Carbinoxamine Maleate (carbinoxamine maleate 4 mg) Dailymed
Generic: carbinoxamine maleate is used for the treatment of Angioedema Breast Feeding Conjunctivitis, Allergic Coronary Disease Hypertension Infant, Newborn Infant, Premature Intestinal Obstruction Peptic Ulcer Rhinitis, Allergic, Perennial Rhinitis, Vasomotor Status Asthmaticus Ureteral Obstruction Urethral Obstruction Glaucoma, Angle-Closure
Go PRO for all pill images
Description
Carbinoxamine maleate is a histamine-H 1 receptor blocking agent.
Each tablet contains 4 mg carbinoxamine maleate and the following inactive ingredients: anhydrous lactose, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, and sodium starch glycolate.
Each 5 mL (teaspoonful) of oral solution contains 4 mg carbinoxamine maleate and the following inactive ingredients: artificial bubble gum flavor, citric acid (anhydrous), glycerin, methylparaben, propylene glycol, propylparaben, purified water, sodium citrate (hydrous) and sorbitol solution.
Carbinoxamine maleate is freely soluble in water. Its structure is:
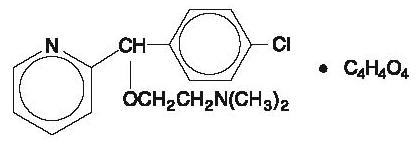
2-[(4-chlorophenyl)-2-pyridinylmethoxy]- N, N -dimethylethanamine (Z)-2-butenedioate (1:1)
C 16H 19CIN 2O∙C 4H 4O 4
MW = 406.86
Clinical Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
Carbinoxamine maleate, an ethanolamine derivative, is an antihistamine with anticholinergic (drying) and sedative properties. Carbinoxamine appears to compete with histamine (type H1) for receptor sites on effector cells in the gastrointestinal tract, blood vessels and respiratory tract.
Pharmacokinetics and Metabolism
Carbinoxamine is well absorbed from the GI tract and appears to be extensively metabolized by the liver, and excreted in the urine as inactive metabolites within 24 hours. Virtually no intact drug is extended in the urine.
In a study comparing a controlled-release suspension and a solution of carbinoxamine, healthy volunteers were administered a single dose of 8 mg carbinoxamine. A time to maximum concentration (Tmax) was between 1.5 hours to 5 hours, a peak plasma concentration (Cmax) of about 24 ng/mL was observed and extent of exposure (AUC) was about 286 ng hr/mL. The serum half-life is reported to be 10 to 20 hours.
Drug/Food Interactions
Carbinoxamine should not be used in patients with hypersensitivity to carbinoxamine. Carbinoxamine may increase the effects of other drugs such as barbiturates, TCAs, MAO inhibitors such as Phenelzine (Nardil), Tranylcypromine (Parnate), or Selegiline (Eldepryl), alcohol, other antihistamines, and CNS depressants. Carbinoxamine can be taken with or without food.
Cardiovascular Effects
Cardiac effects, including prolongation of QT interval have not been adequately studied. Unlike other newer antihistamines, severe adverse cardiovascular effects are uncommon, and usually limited to over dosage situations.
Special Populations
Pediatric Patients
Carbinoxamine should not be used in newborn or premature infants. Neonates have an increased susceptibility to anticholinergic side effects, such as CNS excitation, which may lead to convulsions.
Pregnancy and Lactation
Safe use of carbinoxamine during pregnancy has not been established. Therefore, carbinoxamine should not be used in women who are, or may become pregnant. Carbinoxamine is in the FDA pregnancy Category C.
Women who are breast-feeding should avoid use of carbinoxamine, since small amounts appear to be distributed into breast milk.
Geriatric Patients
Carbinoxamine is more likely to cause dizziness, sedation, and hypotension in elderly patients. The incidence of adverse reactions is higher in the elderly; therefore, a dosing adjustment may be necessary in this sub-population.
Indications And Usage
Carbinoxamine maleate is effective for the symptomatic treatment of:
Seasonal and perennial allergic rhinitis.
Vasomotor rhinitis.
Allergic conjunctivitis due to inhalant allergens and foods.
Mild, uncomplicated allergic skin manifestations of urticaria and angioedema.
Dermatographism.
As therapy for anaphylactic reactions adjunctive to epinephrine and other standard measures after the acute manifestations have been controlled.
Amelioration of the severity of allergic reactions to blood or plasma.
Contraindications
Carbinoxamine maleate is contraindicated in children younger than 2 years of age.
Carbinoxamine maleate is contraindicated in nursing mothers.
Carbinoxamine maleate is contraindicated in patients who are hypersensitive to the drug or on monoamine oxidase inhibitor therapy. (See Drug Interactions section).
Warnings
Deaths have been reported in children less than 2 years of age who were taking antihistamines, including carbinoxamine-containing drug products, therefore, carbinoxamine maleate is contraindicated in children younger than 2 years of age (see CONTRAINDICATIONS).
Antihistamines should be used with considerable caution in patients with: narrow angle glaucoma, stenosing peptic ulcer, symptomatic prostatic hypertrophy, bladder neck obstruction, pyloroduodenal obstruction.
Precautions
General
As many other antihistamines, carbinoxamine maleate has an atropine-like action and, therefore, should be used with caution in patients with: increased intraocular pressure, hyperthyroidism, cardiovascular disease, hypertension.
Antihistamines such as carbinoxamine maleate should not be used to treat lower respiratory tract symptoms, including asthma.
Information for Patients
Carbinoxamine maleate may cause drowsiness; alcohol, sedatives, and tranquilizers may increase the drowsiness effect. Avoid alcoholic beverages while taking this product. Do not take this product if you are taking sedatives or tranquilizers, without first consulting your doctor. Use caution when driving a motor vehicle or operating machinery.
Drug Interactions
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors prolong and intensify the anticholinergic (drying) effects of antihistamines.
Carbinoxamine maleate has additive effects with alcohol and other CNS depressants (hypnotics sedatives, tranquilizers, etc.).
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
No long-term studies in animals have been performed to determine the possible effects of carbinoxamine maleate on carcinogenesis, mutagenesis, and fertility.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category C: Animal reproductive studies have not been conducted with carbinoxamine maleate. It is also not known whether carbinoxamine maleate can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproductive capacity. Carbinoxamine maleate should be given to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed
Nursing Mothers
Because of the higher risk of antihistamines for infants generally and for newborns and prematures in particular, use of carbinoxamine maleate is contraindicated in nursing mothers (see CONTRAINDICATIONS section).
Pediatric Use
Carbinoxamine maleate is contraindicated in children younger than 2 years of age (see CONTRAINDICATIONS).
Neonates have an increased susceptibility to anticholinergic side effects, such as CNS excitation, which may lead to convulsions.
Carbinoxamine maleate may diminish mental alertness in children. In the young child, particularly, they may produce excitation.
Geriatric Use
Carbixonaxime maleate is more likely to cause dizziness, sedation, and hypotension in elderly patients (approximately 60 years or older). Sedating drugs may also cause confusion and over sedation in the elderly. Therefore, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
Adverse Reactions
The most frequent adverse reactions are underlined:
Body as a Whole: Urticaria, drug rash, anaphylactic shock, photosensitivity, excessive perspiration, chills, dryness of mouth, nose and throat.
Cardiovascular: Hypotension, headache, palpitations, tachycardia, extrasystoles.
Hematologic: Hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, agranulocytosis.
Central Nervous System: Sedation, sleepiness, dizziness, disturbed coordination, fatigue, confusion, restlessness, excitation, nervousness, tremor, irritability, insomnia, euphoria, paresthesia, blurred vision, diplopia, vertigo, tinnitus, acute labyrinthitis, hysteria, neuritis, convulsions.
Gastrointestinal: Epigastric distress, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation.
Urogenital: Urinary frequency, difficult urination, urinary retention, early menses.
Respiratory: Thickening of bronchial secretions, tightness of chest and wheezing, nasal stuffiness.
Overdosage
Manifestations: Antihistamine overdosage reactions may vary from central nervous system depression to stimulation. Stimulation is particularly likely in children. Atropine-like signs and symptoms - dry mouth; fixed, dilated pupils; flushing; and gastrointestinal symptoms may also occur.
Especially in infants and children, antihistamine overdosage may cause hallucinations, convulsions, or death.
The oral LD 50 of carbinoxamine maleate in guinea pigs is 411 mg/kg.
Treatement: The treatment of overdosage with carbinoxamine maleate is essentially symptomatic and supportive. Vital signs (including respiration, pulse, blood pressure, and temperature) and EKG should be monitored. Induction of vomiting is not recommended. Activated charcoal should be given and gastric lavage should be considered after ingestion of a potentially life-threatening amount of drug. In the presence of severe anticholinergic effects, physostigmine may be useful. Vasopressors may be used to treat hypotension.
Dosage And Administration
Carbinoxamine maleate is contraindicated in children younger than 2 years of age (see CONTRAINDICATIONS).
Carbinoxamine maleate should be taken on an empty stomach with water.
DOSAGE SHOULD BE INDIVIDUALIZED ACCORDING TO THE NEEDS AND THE RESPONSE OF THE PATIENT.
Carbinoxamine maleate dosage should be based on the severity of the condition and the response of the patient. The drug is well tolerated in adults in doses as high as 24 mg daily, in divided doses, over prolonged periods. On the other hand, some patients respond to as little as 4 mg daily.
Clinical experience suggests the following dosage schedules:
Tablets
Usual Adult Dosage:
1 or 2 tablets (4 to 8 mg) 3 to 4 times daily
Usual Child’s Dosage:
Six to eleven years – 1/2 to 1 tablet (2 to 4 mg) 3 to 4 times daily.
Oral Solution
Usual Adult Dosage:
1 or 2 teaspoonfuls (4 to 8 mg) 3 to 4 times daily
Usual Child's Dosage (approximately 0.2 to 0.4 mg/kg/day, divided into 3 to 4 doses):
Six to eleven years - ½ to 1 teaspoonful (2 to 4 mg) 3 to 4 times daily.
Dosing for children 2 to 5 years of age should be based on weight whenever possible. The usual dosage for children 2 to 5 years of age is approximately 0.2 to 0.4 mg/kg/day, divided into 3 to 4 daily doses. In general, this corresponds to a dose of 1/4 to 1/2 teaspoonful (1 to 2 mg) 3 to 4 times daily.
How Supplied
Carbinoxamine Maleate Tablets, USP 4 mg are supplied as white, round, scored tablets, debossed “109” on one side and score over “C” on the other side, and is supplied in bottles of 100 tablets, NDC 51991-333-01.
Carbinoxamine Maleate Oral Solution, 4 mg/5 mL is supplied as clear, colorless liquid with a bubble gum aroma, and is supplied in 4 fl. oz. bottles, NDC 51991-334-04.
Storage And Handling Section
Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container with a child-resistant closure as defined in the official compendium.
Distributed by:
Breckenridge Pharmaceutical, Inc.
Berlin, CT 06037
Manufactured by:
MIKART, LLC
Atlanta, GA 30318
Code 838F00
Rev. 05/19
Package Label - Principal Display Panel - 100 Count Bottle
Package Label - Principal Display Panel - 4 Fl Oz Bottle
DISCLAIMER:
"This tool does not provide medical advice, and is for informational and educational purposes only, and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, treatment or diagnosis. Call your doctor to receive medical advice. If you think you may have a medical emergency, please dial 911."
"Do not rely on openFDA to make decisions regarding medical care. While we make every effort to ensure that data is accurate, you should assume all results are unvalidated. We may limit or otherwise restrict your access to the API in line with our Terms of Service."
"This product uses publicly available data from the U.S. National Library of Medicine (NLM), National Institutes of Health, Department of Health and Human Services; NLM is not responsible for the product and does not endorse or recommend this or any other product."
PillSync may earn a commission via links on our site