Extended Phenytoin Sodium (phenytoin sodium 100 mg) Dailymed
Generic: phenytoin sodium
Go PRO for all pill images
Clinical Pharmacology
Phenytoin is an antiepileptic drug which can be used in the treatment of epilepsy. The primary site of action appears to be the motor cortex where spread of seizure activity is inhibited. Possibly by promoting sodium efflux from neurons, phenytoin tends to stabilize the threshold against hyperexcitability caused by excessive stimulation or environmental changes capable of reducing membrane sodium gradient. This includes the reduction of posttetanic potentiation at synapses. Loss of posttetanic potentiation prevents cortical seizure foci from detonating adjacent cortical areas. Phenytoin reduces the maximal activity of brain stem centers responsible for the tonic phase of tonic-clonic (grand mal) seizures.
The plasma half-life in man after oral administration of phenytoin averages 22 hours, with a range of 7 to 42 hours. Steady-state therapeutic levels are achieved at least 7 to 10 days (5 to 7 half-lives) after initiation of therapy with recommended doses of 300 mg/day.
When serum level determinations are necessary, they should be obtained at least 5 to 7 half-lives after treatment initiation, dosage change, or addition or subtraction of another drug to the regimen so that equilibrium or steady-state will have been achieved. Trough levels provide information about clinically effective serum level range and confirm patient compliance and are obtained just prior to the patientnext scheduled dose. Peak levels indicate an individual's threshold for emergence of dose-related side effects and are obtained at the time of expected peak concentration. For extended phenytoin sodium capsules, peak serum levels occur 4 to 12 hours after administration.
Optimum control without clinical signs of toxicity occurs more often with serum levels between 10 and 20 mcg/mL, although some mild cases of tonic-clonic (grand mal) epilepsy may be controlled with lower serum levels of phenytoin.
In most patients maintained at a steady dosage, stable phenytoin serum levels are achieved. There may be wide interpatient variability in phenytoin serum levels with equivalent dosages. Patients with unusually low levels may be noncompliant or hypermetabolizers of phenytoin. Unusually high levels result from liver disease, congenital enzyme deficiency, or drug interactions which result in metabolic interference. The patient with large variations in phenytoin plasma levels, despite standard doses, presents a difficult clinical problem. Serum level determinations in such patients may be particularly helpful. As phenytoin is highly protein bound, free phenytoin levels may be altered in patients whose protein binding characteristics differ from normal.
Most of the drug is excreted in the bile as inactive metabolites which are then reabsorbed from the intestinal tract and excreted in the urine. Urinary excretion of phenytoin and its metabolites occurs partly with glomerular filtration but more importantly by tubular secretion. Because phenytoin is hydroxylated in the liver by an enzyme system which is saturable at high plasma levels, small incremental doses may increase the half-life and produce very substantial increases in serum levels, when these are in the upper range. The steady-state level may be disproportionately increased, with resultant intoxication, from an increase in dosage of 10% or more.
Indications & Usage
Extended phenytoin sodium capsules, USP are indicated for the control of generalized tonic-clonic (grand mal) and complex partial (psychomotor, temporal lobe) seizures and prevention and treatment of seizures occurring during or following neurosurgery.
Phenytoin serum level determinations may be necessary for optimal dosage adjustments (see
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATIONand CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGYsections).
Contraindications
Warnings
Precautions
Adverse Reactions
Overdosage
The lethal dose in pediatric patients is not known. The lethal dose in adults is estimated to be 2 to 5 grams. The initial symptoms are nystagmus, ataxia, and dysarthria. Other signs are tremor, hyperreflexia, lethargy, slurred speech, nausea, vomiting. The patient may become comatose and hypotensive. Death is due to respiratory and circulatory depression.
There are marked variations among individuals with respect to phenytoin plasma levels where toxicity may occur. Nystagmus, on lateral gaze, usually appears at 20 mcg/mL, ataxia at 30 mcg/mL; dysarthria and lethargy appear when the plasma concentration is over 40 mcg/mL, but as high a concentration as 50 mcg/mL has been reported without evidence of toxicity. As much as 25 times the therapeutic dose has been taken to result in a
Treatment:
Treatment is nonspecific since there is no known antidote.
The adequacy of the respiratory and circulatory systems should be carefully observed and appropriate supportive measures employed. Hemodialysis can be considered since phenytoin is not completely bound to plasma proteins. Total exchange transfusion has been used in the treatment of severe intoxication in pediatric patients.
In acute overdosage, the possibility of other CNS depressants, including alcohol, should be borne in mind.
Dosage & Administration
How Supplied
Extended Phenytoin Sodium Capsules, USP
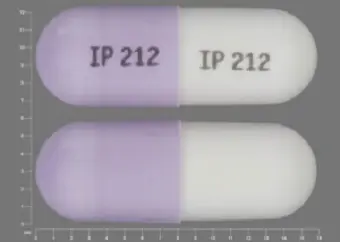
100 mgare supplied as white opaque / light lavender opaque, hard gelatin capsules imprinted with "IP 212" on both cap and body.
They are available as follows:
Bottles of 30: NDC 65162-212-03
Bottles of 100: NDC 65162-212-10
Bottles of 500: NDC 65162-212-50
Bottles of 1000: NDC 65162-212-11
Storage And Handling
Store at 20 to 25 C (68 to 77 F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Preserve in tight, light-resistant containers. Protect from moisture.
Medication Guide
Extended Phenytoin Sodium Capsules
Read this Medication Guide before you start taking extended phenytoin sodium and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking to your healthcare provider about your medical condition or treatment. If you have any questions about extended phenytoin sodium, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist.
What is the most important information I should know about extendedphenytoin sodium?
Do not stop taking extended phenytoin sodium without first talking to your healthcare provider.Stopping extended phenytoin sodium suddenly can cause serious problems.
Extended phenytoin sodium can cause serious side effects including:
1. Like other antiepileptic drugs, extended phenytoin sodium may cause suicidal thoughts or actions in a very small number of people, about 1 in 500.
Call a healthcare provider right away if you have any of these symptoms, especially if they are new, worse, or worry you:
thoughts about suicide or dying
attempts to commit suicide
new or worse depression
new or worse anxiety
feeling agitated or restless
panic attacks
trouble sleeping (insomnia)
new or worse irritability
acting aggressive, being angry, or violent
acting on dangerous impulses
an extreme increase activity and talking (mania)
other unusual changes in behavior or mood
How can I watch for early symptoms of suicidal thoughts and actions?
Pay attention to any changes, especially sudden changes, in mood, behaviors, thoughts, or feelings.
Keep all follow-up visits with your health-care provider as scheduled.
Call your healthcare provider between visits as needed, especially if you are worried about symptoms.
Do not stop taking extended phenytoin sodium without first talking to a healthcare provider.
Stopping extended phenytoin sodium suddenly can cause serious problems. Stopping a seizure medicine suddenly in a patient who has epilepsy can cause seizures that will not stop (status epilepticus).
Suicidal thoughts or actions can be caused by things other than medicines. If you have suicidal
thoughts or actions, your healthcare provider may check for other causes.
2. Extended phenytoin sodium may harm your unborn baby.
If you take extended phenytoin sodium during pregnancy, your baby is at risk for serious birth defects.
Birth defects may occur even in children born to women who are not taking any medicines and do not have other risk factors
If you take extended phenytoin sodium during pregnancy, your baby is also at risk for bleeding problems right after birth. Your healthcare provider may give you and your baby medicine to prevent this.
All women of child-bearing age should talk to their healthcare provider about using other possible treatments instead of extended phenytoin sodium. If the decision is made to use extended phenytoin sodium, you should use effective birth control (contraception) unless you are planning to become pregnant.
Tell your healthcare provider right away if you become pregnant while taking extended phenytoin sodium. You and your healthcare provider should decide if you will take extended phenytoin sodium while you are pregnant.
Pregnancy Registry: If you become pregnant while taking extended phenytoin sodium, talk to your healthcare provider about registering with the North American Antiepileptic Drug Pregnancy Registry. You can enroll in this registry by calling 1-888-233-2334. The purpose of this registry is to collect information about the safety of antiepileptic drugs during pregnancy.
3. Swollen glands (lymph nodes)
4. Allergic reactions or serious problems which may affect organs and other parts of your body like the liver or blood cells. You may or may not have a rash with these types of reactions. Symptoms include:
swelling of your face, eyes, lips, or tongue
trouble swallowing or breathing
a skin rash
hives
fever, swollen glands, or sore throat that do not go away or come and go
painful sores in the mouth or around your eyes
yellowing of your skin or eyes
unusual bruising or bleeding
severe muscle pain
frequent infections or an infection that does not go
Call your healthcare provider right away if you have any of the symptoms uled above.
What is extended phenytoin sodium?
Extended phenytoin sodium is a prescription medicine used to treat tonic-clonic (grand mal), complex partial (psychomotor or temporal lobe) seizures, and to prevent and treat seizures that happen during or after brain surgery.
Who should not take extended phenytoin sodium?
Do not take extended phenytoin sodium if you:
are allergic to phenytoin or any of the ingredients in extended phenytoin sodium capsules. See the end of this leaflet for a complete ul of ingredients in extended phenytoin sodium capsules.
have had an allergic reaction to CEREBYX (fosphenytoin), PEGANONE (ethotoin), or MESANTOIN (mephenytoin).
What should I tell my healthcare provider before taking extended phenytoin sodium?
Before you take extended phenytoin sodium, tell your healthcare provider if you:
Have or had liver disease
Have or had porphyria
Have or had diabetes
Have or have had depression, mood problems, or suicidal thoughts or behavior
Are pregnant or plan to become pregnant.
If you become pregnant while taking extended phenytoin sodium, the level of extended phenytoin sodium in your blood may decrease, causing your seizures to become worse. Your healthcare provider may change your dose of extended phenytoin sodium.
Are breast feeding or plan to breastfeed. Extended phenytoin sodium can pass into breast milk. You and your healthcare provider should decide if you will take extended phenytoin sodium or breastfeed. You should not do both.
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take,including prescription and
non-prescription medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
Taking extended phenytoin sodium with certain other medicines can cause side effects or affect how well they work. Do not start or stop other medicines without talking to your healthcare provider.
Know the medicines you take. Keep a ul of them and show it to your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medicine.
How should I take extended phenytoin sodium capsules?
Take extended phenytoin sodium capsules exactly as prescribed. Your healthcare provider will tell you how much extended phenytoin sodium to take.
Your healthcare provider may change your dose. Do not change your dose of extended phenytoin sodium without talking to your healthcare provider.
Extended phenytoin sodium can cause overgrowth of your gums. Brushing and flossing your teeth and seeing a dentist regularly while taking extended phenytoin sodium can help prevent this.
If you take too much extended phenytoin sodium, call your healthcare provider or local Poison Control Center right away.
Do not stop taking extended phenytoin sodium without first talking to your healthcare provider. Stopping extended phenytoin sodium suddenly can cause serious problems.
What should I avoid while taking extended phenytoin sodium?
Do not drink alcohol while you take extended phenytoin sodium without first talking to your healthcare provider. Drinking alcohol while taking extended phenytoin sodium may change your blood levels of extended phenytoin sodium which can cause serious problems.
Do not drive, operate heavy machinery, or do other dangerous activities until you know how
extended phenytoin sodium affects you. Extended phenytoin sodium can slow your thinking and motor skills.
What are the possible side effects of extended phenytoin sodium?
is the most important information I should know about extended phenytoin sodium
Extended phenytoin sodium may cause other serious side effects including:
Softening of your bones (osteomalacia). This can cause broken bones.
Call your healthcare provider right away, if you have any of the symptoms uled above.
The most common side effects of extended phenytoin sodium include:
problems with walking and coordination
slurred speech
confusion
dizziness
trouble sleeping
nervousness
tremor
headache
nausea
vomiting
constipation
rash
These are not all the possible side effects of extended phenytoin sodium. For more information, ask your health-care provider or pharmacist.
Tell your healthcare provider if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store extended phenytoin sodium capsules?
Store extended phenytoin sodium capsules at room temperature between 68 F to 77 F (20 C to 25 C) in tight, light-resistant containers. Protect from moisture.
Keep extended phenytoin sodiumand all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about extended phenytoin sodium
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those uled in a Medication Guide. Do not use extended phenytoin sodium for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give extended phenytoin sodium to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them.
This Medication Guide summarizes the most important information about extended phenytoin sodium. If you would like more information, talk with your healthcare provider. You can ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for information about extended phenytoin sodium that was written for healthcare professionals.
For more information about extended phenytoin sodium, visit www.amneal.com or call 1-877-835-5472.
What are the ingredients in extended phenytoin sodium capsules?
Extended Oral Capsule
Extended phenytoin sodium capsule 100mg: White opaque/lavender opaque, hard gelatin capsules imprinted212on both cap and body.
Active ingredient: 100 mg phenytoin sodium
Inactive ingredients: D&C Red #28, D&C Red #33, FD&C Blue #1, gelatin, hydroxypropyl cellulose, mannitol, magnesium stearate, talc and titanium dioxide.
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Package Label.principal Display Panel Section
DRUG: Extended Phenytoin Sodium
GENERIC: PHENYTOIN SODIUM
DOSAGE: CAPSULE
ADMINSTRATION: ORAL
NDC: 52125-176-02
STRENGTH:100 mg
COLOR: white
SHAPE: CAPSULE
SCORE: No score
SIZE: 16 mm
IMPRINT: 30
QTY: 30
![]()
DISCLAIMER:
"This tool does not provide medical advice, and is for informational and educational purposes only, and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, treatment or diagnosis. Call your doctor to receive medical advice. If you think you may have a medical emergency, please dial 911."
"Do not rely on openFDA to make decisions regarding medical care. While we make every effort to ensure that data is accurate, you should assume all results are unvalidated. We may limit or otherwise restrict your access to the API in line with our Terms of Service."
"This product uses publicly available data from the U.S. National Library of Medicine (NLM), National Institutes of Health, Department of Health and Human Services; NLM is not responsible for the product and does not endorse or recommend this or any other product."
PillSync may earn a commission via links on our site