AMOXICILLIN AND CLAVULANATE POTASSIUM (amoxicillin 875 mg clavulanate potassium 125 mg) Dailymed
Generic: amoxicillin and clavulanate potassium is used for the treatment of Cholestasis, Extrahepatic Haemophilus Infections Liver Diseases Otitis Media Staphylococcal Infections Actinomycosis Bites, Human Chlamydia Infections Duodenal Ulcer Endocarditis, Bacterial Listeriosis Lyme Disease Sinusitis Streptococcal Infections Urinary Tract Infections Helicobacter Infections Skin Diseases, Bacterial Soft Tissue Infections
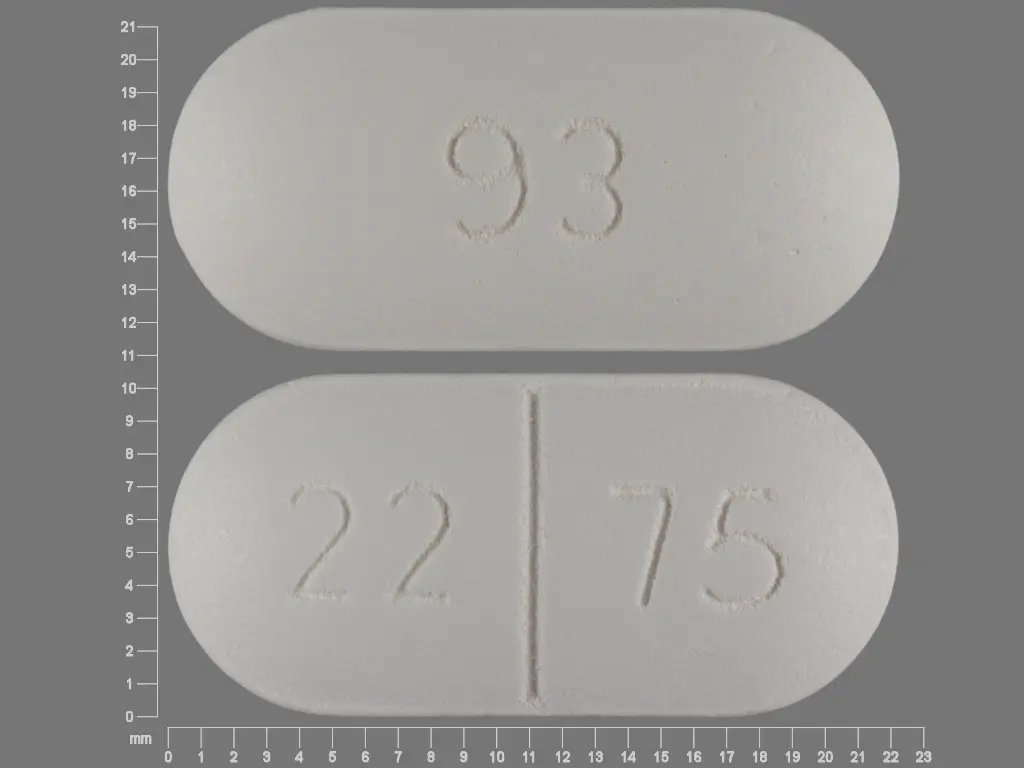
IMPRINT: 93 22 75
SHAPE: oval
COLOR: white SCORE: 2
All Imprints
amoxicillin 875 mgclavulanate potassium 125 mg - 93 22 75 oval white
amoxicillin 875 mg / clavulanate 125 mg oral tablet - 93 22 75 oval white
Go PRO for all pill images
Indications & Usage Section
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of Amoxicillin and Clavulanate Potassium Tablets USP, Amoxicillin and Clavulanate Potassium for Oral Suspension USP, and Amoxicillin and Clavulanate Potassium Tablets USP (Chewable) and other antibacterial drugs, Amoxicillin and Clavulanate Potassium Tablets USP, Amoxicillin and Clavulanate Potassium for Oral Suspension USP, and Amoxicillin and Clavulanate Potassium Tablets USP (Chewable) should be used only to treat infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible bacteria. When culture and susceptibility information are available, they should be considered in selecting or modifying antibacterial therapy. In the absence of such data, local epidemiology and susceptibility patterns may contribute to the empiric selection of therapy.
Amoxicillin and Clavulanate Potassium Tablets USP, Amoxicillin and Clavulanate Potassium for Oral Suspension USP, and Amoxicillin and Clavulanate Potassium Tablets USP (Chewable) are combination penicillin-class antibacterials and beta-lactamase inhibitors indicated in the treatment of infections due to susceptible isolates of the designated bacteria in the conditions uled below*:
1.1 Lower Respiratory Tract Infections – caused by beta-lactamase–producing isolates of Haemophilus influenzae and Moraxella catarrhalis.
1.2 Acute Bacterial Otitis Media – caused by beta-lactamase–producing isolates of H. influenzae and M. catarrhalis.
1.3 Sinusitis – caused by beta-lactamase–producing isolates of H. influenzae and M. catarrhalis.
1.4 Skin and Skin Structure Infections – caused by beta-lactamase–producing isolates of Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, and Klebsiella species.
1.5 Urinary Tract Infections – caused by beta-lactamase–producing isolates of E. coli, Klebsiella species, and Enterobacter species.
1.6 Limitations of Use – When susceptibility test results show susceptibility to amoxicillin, USP, indicating no beta-lactamase production, Amoxicillin and Clavulanate Potassium Tablets USP, Amoxicillin and Clavulanate Potassium for Oral Suspension USP, and Amoxicillin and Clavulanate Potassium Tablets USP (Chewable) should not be used.
Dosage & Administration Section
Amoxicillin and Clavulanate Potassium Tablets, Amoxicillin and Clavulanate Potassium for Oral Suspension, and Amoxicillin and Clavulanate Potassium Tablets (Chewable) may be taken without regard to meals; however, absorption of clavulanate potassium is enhanced when Amoxicillin and Clavulanate Potassium Tablets, Amoxicillin and Clavulanate Potassium for Oral Suspension, and Amoxicillin and Clavulanate Potassium Tablets (Chewable) are administered at the start of a meal. To minimize the potential for gastrointestinal intolerance, Amoxicillin and Clavulanate Potassium Tablets, Amoxicillin and Clavulanate Potassium for Oral Suspension, and Amoxicillin and Clavulanate Potassium Tablets (Chewable) should be taken at the start of a meal.
2.1 Adults
The usual adult dose is one 500 mg/125 mg Amoxicillin and Clavulanate Potassium Tablet every 12 hours or one 250 mg/125 mg Amoxicillin and Clavulanate Potassium Tablet every 8 hours. For more severe infections and infections of the respiratory tract, the dose should be one 875 mg/125 mg Amoxicillin and Clavulanate Potassium Tablet every 12 hours or one 500 mg/125 mg Amoxicillin and Clavulanate Potassium Tablet every 8 hours. Adults who have difficulty swallowing may be given the 125 mg/31.25 mg per 5 mL or 250 mg/62.5 mg per 5 mL suspension in place of the 500 mg/125 mg tablet. The 200 mg/28.5 mg per 5 mL suspension or the 400 mg/57 mg per 5 mL suspension may be used in place of the 875 mg/125 mg tablet.
Two 250 mg/125 mg Amoxicillin and Clavulanate Potassium Tablets should not be substituted for one 500 mg/125 mg Amoxicillin and Clavulanate Potassium Tablet. Since both the 250 mg/125 mg and 500 mg/125 mg Amoxicillin and Clavulanate Potassium Tablets contain the same amount of clavulanic acid (125 mg, as the potassium salt), two 250 mg/125 mg tablets are not equivalent to one 500 mg/125 mg Amoxicillin and Clavulanate Potassium Tablet.
The 250 mg/125 mg Amoxicillin and Clavulanate Potassium Tablet and the 250 mg/62.5 mg chewable tablet should not be substituted for each other, as they are not interchangeable. The 250 mg/125 mg Amoxicillin and Clavulanate Potassium Tablet and the 250 mg/62.5 mg chewable tablet do not contain the same amount of clavulanic acid (as the potassium salt). The 250 mg/125 mg Amoxicillin and Clavulanate Potassium Tablet contains 125 mg of clavulanic acid, whereas the 250 mg/62.5 mg chewable tablet contains 62.5 mg of clavulanic acid.
2.2 Pediatric Patients
Based on the amoxicillin component, Amoxicillin and Clavulanate Potassium for Oral Suspension should be dosed as follows:
Neonates and Infants Aged < 12 Weeks (< 3 Months): The recommended dose of Amoxicillin and Clavulanate Potassium for Oral Suspension is 30 mg/kg/day divided every 12 hours, based on the amoxicillin component. Experience with the 200 mg/28.5 mg per 5 mL formulation in this age group is limited, and thus, use of the 125 mg/31.25 mg per 5 mL oral suspension is recommended.
Patients Aged 12 Weeks (3 Months) and Older: See dosing regimens provided in Table 1. The every 12 hour regimen is recommended as it is associated with significantly less diarrhea [see Clinical Studies (14.2)]. However, the every 12 hour suspension (200 mg/28.5 mg per 5 mL and 400 mg/57 mg per 5 mL) and chewable tablets (200 mg/28.5 mg and 400 mg/57 mg) contain aspartame and should not be used by phenylketonurics. [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
* Each strength of Amoxicillin and Clavulanate Potassium for Oral Suspension is available as a chewable tablet for use by older children. †Duration of therapy studied and recommended for acute otitis media is 10 days.
Table 1: Dosing in Patients Aged 12 Weeks (3 Months) and Older
INFECTION
DOSING REGIMEN
Every 12 hours
Every 8 hours
200 mg/28.5 mg per 5 mL or
400 mg/57 mg per 5 mL
oral suspension*
125 mg/31.25 mg per 5 mL or
250 mg/62.5 mg per 5 mL
oral suspension*
Otitis media†, sinusitis, lower respiratory tract infections, and more severe infections
45 mg/kg/day every 12 hours
40 mg/kg/day every 8 hours
Less severe infections
25 mg/kg/day every 12 hours
20 mg/kg/day every 8 hours
Patients Weighing 40 kg or More: Pediatric patients weighing 40 kg or more should be dosed according to adult recommendations.
The 250 mg/125 mg Amoxicillin and Clavulanate Potassium Tablets should not be used until the child weighs at least 40 kg, due to the different amoxicillin to clavulanic acid ratios in the 250 mg/125 mg Amoxicillin and Clavulanate Potassium Tablets (250/125) versus the 250 mg/62.5 mg Amoxicillin and Clavulanate Potassium Tablets (Chewable) (250/62.5).
2.3 Patients With Renal Impairment
Patients with impaired renal function do not generally require a reduction in dose unless the impairment is severe. Renal impairment patients with a glomerular filtration rate of < 30 mL/min should not receive the 875 mg/125 mg dose. Patients with a glomerular filtration rate of 10 to 30 mL/min should receive 500 mg/125 mg or 250 mg/125 mg every 12 hours, depending on the severity of the infection. Patients with a glomerular filtration rate less than 10 mL/min should receive 500 mg/125 mg or 250 mg/125 mg every 24 hours, depending on severity of the infection.
Hemodialysis patients should receive 500 mg/125 mg or 250 mg/125 mg every 24 hours, depending on severity of the infection. They should receive an additional dose both during and at the end of dialysis.
2.4 Directions for Mixing Oral Suspension
Prepare a suspension at time of dispensing as follows: Tap bottle until all the powder flows freely. Add approximately 2/3 of the total amount of water for reconstitution (see Table 2 below) and shake vigorously to suspend powder. Add remainder of the water and again shake vigorously.
Table 2: Amount of Water for Mixing Oral Suspension
Strength
Bottle Size
Amount of Water for Reconstitution
Contents of Each Teaspoonful (5 mL)
200 mg/28.5 mg per 5 mL
100 mL
92 mL
200 mg amoxicillin and 28.5 mg of clavulanic acid as the potassium salt
400 mg/57 mg per 5 mL
100 mL
87 mL
400 mg amoxicillin and 57 mg of clavulanic acid as the potassium salt
Note: Shake oral suspension well before using. Reconstituted suspension must be stored under refrigeration and discarded after 10 days.
Dosage Forms & Strengths Section
Tablets
500 mg/125 mg Tablets: White, oblong-shaped, biconvex, film-coated, unscored tablets, debossed 93 on one side and 2274 on the other side. Each tablet contains 500 mg amoxicillin as the trihydrate and 125 mg clavulanic acid as the potassium salt.
875 mg/125 mg Tablets: White, capsule-shaped, biconvex, film-coated, scored tablets, debossed 93 on one side and 22 score line 75 on the other side. Each tablet contains 875 mg amoxicillin as the trihydrate and 125 mg clavulanic acid as the potassium salt.
Powder for Oral Suspension
200 mg/28.5 mg per 5 mL: White to off-white, orange-raspberry flavored powder for oral suspension (each 5 mL of reconstituted suspension, when reconstituted according to directions on the container label, contains 200 mg amoxicillin and 28.5 mg of clavulanic acid as the potassium salt).
400 mg/57 mg per 5 mL: White to off-white, orange-raspberry flavored powder for oral suspension (each 5 mL of reconstituted suspension, when reconstituted according to directions on the container label, contains 400 mg amoxicillin and 57 mg of clavulanic acid as the potassium salt).
Chewable Tablets
200 mg/28.5 mg Chewable Tablets: Mottled pink, oval, biconvex, unscored tablets, debossed 93 on one side and 2270 on the other.
400 mg/57 mg Chewable Tablets: Mottled pink, oval, biconvex, unscored tablets, debossed 93 on one side and 2272 on the other.
The 250 mg/125 mg Amoxicillin and Clavulanate Potassium Tablet and the 250 mg/62.5 mg chewable tablet should NOT be substituted for each other, as they are not interchangeable and the 250 mg/125 mg tablet should not be used in children weighing less than 40 kg. The 250 mg/125 mg Amoxicillin and Clavulanate Potassium Tablet and the 250 mg/62.5 mg chewable tablet do not contain the same amount of clavulanic acid. The 250 mg/125 mg Amoxicillin and Clavulanate Potassium Tablet contains 125 mg of clavulanic acid whereas the 250 mg/62.5 mg chewable tablet contains 62.5 mg of clavulanic acid.
Two 250 mg/125 mg Amoxicillin and Clavulanate Potassium Tablets should NOT be substituted for one 500 mg/125 mg Amoxicillin and Clavulanate Potassium Tablet. Since both the 250 mg/125 mg and 500 mg/125 mg Amoxicillin and Clavulanate Potassium Tablets contain the same amount of clavulanic acid (125 mg, as the potassium salt), two 250 mg/125 mg Amoxicillin and Clavulanate Potassium Tablets are not equivalent to one 500 mg/125 mg Amoxicillin and Clavulanate Potassium Tablet.
Contraindications Section
4.1 Serious Hypersensitivity Reactions Amoxicillin/clavulanate potassium is contraindicated in patients with a history of serious hypersensitivity reactions (e.g., anaphylaxis or Stevens-Johnson syndrome) to amoxicillin, clavulanate or to other beta-lactam antibacterial drugs (e.g., penicillins and cephalosporins).
4.2 Cholestatic Jaundice/Hepatic Dysfunction Amoxicillin/clavulanate potassium is contraindicated in patients with a previous history of cholestatic jaundice/hepatic dysfunction associated with amoxicillin/clavulanate potassium.
Adverse Reactions Section
The following are discussed in more detail in other sections of the labeling:
• Anaphylactic reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] • Hepatic Dysfunction [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] • CDAD [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)] 6.1 Clinical Trials Experience Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The most frequently reported adverse reactions were diarrhea/loose stools (9%), nausea (3%), skin rashes and urticaria (3%), vomiting (1%) and vaginitis (1%). Less than 3% of patients discontinued therapy because of drug-related adverse reactions. The overall incidence of adverse reactions, and in particular diarrhea, increased with the higher recommended dose. Other less frequently reported adverse reactions (< 1%) include: Abdominal discomfort, flatulence, and headache.
In pediatric patients (aged 2 months to 12 years), 1 U.S./Canadian clinical trial was conducted which compared 45/6.4 mg/kg/day (divided every 12 hours) of amoxicillin/clavulanate potassium for 10 days versus 40/10 mg/kg/day (divided every 8 hours) of amoxicillin/clavulanate potassium for 10 days in the treatment of acute otitis media. A total of 575 patients were enrolled, and only the suspension formulations were used in this trial. Overall, the adverse reactions seen were comparable to that noted above; however, there were differences in the rates of diarrhea, skin rashes/urticaria, and diaper area rashes. [See Clinical Studies (14.2)]
6.2 Postmarketing Experience In addition to adverse reactions reported from clinical trials, the following have been identified during postmarketing use of amoxicillin/clavulanate potassium. Because they are reported voluntarily from a population of unknown size, estimates of frequency cannot be made. These events have been chosen for inclusion due to a combination of their seriousness, frequency of reporting, or potential causal connection to amoxicillin/clavulanate potassium.
Gastrointestinal: Indigestion, gastritis, stomatitis, glossitis, black “hairy” tongue, mucocutaneous candidiasis, enterocolitis, and hemorrhagic/pseudomembranous colitis. Onset of pseudomembranous colitis symptoms may occur during or after antibiotic treatment. [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
Hypersensitivity Reactions: Pruritus, angioedema, serum sickness–like reactions (urticaria or skin rash accompanied by arthritis, arthralgia, myalgia, and frequently fever), erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis, hypersensitivity vasculitis, and cases of exfoliative dermatitis (including toxic epidermal necrolysis) have been reported. [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
Liver: Hepatic dysfunction, including hepatitis and cholestatic jaundice, increases in serum transaminases (AST and/or ALT), serum bilirubin, and/or alkaline phosphatase, has been reported with amoxicillin/clavulanate potassium. It has been reported more commonly in the elderly, in males, or in patients on prolonged treatment. The histologic findings on liver biopsy have consisted of predominantly cholestatic, hepatocellular, or mixed cholestatic-hepatocellular changes. The onset of signs/symptoms of hepatic dysfunction may occur during or several weeks after therapy has been discontinued. The hepatic dysfunction, which may be severe, is usually reversible. Deaths have been reported. [see Contraindications (4.2), Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
Renal: Interstitial nephritis, hematuria, and crystalluria have been reported. [see Overdosage (10)]
Hemic and Lymphatic Systems: Anemia, including hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, thrombocytopenic purpura, eosinophilia, leukopenia, and agranulocytosis have been reported. These reactions are usually reversible on discontinuation of therapy and are believed to be hypersensitivity phenomena. Thrombocytosis was noted in less than 1% of the patients treated with amoxicillin/clavulanate potassium. There have been reports of increased prothrombin time in patients receiving amoxicillin/clavulanate potassium and anticoagulant therapy concomitantly. [see Drug Interactions (7.2)]
Central Nervous System: Agitation, anxiety, behavioral changes, confusion, convulsions, dizziness, insomnia, and reversible hyperactivity have been reported.
Miscellaneous: Tooth discoloration (brown, yellow, or gray staining) has been reported. Most reports occurred in pediatric patients. Discoloration was reduced or eliminated with brushing or dental cleaning in most cases.
Drug Interactions Section
7.1 Probenecid Probenecid decreases the renal tubular secretion of amoxicillin but does not delay renal excretion of clavulanic acid. Concurrent use with amoxicillin/clavulanate potassium may result in increased and prolonged blood concentrations of amoxicillin. Coadministration of probenecid is not recommended.
7.2 Oral Anticoagulants Abnormal prolongation of prothrombin time (increased international normalized ratio [INR]) has been reported in patients receiving amoxicillin and oral anticoagulants. Appropriate monitoring should be undertaken when anticoagulants are prescribed concurrently with amoxicillin/clavulanate potassium. Adjustments in the dose of oral anticoagulants may be necessary to maintain the desired level of anticoagulation.
7.3 Allopurinol The concurrent administration of allopurinol and amoxicillin increases the incidence of rashes in patients receiving both drugs as compared to patients receiving amoxicillin alone. It is not known whether this potentiation of amoxicillin rashes is due to allopurinol or the hyperuricemia present in these patients.
7.4 Oral Contraceptives Amoxicillin/clavulanate potassium may affect intestinal flora, leading to lower estrogen reabsorption and reduced efficacy of combined oral estrogen/progesterone contraceptives.
7.5 Effects on Laboratory Tests High urine concentrations of amoxicillin may result in false-positive reactions when testing for the presence of glucose in urine using CLINITEST®, Benedict’s Solution, or Fehling’s Solution. Since this effect may also occur with amoxicillin/clavulanate potassium, it is recommended that glucose tests based on enzymatic glucose oxidase reactions be used.
Following administration of amoxicillin to pregnant women, a transient decrease in plasma concentration of total conjugated estriol, estriol-glucuronide, conjugated estrone, and estradiol has been noted.
Use In Specific Populations Section
8.1 Pregnancy Teratogenic Effects
Pregnancy Category B
Reproduction studies performed in pregnant rats and mice given amoxicillin/clavulanate potassium (2:1 ratio formulation of amoxicillin:clavulanate) at oral doses up to 1200 mg/kg/day revealed no evidence of harm to the fetus due to amoxicillin/clavulanate potassium. The amoxicillin doses in rats and mice (based on body surface area) were approximately 4 and 2 times the maximum recommended adult human oral dose (875 mg/125 mg every 12 hours). For clavulanate, these dose multiples were approximately 9 and 4 times the maximum recommended adult human oral dose (125 mg every 8 hours). There are, however, no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Because animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, this drug should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed.
8.2 Labor and Delivery Oral ampicillin-class antibiotics are poorly absorbed during labor. It is not known whether use of amoxicillin/clavulanate potassium in humans during labor or delivery has immediate or delayed adverse effects on the fetus, prolongs the duration of labor, or increases the likelihood of the necessity for an obstetrical intervention.
8.3 Nursing Mothers Amoxicillin has been shown to be excreted in human milk. Amoxicillin/clavulanate potassium use by nursing mothers may lead to sensitization of infants. Caution should be exercised when amoxicillin/clavulanate potassium is administered to a nursing woman.
8.4 Pediatric Use The safety and effectiveness of amoxicillin and clavulanate potassium for oral suspension and amoxicillin and clavulanate potassium tablets (chewable) have been established in pediatric patients. Use of amoxicillin and clavulanate potassium for oral suspension and amoxicillin and clavulanate potassium tablets (chewable) in pediatric patients is supported by evidence from studies of amoxicillin and clavulanate potassium tablets in adults with additional data from a study of amoxicillin and clavulanate potassium for oral suspension in pediatric patients aged 2 months to 12 years with acute otitis media. [see Clinical Studies (14.2)]
Because of incompletely developed renal function in neonates and young infants, the elimination of amoxicillin may be delayed; clavulanate elimination is unaltered in this age group. Dosing of amoxicillin and clavulanate potassium for oral suspension and amoxicillin and clavulanate potassium tablets (chewable) should be modified in pediatric patients aged < 12 weeks (< 3 months). [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)]
8.5 Geriatric Use Of the 3,119 patients in an analysis of clinical studies of amoxicillin/clavulanate potassium, 32% were ≥ 65 years old, and 14% were ≥ 75 years old. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these subjects and younger subjects, and other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients, but greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out.
This drug is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of adverse reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection, and it may be useful to monitor renal function.
8.6 Dosing in Renal Impairment Amoxicillin is primarily eliminated by the kidney and dosage adjustment is usually required in patients with severe renal impairment (GFR < 30 mL/min). See Patients With Renal Impairment (2.3) for specific recommendations in patients with renal impairment.
Overdosage Section
In case of overdosage, discontinue medication, treat symptomatically, and institute supportive measures as required. A prospective study of 51 pediatric patients at a poison-control center suggested that overdosages of less than 250 mg/kg of amoxicillin are not associated with significant clinical symptoms1.
Interstitial nephritis resulting in oliguric renal failure has been reported in patients after overdosage with amoxicillin/clavulanate potassium.
Crystalluria, in some cases leading to renal failure, has also been reported after amoxicillin/clavulanate potassium overdosage in adult and pediatric patients. In case of overdosage, adequate fluid intake and diuresis should be maintained to reduce the risk of amoxicillin/clavulanate potassium crystalluria.
Renal impairment appears to be reversible with cessation of drug administration. High blood levels may occur more readily in patients with impaired renal function because of decreased renal clearance of amoxicillin/clavulanate potassium. Amoxicillin/clavulanate potassium may be removed from circulation by hemodialysis. [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)]
Description Section
Amoxicillin and Clavulanate Potassium Tablets, Amoxicillin and Clavulanate Potassium for Oral Suspension, and Amoxicillin and Clavulanate Potassium Tablets (Chewable) are oral antibacterial combinations consisting of the semisynthetic antibiotic amoxicillin, USP and the beta-lactamase inhibitor, clavulanate potassium, USP (the potassium salt of clavulanic acid). Amoxicillin, USP is an analog of ampicillin, derived from the basic penicillin nucleus, 6-aminopenicillanic acid. Chemically, amoxicillin, USP is (2S,5R,6R)-6-[(R)-(-)-2-Amino-2-(p-hydroxyphenyl)acetamido]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid trihydrate and has the following structural formula:
amoxicillin structural formula C16H19N3O5S•3H2O M.W. 419.45
Clavulanic acid is produced by the fermentation of Streptomyces clavuligerus. It is a beta-lactam structurally related to the penicillins and possesses the ability to inactivate some beta-lactamases by blocking the active sites of these enzymes. Chemically, clavulanate potassium, USP is potassium (Z)-(2R,5R)-3-(2-hydroxyethylidene)-7-oxo-4-oxa-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]-heptane-2-carboxylate, and has the following structural formula:
clavulanic acid structural formula C8H8KNO5 M.W. 237.25
Amoxicillin and Clavulanate Potassium Tablets USP
Each tablet contains 500 mg or 875 mg amoxicillin, USP as the trihydrate and 125 mg clavulanic acid as the potassium salt. Each Amoxicillin and Clavulanate Potassium Tablet USP contains 0.63 mEq potassium.
Inactive Ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, hypromellose, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, polydextrose, polyethylene glycol, sodium starch glycolate, titanium dioxide, and triacetin.
Amoxicillin and Clavulanate Potassium for Oral Suspension USP
After reconstitution each teaspoonful (5 mL) of suspension will contain 200 mg amoxicillin, USP as the trihydrate and 28.5 mg clavulanic acid as the potassium salt or 400 mg amoxicillin, USP as the trihydrate and 57 mg clavulanic acid as the potassium salt. Each 5 mL of reconstituted Amoxicillin and Clavulanate Potassium for Oral Suspension USP, 200 mg/28.5 mg per 5 mL contains 0.14 mEq potassium. Each 5 mL of reconstituted Amoxicillin and Clavulanate Potassium for Oral Suspension USP, 400 mg/57 mg per 5 mL contains 0.29 mEq of potassium.
Inactive Ingredients: Powder for oral suspension: artificial raspberry powder, aspartame*, citric acid, colloidal silicon dioxide, mannitol, hypromellose, natural orange flavor, sodium citrate, sodium saccharin and xanthan gum.
* See Warnings and Precautions (5.6).
Amoxicillin and Clavulanate Potassium Tablets USP (Chewable)
Each chewable tablet contains 200 mg amoxicillin, USP as the trihydrate and 28.5 mg clavulanic acid as the potassium salt or contains 400 mg amoxicillin, USP as the trihydrate and 57 mg clavulanic acid as the potassium salt. Each Amoxicillin and Clavulanate Potassium Tablet USP, (Chewable) 200 mg/28.5 mg contains 0.14 mEq potassium. Each Amoxicillin and Clavulanate Potassium Tablet USP, (Chewable) 400 mg/57 mg contains 0.29 mEq potassium.
Inactive Ingredients: aspartame*, colloidal silicon dioxide, FD&C Red #40 lake, magnesium stearate, mannitol, microcrystalline cellulose, SA84 artificial ripe banana flavor, and artificial cherry flavor powder.
* See Warnings and Precautions (5.6).
Clinical Pharmacology Section
12.1 Mechanism of Action Amoxicillin and clavulanate potassium tablets, amoxicillin and clavulanate potassium for oral suspension, and amoxicillin and clavulanate potassium tablets (chewable) are antibacterial drugs. [see Microbiology 12.4]
12.3 Pharmacokinetics Mean amoxicillin and clavulanate potassium pharmacokinetic parameters in normal adults following administration of amoxicillin and clavulanate potassium tablets are shown in Table 3 and following administration of amoxicillin and clavulanate potassium for oral suspension and chewable tablets are shown in Table 4.
* Mean (± standard deviation) values of 14 normal adults (N = 15 for clavulanate potassium in the low-dose regimens). Peak concentrations occurred approximately 1.5 hours after the dose. †Amoxicillin/clavulanate potassium administered at the start of a light meal. Table 3: Mean (±S.D.) Amoxicillin and Clavulanate Potassium Pharmacokinetic Parameters*,†With Amoxicillin and Clavulanate Potassium Tablets
Dose and Regimen
Cmax (mcg/mL)
AUC0 to 24 (mcg*h/mL)
Amoxicillin/Clavulanate Potassium
Amoxicillin
Clavulanate Potassium
Amoxicillin
Clavulanate Potassium
250 mg/125 mg every 8 hours
3.3 ± 1.12
1.5 ± 0.70
26.7 ± 4.56
12.6 ± 3.25
500 mg/125 mg every 12 hours
6.5 ± 1.41
1.8 ± 0.61
33.4 ± 6.76
8.6 ± 1.95
500 mg/125 mg every 8 hours
7.2 ± 2.26
2.4 ± 0.83
53.4 ± 8.87
15.7 ± 3.86
875 mg/125 mg every 12 hours
11.6 ± 2.78
2.2 ± 0.99
53.5 ± 12.31
10.2 ± 3.04
* Mean ( ± standard deviation) values of 28 normal adults. Peak concentrations occurred approximately 1 hour after the dose. †Amoxicillin/clavulanate potassium administered at the start of a light meal. Table 4: Mean (±S.D.) Amoxicillin and Clavulanate Potassium Pharmacokinetic Parameters*,†With Amoxicillin and Clavulanate Potassium for Oral Suspension and Chewable Tablets
Dose
Cmax (mcg/mL)
AUC0 to 24 (mcg*h/mL)
Amoxicillin/Clavulanate Potassium
Amoxicillin
Clavulanate Potassium
Amoxicillin
Clavulanate Potassium
400 mg/57 mg (5 mL of suspension)
6.94 ± 1.24
1.10 ± 0.42
17.29 ± 2.28
2.34 ± 0.94
400 mg/57 mg (1 chewable tablet)
6.67 ± 1.37
1.03 ± 0.33
17.24 ± 2.64
2.17 ± 0.73
Oral administration of 5 mL of 250 mg/62.5 mg per 5 mL suspension of amoxicillin/clavulanate potassium or the equivalent dose of 10 mL of 125 mg/31.25 mg per 5 mL suspension of amoxicillin/clavulanate potassium provides average peak serum concentrations approximately 1 hour after dosing of 6.9 mcg/mL for amoxicillin and 1.6 mcg/mL for clavulanic acid. The areas under the serum concentration curves obtained during the first 4 hours after dosing were 12.6 mcg*h/mL for amoxicillin and 2.9 mcg*h/mL for clavulanic acid when 5 mL of 250 mg/62.5 mg per 5 mL suspension of amoxicillin/clavulanate potassium or equivalent dose of 10 mL of 125 mg/31.25 mg per 5 mL suspension of amoxicillin/clavulanate potassium were administered to normal adults. One 250 mg/62.5 mg chewable tablet of amoxicillin/clavulanate potassium or two 125 mg/31.25 mg chewable tablets of amoxicillin/clavulanate potassium are equivalent to 5 mL of 250 mg/62.5 mg per 5 mL suspension of amoxicillin/clavulanate potassium and provide similar serum concentrations of amoxicillin and clavulanic acid.
Amoxicillin serum concentrations achieved with amoxicillin/clavulanate potassium are similar to those produced by the oral administration of equivalent doses of amoxicillin alone. Time above the minimum inhibitory concentration of 1 mcg/mL for amoxicillin has been shown to be similar after corresponding every 12 hour and every 8 hour dosing regimens of amoxicillin/clavulanate potassium in adults and children.
Absorption
Dosing in the fasted or fed state has minimal effect on the pharmacokinetics of amoxicillin. While amoxicillin/clavulanate potassium can be given without regard to meals, absorption of clavulanate potassium when taken with food is greater relative to the fasted state. In one study, the relative bioavailability of clavulanate was reduced when amoxicillin/clavulanate potassium was dosed at 30 and 150 minutes after the start of a high-fat breakfast.
Distribution
Neither component in amoxicillin/clavulanate potassium is highly protein-bound; clavulanic acid is approximately 25% bound to human serum and amoxicillin approximately 18% bound.
Amoxicillin diffuses readily into most body tissues and fluids with the exception of the brain and spinal fluid.
Two hours after oral administration of a single 35 mg/kg dose of suspension of amoxicillin/clavulanate potassium to fasting children, average concentrations of 3 mcg/mL of amoxicillin and 0.5 mcg/mL of clavulanic acid were detected in middle ear effusions.
Metabolism and Excretion
The half-life of amoxicillin after the oral administration of amoxicillin/clavulanate potassium is 1.3 hours and that of clavulanic acid is 1 hour.
Approximately 50% to 70% of the amoxicillin and approximately 25% to 40% of the clavulanic acid are excreted unchanged in urine during the first 6 hours after administration of a single 250 mg/125 mg or 500 mg/125 mg tablet of amoxicillin/clavulanate potassium.
12.4 Microbiology Amoxicillin is a semisynthetic antibiotic with in vitro bactericidal activity against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. Amoxicillin is, however, susceptible to degradation by beta-lactamases, and therefore, the spectrum of activity does not include organisms which produce these enzymes. Clavulanic acid is a beta-lactam, structurally related to the penicillins, which possesses the ability to inactivate some beta-lactamase enzymes commonly found in microorganisms resistant to penicillins and cephalosporins. In particular, it has good activity against the clinically important plasmid-mediated beta-lactamases frequently responsible for transferred drug resistance.
The formulation of amoxicillin and clavulanic acid in amoxicillin and clavulanate potassium tablets, amoxicillin and clavulanate potassium for oral suspension, and amoxicillin and clavulanate potassium tablets (chewable) protects amoxicillin from degradation by some beta-lactamase enzymes and extends the antibiotic spectrum of amoxicillin to include many bacteria normally resistant to amoxicillin.
Amoxicillin/clavulanic acid has been shown to be active against most isolates of the following bacteria, both in vitro and in clinical infections as described in the INDICATIONS AND USAGE section.
Gram-Positive Bacteria
Staphylococcus aureus
Gram-Negative Bacteria
Enterobacter species
Escherichia coli
Haemophilus influenzae
Klebsiella species
Moraxella catarrhalis
The following in vitro data are available, but their clinical significance is unknown. At least 90 percent of the following bacteria exhibit an in vitro minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) less than or equal to the susceptible breakpoint for amoxicillin/clavulanic acid. However, the efficacy of amoxicillin/clavulanic acid in treating clinical infections due to these bacteria has not been established in adequate and well-controlled clinical trials.
Gram-Positive Bacteria
Enterococcus faecalis
Staphylococcus epidermidis
Staphylococcus saprophyticus
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Streptococcus pyogenes
Viridans group Streptococcus
Gram-Negative Bacteria
Eikenella corrodens
Proteus mirabilis
Anaerobic Bacteria
Bacteroides species including Bacteroides fragilis
Fusobacterium species
Peptostreptococcus species
Susceptibility Test Methods
When available, the clinical microbiology laboratory should provide the results of in vitro susceptibility test results for antimicrobial drug products used in resident hospitals to the physician as periodic reports that describe the susceptibility profile of nosocomial and community-acquired pathogens. These reports should aid the physician in selecting an antibacterial drug product for treatment.
Dilution Techniques
Quantitative methods are used to determine antimicrobial minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs). These MICs provide estimates of the susceptibility of bacteria to antimicrobial compounds. The MICs should be determined using a standardized test method2,3 (broth and/or agar). The MIC values should be interpreted according to criteria provided in Table 5.
Diffusion Techniques
Quantitative methods that require measurement of zone diameters can also provide reproducible estimates of the susceptibility of bacteria to antimicrobial compounds. The zone size provides an estimate of the susceptibility of bacteria to antimicrobial compounds. The zone size should be determined using a standardized test method3,4. This procedure uses paper disks impregnated with 30 mcg amoxicillin/clavulanic acid (20 mcg amoxicillin plus 10 mcg clavulanic acid) to test the susceptibility of bacteria to amoxicillin/clavulanic acid. The disc diffusion interpretive criteria are provided in Table 5.
Table 5: Susceptibility Test Interpretive Criteria for Amoxicillin Clavulanic Acid
Minimum Inhibitory Concentrations (mcg/mL)
Disk Diffusion (Zone Diameters in mm)
Pathogen
S I R
S I R
Enterobacteriaceae
8/4 16/8 32/16
> 18 14-17 < 13
Haemophilus influenzae and Staphylococcus aureus
4/2 - 8/4
> 20 - < 19
Quality Control
Standardized susceptibility test procedures require the use of laboratory controls to monitor and ensure the accuracy and precision of supplies and reagents used in the assay, and the techniques of the individuals performing the test2,3,4. Standard amoxicillin/clavulanic acid powder should provide the following range of MIC values noted in Table 6 for the diffusion technique using the 30 mcg amoxicillin/clavulanic acid (20 mcg amoxicillin plus 10 mcg clavulanic acid) disk, the criteria in Table 6 should be achieved.
Table 6: Acceptable Quality Control Ranges for Amoxicillin/Clavulanic Acid
QC Strain
Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (mcg/mL)
Disk Diffusion (Zone Diameter in mm)
Escherichia coli ATCC 25922
2/1 to 8/4
18 to 24
Escherichia coli ATCC 35218
4/2 to 16/8
17 to 22
Haemophilus influenzae ATCC 49247
2/1 to 16/8
15 to 23
Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 29213
0.12/0.06 to 0.5/0.25
-
Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 29523
-
28 to 36
Nonclinical Toxicology Section
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility Long-term studies in animals have not been performed to evaluate carcinogenic potential.
Amoxicillin/clavulanate potassium (4:1 ratio formulation of amoxicillin:clavulanate) was non-mutagenic in the Ames bacterial mutation assay, and the yeast gene conversion assay. Amoxicillin/clavulanate potassium was weakly positive in the mouse lymphoma assay, but the trend toward increased mutation frequencies in this assay occurred at doses that were also associated with decreased cell survival. Amoxicillin/clavulanate potassium was negative in the mouse micronucleus test, and in the dominant lethal assay in mice. Potassium clavulanate alone was tested in the Ames bacterial mutation assay and in the mouse micronucleus test, and was negative in each of these assays.
Amoxicillin and clavulanate potassium tablets, amoxicillin and clavulanate potassium for oral suspension, and amoxicillin and clavulanate potassium tablets (chewable) (2:1 ratio formulation of amoxicillin:clavulanate) at oral doses of up to 1,200 mg/kg/day was found to have no effect on fertility and reproductive performance in rats. Based on body surface area, this dose of amoxicillin is approximately 4 times the maximum recommended adult human oral dose (875 mg every 12 hours). For clavulanate, the dose multiple is approximately 9 times higher than the maximum recommended adult human oral dose (125 mg every 8 hours), also based on body surface area.
Clinical Studies Section
14.1 Lower Respiratory Tract and Complicated Urinary Tract Infections Data from 2 pivotal trials in 1,191 patients treated for either lower respiratory tract infections or complicated urinary tract infections compared a regimen of 875 mg/125 mg amoxicillin and clavulanate potassium tablets every 12 hours to 500 mg/125 mg amoxicillin and clavulanate potassium tablets dosed every 8 hours (584 and 607 patients, respectively). Comparable efficacy was demonstrated between the every 12 hours and every 8 hours dosing regimens. There was no significant difference in the percentage of adverse events in each group. The most frequently reported adverse event was diarrhea; incidence rates were similar for the 875 mg/125 mg every 12 hours and 500 mg/125 mg every 8 hours dosing regimens (15% and 14%, respectively); however, there was a statistically significant difference (p < 0.05) in rates of severe diarrhea or withdrawals with diarrhea between the regimens: 1% for 875 mg/125 mg every 12 hours regimen versus 2% for the 500 mg/125 mg every 8 hours regimen.
In one of these pivotal trials, patients with either pyelonephritis (n = 361) or a complicated urinary tract infection (i.e., patients with abnormalities of the urinary tract that predispose to relapse of bacteriuria following eradication, n = 268) were randomized (1:1) to receive either 875 mg/125 mg amoxicillin and clavulanate potassium tablets every 12 hours (n = 308) or 500 mg/125 mg amoxicillin and clavulanate potassium tablets every 8 hours (n = 321).
The number of bacteriologically evaluable patients was comparable between the two dosing regimens. Amoxicillin and clavulanate potassium tablets produced comparable bacteriological success rates in patients assessed 2 to 4 days immediately following end of therapy. The bacteriologic efficacy rates were comparable at one of the follow-up visits (5 to 9 days post-therapy) and at a late post-therapy visit (in the majority of cases, this was 2 to 4 weeks post-therapy), as seen in Table 7.
Table 7: Bacteriologic Efficacy Rates for Amoxicillin and Clavulanate Potassium Tablets
Time Post Therapy
875 mg/125 mg Every 12 Hours % (n)
500 mg/125 mg Every 8 Hours % (n)
2 to 4 days
81% (58)
80% (54)
5 to 9 days
58% (41)
52% (52)
2 to 4 weeks
52% (101)
55% (104)
As noted before, though there was no significant difference in the percentage of adverse events in each group, there was a statistically significant difference in rates of severe diarrhea or withdrawals with diarrhea between the regimens.
14.2 Acute Bacterial Otitis Media and Diarrhea in Pediatric Patients One U.S./Canadian clinical trial was conducted which compared 45/6.4 mg/kg/day (divided every 12 hours) of amoxicillin and clavulanate potassium for oral suspension for 10 days versus 40/10 mg/kg/day (divided every 8 hours) of amoxicillin and clavulanate potassium for oral suspension for 10 days in the treatment of acute otitis media. Only the suspension formulations were used in this trial. A total of 575 pediatric patients (aged 2 months to 12 years) were enrolled, with an even distribution among the 2 treatment groups and a comparable number of patients were evaluable (i.e., ≥ 84%) per treatment group. Otitis media-specific criteria were required for eligibility and a strong correlation was found at the end of therapy and follow-up between these criteria and physician assessment of clinical response. The clinical efficacy rates at the end of therapy visit (defined as 2 to 4 days after the completion of therapy) and at the follow-up visit (defined as 22 to 28 days post-completion of therapy) were comparable for the 2 treatment groups, with the following cure rates obtained for the evaluable patients: At end of therapy, 87% (n = 265) and 82% (n = 260) for 45 mg/kg/day every 12 hours and 40 mg/kg/day every 8 hours, respectively. At follow-up, 67% (n = 249) and 69% (n = 243) for 45 mg/kg/day every 12 hours and 40 mg/kg/day every 8 hours, respectively.
Diarrhea was defined as either: (a) 3 or more watery or 4 or more loose/watery stools in 1 day; OR (b) 2 watery stools per day or 3 loose/watery stools per day for 2 consecutive days. The incidence of diarrhea was significantly lower in patients who received the every 12 hours regimen compared to patients who received the every 8 hours regimen (14% and 34%, respectively). In addition, the number of patients with either severe diarrhea or who were withdrawn with diarrhea was significantly lower in the every 12 hours treatment group (3% and 8% for the every 12 hours/10 day and every 8 hours/10 day, respectively). In the every 12 hours treatment group, 3 patients (1%) were withdrawn with an allergic reaction, while 1 patient in the every 8 hours group was withdrawn for this reason. The number of patients with a candidal infection of the diaper area was 4% and 6% for the every 12 hours and every 8 hours groups, respectively.
It is not known if the finding of a statistically significant reduction in diarrhea with the oral suspensions dosed every 12 hours, versus suspensions dosed every 8 hours, can be extrapolated to the chewable tablets. The presence of mannitol in the chewable tablets may contribute to a different diarrhea profile. The every 12 hour oral suspensions (200 mg/25.8 mg per 5 mL and 400 mg/57 mg per 5 mL) are sweetened with aspartame.
Package Label.principal Display Panel
DISCLAIMER:
"This tool does not provide medical advice, and is for informational and educational purposes only, and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, treatment or diagnosis. Call your doctor to receive medical advice. If you think you may have a medical emergency, please dial 911."
"Do not rely on openFDA to make decisions regarding medical care. While we make every effort to ensure that data is accurate, you should assume all results are unvalidated. We may limit or otherwise restrict your access to the API in line with our Terms of Service."
"This product uses publicly available data from the U.S. National Library of Medicine (NLM), National Institutes of Health, Department of Health and Human Services; NLM is not responsible for the product and does not endorse or recommend this or any other product."
PillSync may earn a commission via links on our site