inhibitors for sulfation of ethinyl estradiol in the gastrointestinal wall, a known pathway of elimination for ethinyl estradiol. CYP 3A4 inhibitors such as indinavir, itraconazole, ketoconazole, fluconazole, and troleandomycin may increase plasma hormone levels. Troleandomycin may also increase the risk of intrahepatic cholestasis during coadministration with combination oral contraceptives.
Changes in Plasma Levels of Coadministered Drugs:
Combination hormonal contraceptives containing some synthetic estrogens (e.g., ethinyl estradiol) may inhibit the metabolism of other compounds. Increased plasma concentrations of cyclosporin, prednisolone and other corticosteroids, and theophylline have been reported with concomitant administration of oral contraceptives. Decreased plasma concentrations of acetaminophen and increased clearance of temazepam, salicylic acid, morphine, and clofibric acid, due to induction of conjugation (particularly glucuronidation), have been noted when these drugs were administered with oral contraceptives.
Concomitant use of Aviane may decrease lamotrigine exposure, which may reduce efficacy of lamotrigine. Adjust lamotrigine dosage as recommended in its Prescribing Information based on Aviane initiation or discontinuation.
Concomitant use of Aviane may increase thyroid-binding globulin concentration. Monitor thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) level and follow the recommendation for the thyroid hormone in accordance with its Prescribing Information.
The prescribing information of concomitant medications should be consulted to identify potential interactions.
10. Interactions with Laboratory Tests
Certain endocrine- and liver-function tests and blood components may be affected by oral contraceptives:
a. Increased prothrombin and factors VII, VIII, IX, and X; decreased antithrombin 3; increased norepinephrine-induced platelet aggregability.
b. Increased thyroid-binding globulin (TBG) leading to increased circulating total thyroid hormone, as measured by protein-bound iodine (PBI), T4 by column or by radioimmunoassay.
c. Other binding proteins may be elevated in serum i.e., corticosteroid binding globulin (CBG), sex hormone-binding globulins (SHBG) leading to increased levels of total circulating corticosteroids and sex steroids respectively.
d. Triglycerides may be increased and levels of various other lipids and lipoproteins may be affected.
e. Glucose tolerance may be decreased.
f. Serum folate levels may be depressed by oral-contraceptive therapy. This may be of clinical significance if a woman becomes pregnant shortly after discontinuing oral contraceptives.
11. Carcinogenesis
See WARNINGS section.
12. Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There is no use for contraception in pregnancy; therefore, Aviane should be discontinued during pregnancy. Epidemiologic studies and meta-analyses have not found an increased risk of genital or nongenital birth defects (including cardiac anomalies and limb-reduction defects) following exposure to COCs before conception or during early pregnancy.
In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4 percent and 15 to 20 percent,
respectively.
Data
Human Data
Epidemiologic studies and meta-analyses have not found an increased risk of genital or nongenital birth defects (including cardiac anomalies and limb-reduction defects) following exposure to COCs before conception or during early pregnancy.
13. Lactation
Contraceptive hormones and metabolites are present in human milk. CHCs can reduce milk production in breastfeeding females. This reduction can occur at any time but is less likely to occur once breastfeeding is well-established. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for Aviane and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from Aviane or from the underlying maternal condition.
14. Pediatric Use
Safety and efficacy of Aviane tablets have been established in women of reproductive age. Safety and efficacy are expected to be the same for postpubertal adolescents under the age of 16 and for users 16 years and older. Use of Aviane before menarche is not indicated.
15. Geriatric Use
Aviane has not been studied in women over 65 years of age and is not indicated in this population.
16. BodyMass Index
The safety and effectiveness of Aviane in females with a BMI > 35 kg/m2 have not been adequately evaluated.
17. Information forthe Patient
See Patient Labeling printed below.
Adverse Reactions
An increased risk of the following serious adverse reactions (see WARNINGS section for additional information) has been associated with the use of oral contraceptives:
Thromboembolic and thrombotic disorders and other vascular problems (including thrombophlebitis and venous thrombosis with or without pulmonary embolism, mesenteric thrombosis, arterial thromboembolism, myocardial infarction, cerebral hemorrhage, cerebral thrombosis), carcinoma of the reproductive organs and breasts, hepatic neoplasia (including hepatic adenomas or benign liver tumors), ocular lesions (including retinal vascular thrombosis), gallbladder disease, carbohydrate and lipid effects, elevated blood pressure, and headache including migraine.
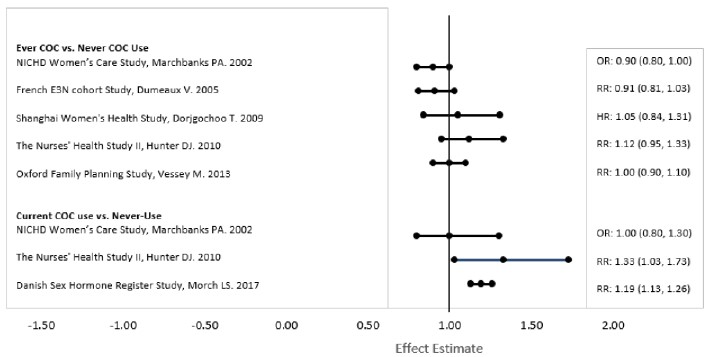
Five studies that compared breast cancer risk between ever-users (current or past use) of COCs and never-users of COCs reported no association between ever use of COCs and breast cancer risk, with effect estimates ranging from 0.90 - 1.12 (Figure 2).
Three studies compared breast cancer risk between current or recent COC users (<6 months since last use) and never users of COCs (Figure 2). One of these studies reported no association between breast cancer risk and COC use. The other two studies found an increased relative risk of 1.19 - 1.33 with current or recent use. Both of these studies found an increased risk of breast cancer with current use of longer duration, with relative risks ranging from 1.03 with less than one year of COC use to approximately 1.4 with more than 8-10 years of COC use.
FIGURE 2: Relevant Studies of Risk of Breast Cancer with Combined Oral Contraceptives
RR = relative risk; OR = odds ratio; HR = hazard ratio. “ever COC” are females with current or past COC use; “never COC use” are females that never used COCs.
The following adverse reactions associated with the use of oral CHCs were identified in clinical studies or postmarketing reports. Because some of these reactions were reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure. Common adverse reactions associated with oral CHCs are headache, abdominal pain, nausea, metrorrhagia, vaginal moniliasis and pain, acne, and vaginitis.
Additional adverse reactions that have been reported include the following:
Eye disorder: intolerance to contact lenses, steepening of corneal curvature
Gastrointestinal disorders: Abdominal bloating, vomiting
General disorders and administration site conditions: Edema, fluid retention
Hepatobiliary disorders: Cholestatic jaundice
Psychiatric disorders: Change in libido, mood changes
Reproductive system and breast disorders: Amenorrhea, breast tenderness, breast pain, breast enlargement, increased cervical mucous, change in menstrual flow, unscheduled bleeding
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: Acne, melasma
Vascular disorders: Budd-Chiari syndrome, aggravation of varicose veins
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE EVENTS, contact Teva at 1-888-838-2872 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or http://www.fda.gov/medwatch for voluntary reporting of adverse reactions.
Overdosage
Symptoms of oral contraceptive overdosage in adults and children may include nausea, vomiting, and drowsiness/fatigue; withdrawal bleeding may occur in females. There is no specific antidote and further treatment of overdose, if necessary, is directed to the symptoms.
Dosage And Administration
To achieve maximum contraceptive effectiveness, Aviane (levonorgestrel and ethinyl estradiol tablets) must be taken exactly as directed and at intervals not exceeding 24 hours. The dosage of Aviane-28 is one orange tablet daily for 21 consecutive days, followed by one light-green inert tablet daily for 7 consecutive days, according to the prescribed schedule. It is recommended that Aviane-28 tablets be taken at the same time each day.
The dispenser should be kept in the wallet supplied to avoid possible fading of the pills. If the pills fade, patients should continue to take them as directed.
During the first cycle of use
The possibility of ovulation and conception prior to initiation of medication should be considered. The patient should be instructed to begin taking Aviane on either the first Sunday after the onset of menstruation (Sunday Start) or on Day 1 of menstruation (Day 1 Start).
Sunday start:
The patient is instructed to begin taking Aviane-28 on the first Sunday after the onset of menstruation. If menstruation begins on a Sunday, the first tablet (orange) is taken that day. One orange tablet should be taken daily for 21 consecutive days, followed by one light-green inert tablet daily for 7 consecutive days. Withdrawal bleeding should usually occur within 3 days following discontinuation of orange tablets and may not have finished before the next pack is started. During the first cycle, contraceptive reliance should not be placed on Aviane-28 until an orange tablet has been taken daily for 7 consecutive days, and a nonhormonal back-up method of birth control should be used during those 7 days.
Day 1 start:
During the first cycle of medication, the patient is instructed to begin taking Aviane-28 during the first 24 hours of her period (day one of her menstrual cycle). One orange tablet should be taken daily for 21 consecutive days, followed by one light-green inert tablet daily for 7 consecutive days. Withdrawal bleeding should usually occur within 3 days following discontinuation of orange tablets and may not have finished before the next pack is started. If medication is begun on day one of the menstrual cycle, no back-up contraception is necessary. If Aviane-28 tablets are started later than day one of the first menstrual cycle or postpartum, contraceptive reliance should not be placed on Aviane-28 tablets until after the first 7 consecutive days of administration, and a nonhormonal back-up method of birth control should be used during those 7 days.
After the first cycle of use
The patient begins her next and all subsequent courses of tablets on the day after taking her last light-green tablet. She should follow the same dosing schedule: 21 days on orange tablets followed by 7 days on light-green tablets. If in any cycle the patient starts tablets later than the proper day, she should protect herself against pregnancy by using a nonhormonal back-up method of birth control until she has taken an orange tablet daily for 7 consecutive days.
Switching from another hormonal method of contraception
When the patient is switching from a 21-day regimen of tablets, she should wait 7 days after her last tablet before she starts Aviane. She will probably experience withdrawal bleeding during that week. She should be sure that no more than 7 days pass after her previous 21-day regimen. When the patient is switching from a 28-day regimen of tablets, she should start her first pack of Aviane on the day after her last tablet. She should not wait any days between packs. The patient may switch any day from a progestin-only pill and should begin Aviane the next day. If switching from an implant or injection, the patient should start Aviane on the day of implant removal or, if using an injection, the day the next injection would be due. In switching from a progestin-only pill, injection, implant, or intrauterine system (IUS), the patient should be advised to use additional nonhormonal contraception (such as condoms) until active tablets have been taken for 7 consecutive days of the first pack.
If spotting or breakthrough bleeding occurs
If spotting or breakthrough bleeding occur, the patient is instructed to continue on the same regimen. This type of bleeding is usually transient and without significance; however, if the bleeding is persistent or prolonged, the patient is advised to consult her physician.
Risk of pregnancy if tablets are missed
While there is little likelihood of ovulation occurring if only one or two orange tablets are missed, the possibility of ovulation increases with each successive day that scheduled orange tablets are missed. Although the occurrence of pregnancy is unlikely if Aviane is taken according to directions, if withdrawal bleeding does not occur, the possibility of pregnancy must be considered. If the patient has not adhered to the prescribed schedule (missed one or more tablets or started taking them on a day later than she should have), the probability of pregnancy should be considered at the time of the first missed period and appropriate diagnostic measures taken. If the patient has adhered to the prescribed regimen and misses two consecutive periods, pregnancy should be ruled out.
The risk of pregnancy increases with each active (orange) tablet missed. For additional patient instructions regarding missed tablets, see the WHAT TO DO IF YOU MISS PILLS section in the DETAILED PATIENT LABELING below.
Use after pregnancy, abortion or miscarriage
Aviane may be initiated no earlier than day 28 postpartum in the nonlactating mother or after a second trimester abortion due to the increased risk for thromboembolism (see C ONTRAINDICATIONS, WARNINGS, and PRECAUTIONS concerning thromboembolic disease). The patient should be advised to use additional nonhormonal contraception (such as condoms) until active tablets have been taken for 7 consecutive days.
Aviane may be initiated immediately after a first trimester abortion or miscarriage. Instruct the patient to use additional nonhormonal contraception (such as condoms) until active tablets have been taken for 7 consecutive days, unless starting Aviane on the day of surgical abortion.
How Supplied
Aviane® (levonorgestrel and ethinyl estradiol tablets USP), 0.10 mg/0.02 mg is available as 28 tablets packaged in cartons (NDC: 0555-9045-58) of six buler card dispensers. Each buler card dispenser contains 21 orange active tablets and 7 light-green inert tablets. Each orange tablet is round, film coated and debossed with dp on one side and 016 on the other side. Each light-green tablet is round and debossed with dp on one side and 519 on the other side.
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Keep this and all medications out of the reach of children.
Brands uled are the registered trademarks of their respective owners.
Teva Pharmaceuticals USA, Inc.
North Wales, PA 19454
Rev. F 7/2024
Aviane 28 Tablets(levonorgestrel And Ethinyl Estradiol Tablets)brief Summary Patient Package Insert
This product (like all oral contraceptives) is intended to prevent pregnancy. Oral contraceptives do not protect against transmission of HIV (AIDS) and other sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) such as chlamydia, genital herpes, genital warts, gonorrhea, hepatitis B, and syphilis.
Oral contraceptives, also known as “birth-control pills” or “the pill,” are taken to prevent pregnancy, and when taken correctly, have a failure rate of approximately 1.0% per year (1 pregnancy per 100 women per year of use) when used without missing any pills. The average failure rate of large numbers of pill users is approximately 5% per year (5 pregnancies per 100 women per year of use) when women who miss pills are included. For most women oral contraceptives are also free of serious or unpleasant side effects. However, forgetting to take pills considerably increases the chances of pregnancy.
For the majority of women, oral contraceptives can be taken safely. But there are some women who are at high risk of developing certain serious diseases that can be life-threatening or may cause temporary or permanent disability or death. The risks associated with taking oral contraceptives increase significantly if you:
- smoke.
- have high blood pressure, diabetes, high cholesterol, or a tendency to form blood clots.
- have or have had clotting disorders, heart attack, stroke, angina pectoris, cancer of the breast or sex organs, jaundice, malignant or benign liver tumors, or major surgery with prolonged immobilization.
- have headaches with neurological symptoms.
You should not take the pill if you take any Hepatitis C drug combination containing ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir, with or without dasabuvir. This may increase levels of the liver enzyme “alanine aminotransferase” (ALT) in the blood.
You should not take the pill if you suspect you are pregnant or have unexplained vaginal bleeding.
Although cardiovascular disease risks may be increased with oral-contraceptive use after age 40 in healthy, nonsmoking women, there are also greater potential health risks associated with pregnancy in older women.
BOXED WARNING SECTION
WARNING: CIGARETTE SMOKING AND SERIOUS CARDIOVASCULAR EVENTS Cigarette smoking increases the risk of serious cardiovascular events from combined oral contraceptives (COC) use. This risk increases with age, particularly in women over 35 years of age, and with the number of cigarettes smoked. For this reason, COCs, including Aviane (levonorgestrel and ethinyl estradiol tablets), are contraindicated in women who are over 35 years of age and smoke (see CONTRAINDICATIONS and WARNINGS).
Most side effects of the pill are not serious. The most common such effects are nausea, vomiting, bleeding between menstrual periods, weight gain, breast tenderness, and difficulty wearing contact lenses. These side effects, especially nausea and vomiting, may subside within the first three months of use.
The serious side effects of the pill occur very infrequently, especially if you are in good health and do not smoke. However, you should know that the following medical conditions have been associated with or made worse by the pill:
- Blood clots in the legs (thrombophlebitis) and lungs (pulmonary embolism), blockage or rupture of a blood vessel in the brain (stroke), blockage of blood vessels in the heart (heart attack and angina pectoris) or other organs of the body. As mentioned above, smoking increases the risk of heart attacks and strokes and subsequent serious medical consequences. Women with migraine also may be at increased risk of stroke with pill use.
- Liver tumors, which may rupture and cause severe bleeding. A possible but not definite association has been found with the pill and liver cancer. However, liver cancers are extremely rare. The chance of developing liver cancer from using the pill is thus even rarer.
- High blood pressure, although blood pressure usually returns to normal when the pill is stopped.
The symptoms associated with these serious side effects are discussed in the detailed leaflet given to you with your supply of pills. Notify your health-care provider if you notice any unusual physical disturbances while taking the pill. In addition, drugs such as rifampin, as well as some anticonvulsants and some antibiotics, herbal preparations containing St. John's Wort (Hypericum perforatum), and HIV/AIDS drugs may decrease oral-contraceptive effectiveness.
There may be slight increases in the risk of breast cancer among current users of hormonal birth control pills with longer duration of use of 8 years or more.
Some studies have found an increase in the incidence of cancer of the cervix in women who use oral contraceptives. However, this finding may be related to factors other than the use of oral contraceptives.
Be sure to discuss any medical condition you may have with your health-care provider. Your health-care provider will take a medical and family history before prescribing oral contraceptives and will examine you. The physical examination may be delayed to another time if you request it and the health-care provider believes that it is appropriate to postpone it. You should be reexamined at least once a year while taking oral contraceptives. The detailed patient information leaflet gives you further information which you should read and discuss with your health-care provider.
HOW TO TAKE THE PILL
IMPORTANT POINTS TO REMEMBER
BEFORE YOU START TAKING YOUR PILLS:
- BE SURE TO READ THESE DIRECTIONS: Before you start taking your pills. And Anytime you are not sure what to do.
- THE RIGHT WAY TO TAKE THE PILL IS TO TAKE ONE PILL EVERY DAY AT THE SAME TIME. If you miss pills you could get pregnant. This includes starting the pack late. The more pills you miss, the more likely you are to get pregnant. See “WHAT TO DO IF YOU MISS PILLS” below.
- MANY WOMEN HAVE SPOTTING OR LIGHT BLEEDING, OR MAY FEEL SICK TO THEIR STOMACH DURING THE FIRST 1 TO 3 PACKS OF PILLS. If you feel sick to your stomach, do not stop taking the pill. The problem will usually go away. If it doesn't go away, check with your health-care provider.
- MISSING PILLS CAN ALSO CAUSE SPOTTING OR LIGHT BLEEDING, even when you make up these missed pills. On the days you take 2 pills to make up for missed pills, you could also feel a little sick to your stomach.
- IF YOU HAVE VOMITING (within 4 hours after you take your pill), you should follow the instructions for WHAT TO DO IF YOU MISS PILLS. IF YOU HAVE DIARRHEA or IF YOU TAKE SOME MEDICINES, including some antibiotics, your pills may not work as well. Use a back-up nonhormonal method (such as condoms or spermicide) until you check with your health-care provider.
- IF YOU HAVE TROUBLE REMEMBERING TO TAKE THE PILL, talk to your health-care provider about how to make pill-taking easier or about using another method of birth control.
- IF YOU HAVE ANY QUESTIONS OR ARE UNSURE ABOUT THE INFORMATION IN THIS LEAFLET, call your health-care provider.
BEFORE YOU START TAKING YOUR PILLS
- DECIDE WHAT TIME OF DAY YOU WANT TO TAKE YOUR PILL. It is important to take it at about the same time every day.
- LOOK AT YOUR PILL PACK: The 28 pill pack has 21 “active” orange pills (with hormones) to take for 3 weeks, followed by 1 week of reminder light-green pills (without hormones).
- FIND: 1) where on the pack to start taking pills, 2) in what order to take the pills (follow the arrows) and 3) the week numbers printed on the pack.
- BE SURE YOU HAVE READY AT ALL TIMES: ANOTHER KIND OF BIRTH CONTROL (such as condoms or spermicide) to use as a back-up in case you miss pills. AN EXTRA, FULL PILL PACK.
WHEN TO START THE FIRST PACK OF PILLS
You have a choice of which day to start taking your first pack of pills.
Decide with your health-care provider which is the best day for you. Pick a time of day which will be easy to remember.
DAY 1 START
- Pick the day label strip that starts with the first day of your period (this is the day you start bleeding or spotting, even if it is almost midnight when the bleeding begins).
- Place this day label strip on the cycle tablet dispenser over the area that has the days of the week (starting with Sunday) printed on the dispensing card. Note: If the first day of your period is a Sunday, you can skip steps #1 and #2.
- Take the first “active” orange pill of the first pack during the first 24 hours of your period.
- You will not need to use a back-up nonhormonal method of birth control, since you are starting the pill at the beginning of your period.
SUNDAY START
- Take the first “active” orange pill of the first pack on the Sunday after your period starts, even if you are still bleeding. If your period begins on Sunday, start the pack that same day.
- Use a nonhormonal method of birth control (such as condoms or spermicide) as a back-up method if you have sex anytime from the Sunday you start your first pack until the next Sunday (7 days).
WHAT TO DO DURING THE MONTH
- Take one pill at the same time every day until the pack is empty. Do not skip pills even if you are spotting or bleeding between monthly periods or feel sick to your stomach (nausea). Do not skip pills even if you do not have sex very often.
- When you finish a pack: Start the next pack on the day after your last “reminder” pill. Do not wait any days between packs.
IF YOU SWITCH FROM ANOTHER BRAND OF COMBINATION PILLS
If your previous brand had 21 pills: Wait 7 days to start taking Aviane. You will probably have your period during that week. Be sure that no more than 7 days pass between the 21-day pack and taking the first orange Aviane pill (“active” with hormone).
If your previous brand had 28 pills: Start taking the first orange Aviane pill (“active” with hormone) on the day after your last reminder pill. Do not wait any days between packs.
WHAT TO DO IF YOU MISS PILLS
Aviane may not be as effective if you miss orange “active” pills, and particularly if you miss the first few or the last few orange “active” pills in a pack.
If you MISS 1 orange “active” pill:
- Take it as soon as you remember. Take the next pill at your regular time. This means you may take 2 pills in 1 day.
- You COULD BECOME PREGNANT if you have sex in the 7 days after you restart your pills. You MUST use a nonhormonal birth-control method (such as condoms or spermicide) as a back-up for those 7 days.
If you MISS 2 orange “active” pills in a row in WEEK 1 OR WEEK 2 of your pack:
- Take 2 pills on the day you remember and 2 pills the next day.
- Then take 1 pill a day until you finish the pack.
- You COULD BECOME PREGNANT if you have sex in the 7 days after you restart your pills. You MUST use a nonhormonal birth-control method (such as condoms or spermicide) as a back-up for those 7 days.
If you MISS 2 orange “active” pills in a row in THE 3rd WEEK:
- If you are a Day 1 Starter: THROW OUT the rest of the pill pack and start a new pack that same day. If you are a Sunday Starter: Keep taking 1 pill every day until Sunday. On Sunday, THROW OUT the rest of the pack and start a new pack of pills that same day.
- You may not have your period this month but this is expected. However, if you miss your period 2 months in a row, call your health-care provider because you might be pregnant.
- You COULD BECOME PREGNANT if you have sex in the 7 days after you restart your pills. You MUST use a nonhormonal birth-control method (such as condoms or spermicide) as a back-up for those 7 days.
If you MISS 3 OR MORE orange “active” pills in a row (during the first 3 weeks):
- If you are a Day 1 Starter: THROW OUT the rest of the pill pack and start a new pack that same day. If you are a Sunday Starter: Keep taking 1 pill every day until Sunday. On Sunday, THROW OUT the rest of the pack and start a new pack of pills that same day.
- You may not have your period this month but this is expected. However, if you miss your period 2 months in a row, call your health-care provider because you might be pregnant.
- You COULD BECOME PREGNANT if you have sex in the 7 days after you restart your pills. You MUST use a nonhormonal birth-control method (such as condoms or spermicide) as a back-up for those 7 days.
If you forget any of the 7 light-green “reminder” pills in WEEK 4:
THROW AWAY the pills you missed.
Keep taking 1 pill each day until the pack is empty.
You do not need a back-up nonhormonal birth-control method if you start your next pack on time.
FINALLY, IF YOU ARE STILL NOT SURE WHAT TO DO ABOUT THE PILLS YOU HAVE MISSED
Use a BACK-UP NONHORMONAL BIRTH-CONTROL METHOD anytime you have sex.
KEEP TAKING ONE PILL EACH DAY until you can reach your health-care provider.
BIRTH CONTROL AFTER STOPPING THE PILL
If you do not wish to become pregnant after stopping the pill, speak to your health-care provider about another method of birth control.
Teva Pharmaceuticals USA, Inc. North Wales, PA 19454
Rev. F 7/2024
Aviane28 Tablets(levonorgestrel and ethinyl estradiol tablets)DETAILED PATIENT LABELING
This product (like all oral contraceptives) is intended to prevent pregnancy. Oral contraceptives do not protect against transmission of HIV (AIDS) and other sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) such as chlamydia, genital herpes, genital warts, gonorrhea, hepatitis B, and syphilis.
INTRODUCTION
Any woman who considers using oral contraceptives (the “birth-control pill” or “the pill”) should understand the benefits and risks of using this form of birth control. This leaflet will give you much of the information you will need to make this decision and will also help you determine if you are at risk of developing any of the serious side effects of the pill. It will tell you how to use the pill properly so that it will be as effective as possible. However, this leaflet is not a replacement for a careful discussion between you and your health-care provider. You should discuss the information provided in this leaflet with him or her, both when you first start taking the pill and during your revisits. You should also follow your health-care provider's advice with regard to regular check-ups while you are on the pill.
EFFECTIVENESS OF ORAL CONTRACEPTIVES
Oral contraceptives or “birth-control pills” or “the pill” are used to prevent pregnancy and are more effective than most other nonsurgical methods of birth control. When they are taken correctly, without missing any pills, the chance of becoming pregnant is approximately 1% per year (1 pregnancy per 100 women per year of use). Typical failure rates are approximately 5% per year (5 pregnancies per 100 women per year of use) when women who miss pills are included. The chance of becoming pregnant increases with each missed pill during each 28-day cycle of use.
In comparison, average failure rates for other methods of birth control during the first year of use are as follows:
IUD: 0.1 to 2%
Female condom alone: 21%
Depo-Provera® (injectable progestogen): 0.3%
Cervical cap
Norplant® System (levonorgestrel implants): 0.05%
Never given birth: 20%
Diaphragm with spermicides: 20%
Given birth: 40%
Spermicides alone: 26%
Periodic abstinence: 25%
Male condom alone: 14%
No methods: 85%
WHO SHOULD NOT TAKE ORAL CONTRACEPTIVES
WARNING: CIGARETTE SMOKING AND SERIOUS CARDIOVASCULAR EVENTS Cigarette smoking increases the risk of serious cardiovascular events from combined oral contraceptives (COC) use. This risk increases with age, particularly in women over 35 years of age, and with the number of cigarettes smoked. For this reason, COCs, including Aviane (levonorgestrel and ethinyl estradiol tablets), are contraindicated in women who are over 35 years of age and smoke.
Some women should not use the pill. For example, you should not take the pill if you have any of the following conditions:
- History of heart attack or stroke.
- Blood clots in the legs (thrombophlebitis), lungs (pulmonary embolism), or eyes.
- A history of blood clots in the deep veins of your legs.
- A problem with your blood that makes it clot more than normal.
- Chest pain (angina pectoris).
- Known or suspected breast cancer or cancer sensitive to female hormones.
- Unexplained vaginal bleeding (until a diagnosis is reached by your health-care provider).
- Liver tumor (benign or cancerous) or active liver disease.
- Yellowing of the whites of the eyes or of the skin (jaundice) during pregnancy or during previous use of the pill.
- Known or suspected pregnancy.
- A need for surgery with prolonged bedrest.
- Heart valve or heart rhythm disorders that may be associated with formation of blood clots.
- Diabetes affecting your circulation.
- Certain kinds of severe migraine headaches with aura, numbness, weakness or changes in vision, or any migraine headaches if you are over 35 years of age.
- Uncontrolled high blood pressure.
Tell your health-care provider if you have had any of these conditions. Your health-care provider can recommend another method of birth control.
You should not take the pill if you take any Hepatitis C drug combination containing ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir, with or without dasabuvir. This may increase levels of the liver enzyme “alanine aminotransferase” (ALT) in the blood.
OTHER CONSIDERATIONS BEFORE TAKING ORAL CONTRACEPTIVES Tell your health-care provider if you have ever had:
- An abnormal mammogram.
- Diabetes.
- Elevated cholesterol or triglycerides.
- High blood pressure.
- A tendency to form blood clots.
- Migraine or other headaches or epilepsy.
- Depression.
- Gallbladder, liver, heart, or kidney disease.
- History of scanty or irregular menstrual periods.
Women with any of these conditions should be checked often by their health-care provider if they choose to use oral contraceptives. Also, be sure to inform your health-care provider if you smoke or are on any medications.
Although cardiovascular disease risks may be increased with oral contraceptive use in healthy, non-smoking women over 40 (even with the newer low-dose formulations), there are also greater potential health risks associated with pregnancy in older women.
RISKS OF TAKING ORAL CONTRACEPTIVES
1. Risks of Developing Blood Clots
Blood clots and blockage of blood vessels are the most serious side effects of taking oral contraceptives and can cause death or serious disability. In particular, a clot in the legs can cause thrombophlebitis and a clot that travels to the lungs can cause a sudden blocking of the vessel carrying blood to the lungs. Rarely, clots occur in the blood vessels of the eye and may cause blindness, double vision, or impaired vision.
Users of combination oral contraceptives have a higher risk of developing blood clots compared to non-users. This risk is highest during the first year of combination oral-contraceptive use.
If you take oral contraceptives and need elective surgery, need to stay in bed for a prolonged illness or injury, or have recently delivered a baby, you may be at risk of developing blood clots. You should consult your health-care provider about stopping oral contraceptives three to four weeks before surgery and not taking oral contraceptives for two weeks after surgery or during bed rest. You should also not take oral contraceptives soon after delivery of a baby or after a mid-trimester pregnancy termination. It is advisable to wait for at least four weeks after delivery if you are not breastfeeding. If you are breastfeeding, you should wait until you have weaned your child before using the pill (see also the section While Breastfeeding in GENERAL PRECAUTIONS).
The risk of blood clots is greater in users of combination oral contraceptives compared to nonusers. The risk of abnormal blood clotting increases with age in both users and nonusers of combination oral contraceptives, but the increased risk from the oral contraceptive appears to be present at all ages.
The excess risk of blood clots is highest during the first year a woman ever uses a combined oral contraceptive. This increased risk is lower than blood clots associated with pregnancy. The use of combination oral contraceptives also increases the risk of other clotting disorders, including heart attack and stroke. Blood clots in veins cause death in 1% to 2% of cases. The risk of clotting is further increased in women with other conditions. Examples include: smoking, high blood pressure, abnormal lipid levels, certain inherited or acquired clotting disorders, obesity, surgery or injury with prolonged inactivity or bedrest, recent delivery or second trimester abortion. Discuss with your healthcare provider whether combination oral contraceptives should be stopped before surgery with prolonged inactivity or bedrest.
Cigarette smoking increases the risk of serious cardiovascular events from COC use. This risk increases with age and amount of smoking and is quite pronounced in women over 35. Women who use combination oral contraceptives should be strongly advised not to smoke. If you smoke you should not use combination oral contraceptives.
2. Heart Attacks and Strokes
Oral contraceptives may increase the tendency to develop strokes or transient ischemic attacks (blockage or rupture of blood vessels in the brain) and angina pectoris and heart attacks (blockage of blood vessels in the heart). Any of these conditions can cause death or serious disability.
Smoking greatly increases the possibility of suffering heart attacks and strokes. Furthermore, smoking and the use of oral contraceptives greatly increase the chances of developing and dying of heart disease.
Women with migraine (especially migraine/headache with neurological symptoms) who take oral contraceptives also may be at higher risk of stroke and must not use combination oral contraceptives (see section WHO SHOULD NOT TAKE ORAL CONTRACEPTIVES).
3. Gallbladder Disease
Oral-contraceptive users probably have a greater risk than nonusers of having gallbladder disease. Oral-contraceptives may worsen existing gallbladder disease or accelerate the development of gallbladder disease in women previously without symptoms.
4. Liver Tumors
In rare cases, oral contraceptives can cause benign but dangerous liver tumors. These benign liver tumors can rupture and cause fatal internal bleeding. In addition, a possible but not definite association has been found with the pill and liver cancers in two studies in which a few women who developed these very rare cancers were found to have used oral contraceptives for long periods. However, liver cancers are extremely rare. The chance of developing liver cancer from using the pill is thus even rarer.
5. Risk of Cancer
It is not known if hormonal birth control pills causes breast cancer. Some studies, but not all, suggest that there could be a slight increase in the risk of breast cancer among current users with longer duration of use.
If you have breast cancer now, or have had it in the past, do not use hormonal birth control because some breast cancers are sensitive to hormones.
Some studies have found an increase in the incidence of cancer of the cervix in women who use oral contraceptives. However, this finding may be related to factors other than the use of oral contraceptives.
6. Lipid Metabolism and Pancreatitis
There have been reports of increases of blood cholesterol and triglycerides in users of combination oral contraceptives. Increases in triglycerides have led to inflammation of the pancreas (pancreatitis) in some cases.
WARNING SIGNALS
If any of these adverse effects occur while you are taking oral contraceptives, call your health-care provider immediately:
- Sharp chest pain, coughing of blood, or sudden shortness of breath (indicating a possible clot in the lung).
- Pain in the calf (indicating a possible clot in the leg).
- Crushing chest pain or heaviness in the chest (indicating a possible heart attack).
- Sudden severe headache or vomiting, dizziness or fainting, disturbances of vision or speech, weakness, or numbness in an arm or leg (indicating a possible stroke).
- Sudden partial or complete loss of vision (indicating a possible clot in the eye).
- Severe pain or tenderness in the stomach area (indicating a possibly ruptured liver tumor).
- Difficulty in sleeping, weakness, lack of energy, fatigue, or change in mood (possibly indicating severe depression).
- Jaundice or a yellowing of the skin or eyeballs, accompanied frequently by fever, fatigue, loss of appetite, dark-colored urine, or light-colored bowel movements (indicating possible liver problems).
SIDE EFFECTS OF ORAL CONTRACEPTIVES
1. Unscheduled or Breakthrough Vaginal Bleeding or Spotting
Unscheduled vaginal bleeding or spotting may occur while you are taking the pills. Unscheduled bleeding may vary from slight staining between menstrual periods to breakthrough bleeding which is a flow much like a regular period. Unscheduled bleeding occurs most often during the first few months of oral-contraceptive use, but may also occur after you have been taking the pill for some time. Such bleeding may be temporary and usually does not indicate any serious problems. It is important to continue taking your pills on schedule. If the bleeding occurs in more than one cycle or lasts for more than a few days, talk to your health-care provider.
2. Possible cancer that is sensitive to female hormones or possible cancer of the cervix
Women who have or have ever had breast cancer, or any cancer sensitive to female hormones – such as skin cancer (melanoma), lung cancer, and brain cancer, should not use Aviane. However, birth control pills do not seem to cause cancer.
Women who use birth control pills may have a slightly higher chance of getting cervical cancer. However, this may be due to other reasons, such as having more sexual partners.
3. Contact Lenses
If you wear contact lenses and notice a change in vision or an inability to wear your lenses, contact your health-care provider.
4. Fluid Retention
Oral contraceptives may cause edema (fluid retention) with swelling of the fingers or ankles and may raise your blood pressure. If you experience fluid retention, contact your health-care provider.
5. Melasma
A spotty darkening of the skin is possible, particularly of the face.
6. Other Side Effects
Other side effects may include nausea, breast tenderness, change in appetite, headache, nervousness, depression, dizziness, loss of scalp hair, rash, vaginal infections, inflammation of the pancreas, and allergic reactions.
If any of these side effects bother you, call your health-care provider.
GENERAL PRECAUTIONS
1. Missed Periods and Use of Oral Contraceptives Before or During Early Pregnancy
There may be times when you may not menstruate regularly after you have completed taking a cycle of pills. If you have taken your pills regularly and miss one menstrual period, continue taking your pills for the next cycle but be sure to inform your health-care provider before doing so. If you have not taken the pills daily as instructed and missed a menstrual period, or if you missed two consecutive menstrual periods, you may be pregnant. Check with your health-care provider immediately to determine whether you are pregnant. Stop taking oral contraceptives if you are pregnant.
There is no conclusive evidence that oral-contraceptive use is associated with an increase in birth defects, when taken inadvertently during early pregnancy. Previously, a few studies had reported that oral contraceptives might be associated with birth defects, but these studies have not been confirmed. Nevertheless, oral contraceptives should not be used during pregnancy. You should check with your health-care provider about risks to your unborn child of any medication taken during pregnancy.
2. While Breastfeeding
If you are breastfeeding, consult your health-care provider before starting oral contraceptives. Some of the drug will be passed on to the child in the milk. A few adverse effects on the child have been reported, including yellowing of the skin (jaundice) and breast enlargement. In addition, oral contraceptives may decrease the amount and quality of your milk. If possible, do not use oral contraceptives while breastfeeding. You should use another method of contraception since breastfeeding provides only partial protection from becoming pregnant and this partial protection decreases significantly as you breastfeed for longer periods of time. You should consider starting oral contraceptives only after you have weaned your child completely.
3. Laboratory Tests
If you are scheduled for any laboratory tests, tell your doctor you are taking birth-control pills. Certain blood tests may be affected by birth-control pills.
4. Drug Interactions
Certain drugs may interact with birth-control pills to make them less effective in preventing pregnancy or cause an increase in breakthrough bleeding. Such drugs include rifampin, drugs used for epilepsy such as barbiturates (for example, phenobarbital) and phenytoin (Dilantin® is one brand of this drug), primidone (Mysoline®), topiramate (Topamax®), carbamazepine (Tegretol® is one brand of this drug), phenylbutazone (Butazolidin® is one brand), some drugs used for HIV or AIDS such as ritonavir (Norvir®), modafinil (Provigil®) and possibly certain antibiotics (such as ampicillin and other penicillins, and tetracyclines), and herbal products containing St. John's Wort (Hypericum perforatum). You may also need to use a nonhormonal method of contraception during any cycle in which you take drugs that can make oral contraceptives less effective.
You may be at higher risk of a specific type of liver dysfunction if you take troleandomycin and oral contraceptives at the same time.
You should inform your health-care provider about all medicines you are taking, including nonprescription products.
5. Sexually Transmitted Diseases
This product (like all oral contraceptives) is intended to prevent pregnancy. It does not protect against transmission of HIV (AIDS) and other sexually transmitted diseases such as chlamydia, genital herpes, genital warts, gonorrhea, hepatitis B, and syphilis.
HOW TO TAKE THE PILL
IMPORTANT POINTS TO REMEMBER
BEFORE YOU START TAKING YOUR PILLS:
- BE SURE TO READ THESE DIRECTIONS: Before you start taking your pills. And Anytime you are not sure what to do.
- THE RIGHT WAY TO TAKE THE PILL IS TO TAKE ONE PILL EVERY DAY AT THE SAME TIME. If you miss pills you could get pregnant. This includes starting the pack late. The more pills you miss, the more likely you are to get pregnant. See “WHAT TO DO IF YOU MISS PILLS” below.
- MANY WOMEN HAVE SPOTTING OR LIGHT BLEEDING, OR MAY FEEL SICK TO THEIR STOMACH DURING THE FIRST 1 TO 3 PACKS OF PILLS. If you feel sick to your stomach, do not stop taking the pill. The problem will usually go away. If it doesn't go away, check with your health-care provider.
- MISSING PILLS CAN ALSO CAUSE SPOTTING OR LIGHT BLEEDING, even when you make up these missed pills. On the days you take 2 pills to make up for missed pills, you could also feel a little sick to your stomach.
- IF YOU HAVE VOMITING (within 4 hours after you take your pill), you should follow the instructions for WHAT TO DO IF YOU MISS PILLS. IF YOU HAVE DIARRHEA or IF YOU TAKE SOME MEDICINES, including some antibiotics, your pills may not work as well. Use a back-up nonhormonal method (such as condoms or spermicide) until you check with your health-care provider.
- IF YOU HAVE TROUBLE REMEMBERING TO TAKE THE PILL, talk to your health-care provider about how to make pill-taking easier or about using another method of birth control.
- IF YOU HAVE ANY QUESTIONS OR ARE UNSURE ABOUT THE INFORMATION IN THIS LEAFLET, contact your health-care provider.
BEFORE YOU START TAKING YOUR PILLS
- DECIDE WHAT TIME OF DAY YOU WANT TO TAKE YOUR PILL. It is important to take it at about the same time every day.
- LOOK AT YOUR PILL PACK: The 28 pill pack has 21 “active” orange pills (with hormones) to take for 3 weeks, followed by 1 week of reminder light-green pills (without hormones).
- FIND: 1) where on the pack to start taking pills, 2) in what order to take the pills (follow the arrows) and 3) the week numbers printed on the pack.

- BE SURE YOU HAVE READY AT ALL TIMES: ANOTHER KIND OF BIRTH CONTROL (such as condoms or spermicide) to use as a back-up in case you miss pills. AN EXTRA, FULL PILL PACK.
WHEN TO START THE FIRST PACK OF PILLS
You have a choice of which day to start taking your first pack of pills.
Decide with your health-care provider which is the best day for you. Pick a time of day which will be easy to remember.
DAY 1 START:
- Pick the day label strip that starts with the first day of your period (this is the day you start bleeding or spotting, even if it is almost midnight when the bleeding begins).
- Place this day label strip on the cycle tablet dispenser over the area that has the days of the week (starting with Sunday) printed on the dispensing card. Note: If the first day of your period is a Sunday, you can skip steps #1 and #2.
- Take the first “active” orange pill of the first pack during the first 24 hours of your period.
- You will not need to use a back-up nonhormonal method of birth control, since you are starting the pill at the beginning of your period.
SUNDAY START:
- Take the first “active” orange pill of the first pack on the Sunday after your period starts, even if you are still bleeding. If your period begins on Sunday, start the pack that same day.
- Use a nonhormonal method of birth control (such as condoms or spermicide) as a back-up method if you have sex anytime from the Sunday you start your first pack until the next Sunday (7 days).
WHAT TO DO DURING THE MONTH
- Take one pill at the same time every day until the pack is empty. Do not skip pills even if you are spotting or bleeding between monthly periods or feel sick to your stomach (nausea). Do not skip pills even if you do not have sex very often.
- When you finish a pack: Start the next pack on the day after your last “reminder” pill. Do not wait any days between packs.
IF YOU SWITCH FROM ANOTHER BRAND OF COMBINATION PILLS:
If your previous brand had 21 pills: Wait 7 days to start taking Aviane. You will probably have your period during that week. Be sure that no more than 7 days pass between the 21-day pack and taking the first orange Aviane pill (“active” with hormone).
If your previous brand had 28 pills: Start taking the first orange Aviane pill (“active” with hormone) on the day after your last reminder pill. Do not wait any days between packs.
WHAT TO DO IF YOU MISS PILLS
Aviane may not be as effective if you miss orange “active” pills, and particularly if you miss the first few or the last few orange “active” pills in a pack.
If you MISS 1 orange “active” pill:
- Take it as soon as you remember. Take the next pill at your regular time. This means you may take 2 pills in 1 day.
If you MISS 2 orange “active” pills in a row in WEEK 1 OR WEEK 2 of your pack:
- Take 2 pills on the day you remember and 2 pills the next day.
- Then take 1 pill a day until you finish the pack.
- You COULD BECOME PREGNANT if you have sex in the 7 days after you restart your pills. You MUST use a nonhormonal birth-control method (such as condoms or spermicide) as a back-up for those 7 days.
If you MISS 2 orange “active” pills in a row in THE 3rd WEEK:
- If you are a Day 1 Starter: THROW OUT the rest of the pill pack and start a new pack that same day. If you are a Sunday Starter: Keep taking 1 pill every day until Sunday. On Sunday, THROW OUT the rest of the pack and start a new pack of pills that same day.
- You may not have your period this month but this is expected. However, if you miss your period 2 months in a row, call your health-care provider because you might be pregnant.
- You COULD BECOME PREGNANT if you have sex in the 7 days after you restart your pills. You MUST use a nonhormonal birth-control method (such as condoms or spermicide) as a back-up for those 7 days.
If you MISS 3 OR MORE orange “active” pills in a row (during the first 3 weeks):
- If you are a Day 1 Starter: THROW OUT the rest of the pill pack and start a new pack that same day. If you are a Sunday Starter: Keep taking 1 pill every day until Sunday. On Sunday, THROW OUT the rest of the pack and start a new pack of pills that same day.
- You may not have your period this month but this is expected. However, if you miss your period 2 months in a row, call your health-care provider because you might be pregnant.
- You COULD BECOME PREGNANT if you have sex in the 7 days after you restart your pills. You MUST use a nonhormonal birth-control method (such as condoms or spermicide) as a back-up for those 7 days.
If you forget any of the 7 light-green “reminder” pills in WEEK 4:
THROW AWAY the pills you missed.
Keep taking 1 pill each day until the pack is empty.
You do not need a back-up nonhormonal birth-control method if you start your next pack on time.
FINALLY, IF YOU ARE STILL NOT SURE WHAT TO DO ABOUT THE PILLS YOU HAVE MISSED
Use a BACK-UP NONHORMONAL BIRTH-CONTROL METHOD anytime you have sex.
KEEP TAKING ONE PILL EACH DAY until you can reach your health-care provider.
PREGNANCY DUE TO PILL FAILURE
The incidence of pill failure resulting in pregnancy is approximately 1 per year (1 pregnancy per 100 women per year of use) if taken every day as directed, but the more typical failure rate is approximately 5% per year (5 pregnancies per 100 women per year of use) including women who do not always take the pill exactly as directed without missing any pills. If you do become pregnant, the risk to the fetus is minimal, but you should stop taking your pills and discuss the pregnancy with your health-care provider.
PREGNANCY AFTER STOPPING THE PILL
There may be some delay in becoming pregnant after you stop using oral contraceptives, especially if you had irregular menstrual cycles before you used oral contraceptives. It may be advisable to postpone conception until you begin menstruating regularly once you have stopped taking the pill and desire pregnancy.
There does not appear to be any increase in birth defects in newborn babies when pregnancy occurs soon after stopping the pill.
BIRTH CONTROL AFTER STOPPING THE PILL
If you do not wish to become pregnant after stopping the pill, you should use another method of birth control immediately after stopping Aviane. Speak to your health-care provider about another method of birth control.
OVERDOSAGE
Overdosage may cause nausea, vomiting, breast tenderness, dizziness, abdominal pain and fatigue/drowsiness. Withdrawal bleeding may occur in females. In case of overdosage, contact your health-care provider or pharmacist.
OTHER INFORMATION
Your health-care provider will take a medical and family history before prescribing oral contraceptives and will examine you. The physical examination may be delayed to another time if you request it and your health-care provider believes that it is appropriate to postpone it. You should be reexamined at least once a year. Be sure to inform your health-care provider if there is a family history of any of the conditions uled previously in this leaflet. Be sure to keep all appointments with your health-care provider, because this is a time to determine if there are early signs of side effects of oral-contraceptive use.
Do not use the drug for any condition other than the one for which it was prescribed. This drug has been prescribed specifically for you; do not give it to others who may want birth-control pills.
If you want more information about birth-control pills, ask your health-care provider or pharmacist. They have a more technical leaflet called the Professional Labeling which you may wish to read.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Keep this and all medications out of the reach of children.
Brands uled are the registered trademarks of their respective owners.
Teva Pharmaceuticals USA, Inc. North Wales, PA 19454
Rev. F 7/2024
Package/label Display Panel, Part1 Of 2
NDC 0555-9045-58
6 Buler Cards, 28 Tablets Each
Aviane®
(levonorgestrel and ethinyl
estradiol tablets USP)
0.10 mg/0.02 mg
Contains 6 buler cards, each containing 28 tablets. Twenty-one
orange tablets, each containing 0.10 mg levonorgestrel, USP with
0.02 mg ethinyl estradiol, USP and seven light-green inert tablets.
Rx only
SHAPING
WOMEN’S HEALTH®
TEVA

Package/label Display Panel, Part2 Of 2
DISCLAIMER:
"This tool does not provide medical advice, and is for informational and educational purposes only, and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, treatment or diagnosis. Call your doctor to receive medical advice. If you think you may have a medical emergency, please dial 911."
"Do not rely on openFDA to make decisions regarding medical care. While we make every effort to ensure that data is accurate, you should assume all results are unvalidated. We may limit or otherwise restrict your access to the API in line with our Terms of Service."
"This product uses publicly available data from the U.S. National Library of Medicine (NLM), National Institutes of Health, Department of Health and Human Services; NLM is not responsible for the product and does not endorse or recommend this or any other product."
PillSync may earn a commission via links on our site