Sonata (zaleplon 10 mg) Dailymed
Generic: zaleplon is used for the treatment of Sleep Initiation and Maintenance Disorders
IMPRINT: 10 MG SONATA
SHAPE: capsule
COLOR: green
All Imprints
sonata 10 mg oral capsule - 10 mg sonata capsule green
Go PRO for all pill images
CIV
RX only
Description
Zaleplon is a nonbenzodiazepine hypnotic from the pyrazolopyrimidine class. The chemical name of zaleplon is N-[3-(3-cyanopyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-7-yl)phenyl]-N-ethylacetamide. Its empirical formula is C17H15N5O, and its molecular weight is 305.34. The structural formula is shown below.
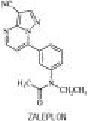
ZALEPLON
Zaleplon is a white to off-white powder that is practically insoluble in water and sparingly soluble in alcohol or propylene glycol. Its partition coefficient in octanol/water is constant (log PC = 1.23) over the pH range of 1 to 7.
Sonata¬ģ capsules contain zaleplon as the active ingredient. Inactive ingredients consist of microcrystalline cellulose, pregelatinized starch, silicon dioxide, sodium lauryl sulfate, magnesium stearate, lactose, gelatin, titanium dioxide, D&C yellow #10, FD&C blue #1, FD&C green #3, and FD&C yellow #5.
Clinical Pharmacology
Pharmacodynamics and Mechanism of Action
While Sonata (zaleplon) is a hypnotic agent with a chemical structure unrelated to benzodiazepines, barbiturates, or other drugs with known hypnotic properties, it interacts with the gamma-aminobutyric acid-benzodiazepine (GABA-BZ) receptor complex. Subunit modulation of the GABA-BZ receptor chloride channel macromolecular complex is hypothesized to be responsible for some of the pharmacological properties of benzodiazepines, which include sedative, anxiolytic, muscle relaxant, and anticonvulsive effects in animal models.
Other nonclinical studies have also shown that zaleplon binds selectively to the brain omega-1 receptor situated on the alpha subunit of the GABAA/chloride ion channel receptor complex and potentiates t-butyl-bicyclophosphorothionate (TBPS) binding. Studies of binding of zaleplon to recombinant GABAA receptors (őĪ1ő≤1ő≥2 [omega-1] and őĪ2ő≤1ő≥2 [omega-2]) have shown that zaleplon has a low affinity for these receptors, with preferential binding to the omega-1 receptor.
Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics of zaleplon have been investigated in more than 500 healthy subjects (young and elderly), nursing mothers, and patients with hepatic disease or renal disease. In healthy subjects, the pharmacokinetic profile has been examined after single doses of up to 60 mg and once-daily administration at 15 mg and 30 mg for 10 days. Zaleplon was rapidly absorbed with a time to peak concentration (tmax) of approximately 1 hour and a terminal-phase elimination half-life (t1/2) of approximately 1 hour. Zaleplon does not accumulate with once-daily administration and its pharmacokinetics are dose proportional in the therapeutic range.
Absorption
Zaleplon is rapidly and almost completely absorbed following oral administration. Peak plasma concentrations are attained within approximately 1 hour after oral administration. Although zaleplon is well absorbed, its absolute bioavailability is approximately 30% because it undergoes significant presystemic metabolism.
Distribution
Zaleplon is a lipophilic compound with a volume of distribution of approximately 1.4 L/kg following intravenous (IV) administration, indicating substantial distribution into extravascular tissues. The in vitro plasma protein binding is approximately 60%¬Ī15% and is independent of zaleplon concentration over the range of 10 ng/mL to 1000 ng/mL. This suggests that zaleplon disposition should not be sensitive to alterations in protein binding. The blood to plasma ratio for zaleplon is approximately 1, indicating that zaleplon is uniformly distributed throughout the blood with no extensive distribution into red blood cells.
Metabolism
After oral administration, zaleplon is extensively metabolized, with less than 1% of the dose excreted unchanged in urine. Zaleplon is primarily metabolized by aldehyde oxidase to form 5-oxo-zaleplon. Zaleplon is metabolized to a lesser extent by cytochrome P450 (CYP) 3A4 to form desethylzaleplon, which is quickly converted, presumably by aldehyde oxidase, to 5-oxo-desethylzaleplon. These oxidative metabolites are then converted to glucuronides and eliminated in urine. All of zaleplon's metabolites are pharmacologically inactive.
Elimination
After either oral or IV administration, zaleplon is rapidly eliminated with a mean t1/2 of approximately 1 hour. The oral-dose plasma clearance of zaleplon is about 3 L/h/kg and the IV zaleplon plasma clearance is approximately 1 L/h/kg. Assuming normal hepatic blood flow and negligible renal clearance of zaleplon, the estimated hepatic extraction ratio of zaleplon is approximately 0.7, indicating that zaleplon is subject to high first-pass metabolism.
After administration of a radiolabeled dose of zaleplon, 70% of the administered dose is recovered in urine within 48 hours (71% recovered within 6 days), almost all as zaleplon metabolites and their glucuronides. An additional 17% is recovered in feces within 6 days, most as 5-oxo-zaleplon.
Effect of Food
In healthy adults a high-fat/heavy meal prolonged the absorption of zaleplon compared to the fasted state, delaying tmax by approximately 2 hours and reducing Cmax by approximately 35%. Zaleplon AUC and elimination half-life were not significantly affected. These results suggest that the effects of Sonata on sleep onset may be reduced if it is taken with or immediately after a high-fat/heavy meal.
Special Populations
Age: The pharmacokinetics of Sonata (zaleplon) have been investigated in three studies with elderly men and women ranging in age from 65 to 85 years. The pharmacokinetics of Sonata in elderly subjects, including those over 75 years of age, are not significantly different from those in young healthy subjects.
Gender: There is no significant difference in the pharmacokinetics of Sonata in men and women.
Race: The pharmacokinetics of zaleplon have been studied in Japanese subjects as representative of Asian populations. For this group, Cmax and AUC were increased 37% and 64%, respectively. This finding can likely be attributed to differences in body weight, or alternatively, may represent differences in enzyme activities resulting from differences in diet, environment, or other factors. The effects of race on pharmacokinetic characteristics in other ethnic groups have not been well characterized.
Hepatic impairment: Zaleplon is metabolized primarily by the liver and undergoes significant presystemic metabolism. Consequently, the oral clearance of zaleplon was reduced by 70% and 87% in compensated and decompensated cirrhotic patients, respectively, leading to marked increases in mean Cmax and AUC (up to 4-fold and 7-fold in compensated and decompensated patients, respectively), in comparison with healthy subjects. The dose of Sonata should therefore be reduced in patients with mild to moderate hepatic impairment (seeDOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION ). Sonata is not recommended for use in patients with severe hepatic impairment.
Renal impairment: Because renal excretion of unchanged zaleplon accounts for less than 1% of the administered dose, the pharmacokinetics of zaleplon are not altered in patients with renal insufficiency. No dose adjustment is necessary in patients with mild to moderate renal impairment. Sonata has not been adequately studied in patients with severe renal impairment.
Drug-Drug Interactions
Because zaleplon is primarily metabolized by aldehyde oxidase, and to a lesser extent by CYP3A4, inhibitors of these enzymes might be expected to decrease zaleplon's clearance and inducers of these enzymes might be expected to increase its clearance. Zaleplon has been shown to have minimal effects on the kinetics of warfarin (both R- and S- forms), imipramine, ethanol, ibuprofen, diphenhydramine, thioridazine, and digoxin. However, the effects of zaleplon on inhibition of enzymes involved in the metabolism of other drugs have not been studied. (SeeDrug Interactions under PRECAUTIONS. )
Clinical Trials Controlled Trials Supporting Effectiveness
Sonata (typically administered in doses of 5 mg, 10 mg, or 20 mg) has been studied in patients with chronic insomnia (n = 3,435) in 12 placebo- and active-drug-controlled trials. Three of the trials were in elderly patients (n = 1,019). It has also been studied in transient insomnia (n = 264). Because of its very short half-life, studies focused on decreasing sleep latency, with less attention to duration of sleep and number of awakenings, for which consistent differences from placebo were not demonstrated. Studies were also carried out to examine the time course of effects on memory and psychomotor function, and to examine withdrawal phenomena.
Transient Insomnia
Normal adults experiencing transient insomnia during the first night in a sleep laboratory were evaluated in a double-blind, parallel-group trial comparing the effects of two doses of Sonata (5 mg and 10 mg) with placebo. Sonata 10 mg, but not 5 mg, was superior to placebo in decreasing latency to persistent sleep (LPS), a polysomnographic measure of time to onset of sleep.
Chronic Insomnia Non-elderly patients:
Adult outpatients with chronic insomnia were evaluated in three double-blind, parallel-group outpatient studies, one of 2 weeks duration and two of 4 weeks duration, that compared the effects of Sonata at doses of 5 mg (in two studies), 10 mg, and 20 mg with placebo on a subjective measure of time to sleep onset (TSO). Sonata 10 mg and 20 mg were consistently superior to placebo for TSO, generally for the full duration of all three studies. Although both doses were effective, the effect was greater and more consistent for the 20-mg dose. The 5-mg dose was less consistently effective than were the 10-mg and 20-mg doses. Sleep latency with Sonata 10 mg and 20 mg was on the order of 10-20 minutes (15%-30%) less than with placebo in these studies.
Adult outpatients with chronic insomnia were evaluated in six double-blind, parallel-group sleep laboratory studies that varied in duration from a single night up to 35 nights. Overall, these studies demonstrated a superiority of Sonata 10 mg and 20 mg over placebo in reducing LPS on the first 2 nights of treatment. At later time points in 5-, 14-, and 28-night studies, a reduction in LPS from baseline was observed for all treatment groups, including the placebo group, and thus, a significant difference between Sonata and placebo was not seen beyond 2 nights. In a 35-night study, Sonata 10 mg was significantly more effective than placebo in reducing LPS at the primary efficacy endpoint on nights 29 and 30.
Elderly patients:
Elderly outpatients with chronic insomnia were evaluated in two 2-week, double-blind, parallel-group outpatient studies that compared the effects of Sonata 5 mg and 10 mg with placebo on a subjective measure of time to sleep onset (TSO). Sonata at both doses was superior to placebo on TSO, generally for the full duration of both studies, with an effect size generally similar to that seen in younger persons. The 10-mg dose tended to have a greater effect in reducing TSO.
Elderly outpatients with chronic insomnia were also evaluated in a 2-night sleep laboratory study involving doses of 5 mg and 10 mg. Both 5-mg and 10-mg doses of Sonata were superior to placebo in reducing latency to persistent sleep (LPS).
Generally in these studies, there was a slight increase in sleep duration, compared to baseline, for all treatment groups, including placebo, and thus, a significant difference from placebo on sleep duration was not demonstrated.
Studies Pertinent to Safety Concerns for Sedative/Hypnotic Drugs Memory Impairment
Studies involving the exposure of normal subjects to single fixed doses of Sonata (10 mg or 20 mg) with structured assessments of short-term memory at fixed times after dosing (eg, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 8, and 10 hours) generally revealed the expected impairment of short-term memory at 1 hour, the time of peak exposure to zaleplon, for both doses, with a tendency for the effect to be greater after 20 mg. Consistent with the rapid clearance of zaleplon, memory impairment was no longer present as early as 2 hours post dosing in one study, and in none of the studies after 3-4 hours. Nevertheless, spontaneous reporting of adverse events in larger premarketing clinical trials revealed a difference between Sonata and placebo in the risk of next-day amnesia (3% vs 1%), and an apparent dose-dependency for this event (see ADVERSE REACTIONS ).
Sedative/Psychomotor Effects
Studies involving the exposure of normal subjects to single fixed doses of Sonata (zaleplon) (10 mg or 20 mg) with structured assessments of sedation and psychomotor function (eg, reaction time and subjective ratings of alertness) at fixed times after dosing (eg, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 8, and 10 hours) generally revealed the expected sedation and impairment of psychomotor function at 1 hour, the time of peak exposure to zaleplon, for both doses. Consistent with the rapid clearance of zaleplon, impairment of psychomotor function was no longer present as early as 2 hours post dosing in one study, and in none of the studies after 3-4 hours. Spontaneous reporting of adverse events in larger premarketing clinical trials did not suggest a difference between Sonata and placebo in the risk of next-day somnolence (see ADVERSE REACTIONS ).
Withdrawal-Emergent Anxiety and Insomnia
During nightly use for an extended period, pharmacodynamic tolerance or adaptation to some effects of hypnotics may develop. If the drug has a short elimination half-life, it is possible that a relative deficiency of the drug or its active metabolites (ie, in relationship to the receptor site) may occur at some point in the interval between each night's use. This sequence of events is believed to be responsible for two clinical findings reported to occur after several weeks of nightly use of other rapidly eliminated hypnotics: increased wakefulness during the last quarter of the night and the appearance of increased signs of daytime anxiety.
Zaleplon has a short half-life and no active metabolites. At the primary efficacy endpoint (nights 29 and 30) in a 35-night sleep laboratory study, polysomnographic recordings showed that wakefulness was not significantly longer with Sonata than with placebo during the last quarter of the night. No increase in the signs of daytime anxiety was observed in clinical trials with Sonata. In two sleep laboratory studies involving 14- and 28-nightly doses of Sonata (5 mg and 10 mg in one study and 10 mg and 20 mg in the second) and structured assessments of daytime anxiety, no increases in daytime anxiety were detected. Similarly, in a pooled analysis (all the parallel-group, placebo-controlled studies) of spontaneously reported daytime anxiety, no difference was observed between Sonata and placebo.
Rebound insomnia, defined as a dose-dependent temporary worsening in sleep parameters (latency, total sleep time, and number of awakenings) compared to baseline following discontinuation of treatment, is observed with short- and intermediate-acting hypnotics. Rebound insomnia following discontinuation of Sonata relative to baseline was examined at both nights 1 and 2 following discontinuation in three sleep laboratory studies (14, 28, and 35 nights) and five outpatient studies utilizing patient diaries (14 and 28 nights). Overall, the data suggest that rebound insomnia may be dose dependent. At 20 mg, there appeared to be both objective (polysomnographic) and subjective (diary) evidence of rebound insomnia on the first night after discontinuation of treatment with Sonata. At 5 mg and 10 mg, there was no objectiveand minimal subjective evidence of rebound insomnia on the first night after discontinuation of treatment with Sonata. At all doses, the rebound effect appeared to resolve by the second night following withdrawal. In the 35-night study, there was a worsening in sleep on the first night off for both the 10-mg and 20-mg groups compared to placebo, but not to baseline. This discontinuation-emergent effect was mild, had the characteristics of the return of the symptoms of chronic insomnia, and appeared to resolve by the second night after zaleplon discontinuation.
Other Withdrawal-Emergent Phenomena
The potential for other withdrawal phenomena was also assessed in 14- to 28-night studies, including both the sleep laboratory studies and the outpatient studies, and in open-label studies of 6- and 12-month durations. The Benzodiazepine Withdrawal Symptom Questionnaire was used in several of these studies, both at baseline and then during days 1 and 2 following discontinuation. Withdrawal was operationally defined as the emergence of 3 or more new symptoms after discontinuation. Sonata was not distinguishable from placebo at doses of 5 mg, 10 mg, or 20 mg on this measure, nor was Sonata distinguishable from placebo on spontaneously reported withdrawal-emergent adverse events. There were no instances of withdrawal delirium, withdrawal associated hallucinations, or any other manifestations of severe sedative/hypnotic withdrawal.
Indications And Usage
Sonata is indicated for the short-term treatment of insomnia. Sonata has been shown to decrease the time to sleep onset for up to 30 days in controlled clinical studies (see Clinical Trials under CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY ). It has not been shown to increase total sleep time or decrease the number of awakenings.
The clinical trials performed in support of efficacy ranged from a single night to 5 weeks in duration. The final formal assessments of sleep latency were performed at the end of treatment.
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to zaleplon or any excipients in the formulation (see also PRECAUTIONS ).
Warnings
Because sleep disturbances may be the presenting manifestation of a physical and/or psychiatric disorder, symptomatic treatment of insomnia should be initiated only after a careful evaluation of the patient. The failure of insomnia to remit after 7 to 10 days of treatment may indicate the presence of a primary psychiatric and/or medical illness that should be evaluated. Worsening of insomnia or the emergence of new thinking or behavior abnormalities may be the consequence of an unrecognized psychiatric or physical disorder. Such findings have emerged during the course of treatment with sedative/hypnotic drugs, including Sonata. Because some of the important adverse effects of Sonata appear to be dose-related, it is important to use the lowest possible effective dose, especially in the elderly (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION ).
A variety of abnormal thinking and behavior changes have been reported to occur in association with the use of sedative/hypnotics. Some of these changes may be characterized by decreased inhibition (eg, aggressiveness and extroversion that seem out of character), similar to effects produced by alcohol and other CNS depressants. Other reported behavioral changes have included bizarre behavior, agitation, hallucinations, and depersonalization. Amnesia and other neuropsychiatric symptoms may occur unpredictably. In primarily depressed patients, worsening of depression, including suicidal thinking, has been reported in association with the use of sedative/hypnotics.
It can rarely be determined with certainty whether a particular instance of the abnormal behaviors uled above is drug induced, spontaneous in origin, or a result of an underlying psychiatric or physical disorder. Nonetheless, the emergence of any new behavioral sign or symptom of concern requires careful and immediate evaluation.
Following rapid dose decrease or abrupt discontinuation of the use of sedative/hypnotics, there have been reports of signs and symptoms similar to those associated with withdrawal from other CNS-depressant drugs (see DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE ).
Sonata, like other hypnotics, has CNS-depressant effects. Because of the rapid onset of action, Sonata should only be ingested immediately prior to going to bed or after the patient has gone to bed and has experienced difficulty falling asleep. Patients receiving Sonata should be cautioned against engaging in hazardous occupations requiring complete mental alertness or motor coordination (eg, operating machinery or driving a motor vehicle) after ingesting the drug, including potential impairment of the performance of such activities that may occur the day following ingestion of Sonata. Sonata, as well as other hypnotics, may produce additive CNS-depressant effects when coadministered with other psychotropic medications, anticonvulsants, antihistamines, narcotic analgesics, anesthetics, ethanol, and other drugs that themselves produce CNS depression. Sonata should not be taken with alcohol. Dosage adjustment may be necessary when Sonata is administered with other CNS-depressant agents because of the potentially additive effects.
Precautions
General Timing of Drug Administration
Sonata should be taken immediately before bedtime or after the patient has gone to bed and has experienced difficulty falling asleep. As with all sedative/hypnotics, taking Sonata while still up and about may result in short-term memory impairment, hallucinations, impaired coordination, dizziness, and lightheadedness.
Use in the elderly and/or debilitated patients
Impaired motor and/or cognitive performance after repeated exposure or unusual sensitivity to sedative/hypnotic drugs is a concern in the treatment of elderly and/or debilitated patients. A dose of 5 mg is recommended for elderly patients to decrease the possibility of side effects (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION ). Elderly and/or debilitated patients should be monitored closely.
Use in patients with concomitant illness
Clinical experience with Sonata in patients with concomitant systemic illness is limited. Sonata should be used with caution in patients with diseases or conditions that could affect metabolism or hemodynamic responses.
Although preliminary studies did not reveal respiratory depressant effects at hypnotic doses of Sonata in normal subjects, caution should be observed if Sonata (zaleplon) is prescribed to patients with compromised respiratory function, because sedative/hypnotics have the capacity to depress respiratory drive. Controlled trials of acute administration of Sonata 10 mg in patients with mild to moderate chronic obstructive pulmonary disease or moderate obstructive sleep apnea showed no evidence of alterations in blood gases or apnea/hypopnea index, respectively. However, patients with compromised respiration due to preexisting illness should be monitored carefully.
The dose of Sonata should be reduced to 5 mg in patients with mild to moderate hepatic impairment (seeDOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION ). It is not recommended for use in patients with severe hepatic impairment.
No dose adjustment is necessary in patients with mild to moderate renal impairment. Sonata has not been adequately studied in patients with severe renal impairment.
Use in patients with depression
As with other sedative/hypnotic drugs, Sonata should be administered with caution to patients exhibiting signs or symptoms of depression. Suicidal tendencies may be present in such patients and protective measures may be required. Intentional overdosage is more common in this group of patients (see OVERDOSAGE ); therefore, the least amount of drug that is feasible should be prescribed for the patient at any one time.
This product contains FD&C Yellow No. 5 (tartrazine) which may cause allergic-type reactions (including bronchial asthma) in certain susceptible persons. Although the overall incidence of FD&C Yellow No. 5 (tartrazine) sensitivity in the general population is low, it is frequently seen in patients who also have aspirin hypersensitivity.
Information for Patients
Patient information is printed at the end of this insert. To assure safe and effective use of Sonata, the information and instructions provided in the patient information section should be discussed with patients.
Laboratory Tests
There are no specific laboratory tests recommended.
Drug Interactions
As with all drugs, the potential exists for interaction with other drugs by a variety of mechanisms.
CNS-Active Drugs
Ethanol: Sonata 10 mg potentiated the CNS-impairing effects of ethanol 0.75 g/kg on balance testing and reaction time for 1 hour after ethanol administration and on the digit symbol substitution test (DSST), symbol copying test, and the variability component of the divided attention test for 2.5 hours after ethanol administration. The potentiation resulted from a CNS pharmacodynamic interaction; zaleplon did not affect the pharmacokinetics of ethanol.
Imipramine: Coadministration of single doses of Sonata 20 mg and imipramine 75 mg produced additive effects on decreased alertness and impaired psychomotor performance for 2 to 4 hours after administration. The interaction was pharmacodynamic with no alteration of the pharmacokinetics of either drug.
Paroxetine: Coadministration of a single dose of Sonata 20 mg and paroxetine 20 mg daily for 7 days did not produce any interaction on psychomotor performance. Additionally, paroxetine did not alter the pharmacokinetics of Sonata, reflecting the absence of a role of CYP2D6 in zaleplon's metabolism.
Thioridazine: Coadministration of single doses of Sonata 20 mg and thioridazine 50 mg produced additive effects on decreased alertness and impaired psychomotor performance for 2 to 4 hours after administration. The interaction was pharmacodynamic with no alteration of the pharmacokinetics of either drug.
Venlafaxine: Coadministration of a single dose of zaleplon 10 mg and multiple doses of venlafaxine ER (extended release) 150 mg did not result in any significant changes in the pharmacokinetics of either zaleplon of venlafaxine. In addition, there was no pharmacodynamic interaction as a result of coadministration of zaleplon and venlafaxine ER.
Promethazine: Coadministration of a single dose of zaleplon and promethazine (10 and 25 mg, respectively) resulted in a 15% decrease in maximal plasma concentrations of zaleplon, but no change in the area under the plasma concentration-time curve. however, the pharmacodynamics of coadministration of zaleplon and promethazine have not been evaluated. Caution should be exercised when these 2 agents are coadministered.
Drugs That Induce CYP3A4
Rifampin: CYP3A4 is ordinarily a minor metabolizing enzyme of zaleplon. Multiple-dose administration of the potent CYP3A4 inducer rifampin (600 mg every 24 hours, q24h, for 14 days), however, reduced zaleplon Cmax and AUC by approximately 80%. The coadministration of a potent CYP3A4 enzyme inducer, although not posing a safety concern, thus could lead to ineffectiveness of zaleplon. An alternative non-CYP3A4 substrate hypnotic agent may be considered in patients taking CYP3A4 inducers such as rifampin, phenytoin, carbamazepine, and phenobarbital.
Drugs That Inhibit CYP3A4
CYP3A4 is a minor metabolic pathway for the elimination of zaleplon because the sum of desethylzaleplon (formed via CYP3A4 in vitro) and its metabolites, 5-oxo-desethylzaleplon and 5-oxo-desethylzaleplon glucuronide, account for only 9% of the urinary recovery of a zaleplon dose. Coadministration of single, oral doses of zaleplon with erythromycin (10 mg and 800 mg respectively), a strong, selective CYP3A4 inhibitor, produced a 34% increase in zaleplon's maximal plasma concentrations and a 20% increase in the area under the plasma concentration-time curve. The magnitude of interaction with multiple doses of erythromycin is unknown. Other strong selective CYP3A4 inhibitors such as ketoconazole can also be expected to increase the exposure of zaleplon. A routine dosage adjustment of zaleplon is not considered necessary.
Drugs That Inhibit Aldehyde Oxidase
The aldehyde oxidase enzyme system is less well studied than the cytochrome P450 enzyme system.
Diphenhydramine: Diphenhydramine is reported to be a weak inhibitor of aldehyde oxidase in rat liver, but its inhibitory effects in human liver are not known. There is no pharmacokinetic interaction between zaleplon and diphenhydramine following the administration of a single dose (10 mg and 50 mg, respectively) of each drug. However, because both of these compounds have CNS effects, an additive pharmacodynamic effect is possible.
Drugs That Inhibit Both Aldehyde Oxidase and CYP3A4
Cimetidine: Cimetidine inhibits both aldehyde oxidase (in vitro) and CYP3A4 (in vitro and in vivo), the primary and secondary enzymes, respectively, responsible for zaleplon metabolism. Concomitant administration of Sonata (10 mg) and cimetidine (800 mg) produced an 85% increase in the mean Cmax and AUC of zaleplon. An initial dose of 5 mg should be given to patients who are concomitantly being treated with cimetidine (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION ).
Drugs Highly Bound to Plasma Protein
Zaleplon is not highly bound to plasma proteins (fraction bound 60%¬Ī15%); therefore, the disposition of zaleplon is not expected to be sensitive to alterations in protein binding. In addition, administration of Sonata to a patient taking another drug that is highly protein bound should not cause transient increase in free concentrations of the other drug.
Drugs with a Narrow Therapeutic Index
Digoxin: Sonata (10 mg) did not affect the pharmacokinetic or pharmacodynamic profile of digoxin (0.375 mg q24h for 8 days).
Warfarin: Multiple oral doses of Sonata (20 mg q24h for 13 days) did not affect the pharmacokinetics of warfarin (R+)- or (S-)-enantiomers or the pharmacodynamics (prothrombin time) following a single 25-mg oral dose of warfarin.
Drugs That Alter Renal Excretion
Ibuprofen: Ibuprofen is known to affect renal function and, consequently, alter the renal excretion of other drugs. There was no apparent pharmacokinetic interaction between zaleplon and ibuprofen following single dose administration (10 mg and 600 mg, respectively) of each drug. This was expected because zaleplon is primarily metabolized and renal excretion of unchanged zaleplon accounts for less than 1% of the administered dose.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, and Impairment of Fertility Carcinogenesis
Lifetime carcinogenicity studies of zaleplon were conducted in mice and rats. Mice received doses of 25 mg/kg/day, 50 mg/kg/day, 100 mg/kg/day, and 200 mg/kg/day in the diet for two years. These doses are equivalent to 6 to 49 times the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 20 mg on a mg/m2 basis. There was a significant increase in the incidence of hepatocellular adenomas in female mice in the high dose group. Rats received doses of 1 mg/kg/day, 10 mg/kg/day, and 20 mg/kg/day in the diet for two years. These doses are equivalent to 0.5 to 10 times the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 20 mg on a mg/m2 basis. Zaleplon was not carcinogenic in rats.
Mutagenesis
Zaleplon was clastogenic, both in the presence and absence of metabolic activation, causing structural and numerical aberrations (polyploidy and endoreduplication), when tested for chromosomal aberrations in the in vitro Chinese hamster ovary cell assay. In the in vitro human lymphocyte assay, zaleplon caused numerical, but not structural, aberrations only in the presence of metabolic activation at the highest concentrations tested. In other in vitro assays, zaleplon was not mutagenic in the Ames bacterial gene mutation assay or the Chinese hamster ovary HGPRT gene mutation assay. Zaleplon was not clastogenic in two in vivo assays, the mouse bone marrow micronucleus assay and the rat bone marrow chromosomal aberration assay, and did not cause DNA damage in the rat hepatocyte unscheduled DNA synthesis assay.
Impairment of Fertility
In a fertility and reproductive performance study in rats, mortality and decreased fertility were associated with administration of an oral dose of zaleplon of 100 mg/kg/day to males and females prior to and during mating. This dose is equivalent to 49 times the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 20 mg on a mg/m2 basis. Follow-up studies indicated that impaired fertility was due to an effect on the female.
Pregnancy: Pregnancy Category C
In embryofetal development studies in rats and rabbits, oral administration of up to 100 mg/kg/day and 50 mg/kg/day, respectively, to pregnant animals throughout organogenesis produced no evidence of teratogenicity. These doses are equivalent to 49 (rat) and 48 (rabbit) times the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 20 mg on a mg/m2 basis. In rats, pre- and postnatal growth was reduced in the offspring of dams receiving 100 mg/kg/day. This dose was also maternally toxic, as evidenced by clinical signs and decreased maternal body weight gain during gestation. The no-effect dose for rat offspring growth reduction was 10 mg/kg (a dose equivalent to 5 times the MRHD of 20 mg on a mg/m2 basis). No adverse effects on embryofetal development were observed in rabbits at the doses examined.
In a pre- and postnatal development study in rats, increased stillbirth and postnatal mortality, and decreased growth and physical development, were observed in the offspring of females treated with doses of 7 mg/kg/day or greater during the latter part of gestation and throughout lactation. There was no evidence of maternal toxicity at this dose. The no-effect dose for offspring development was 1 mg/kg/day (a dose equivalent to 0.5 times the MRHD of 20 mg on a mg/m2 basis). When the adverse effects on offspring viability and growth were examined in a cross-fostering study, they appeared to result from both in utero and lactational exposure to the drug.
There are no studies of zaleplon in pregnant women; therefore, Sonata¬ģ (zaleplon)is not recommended for use in women during pregnancy.
Labor and Delivery
Sonata has no established use in labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
A study in lactating mothers indicated that the clearance and half-life of zaleplon is similar to that in young normal subjects. A small amount of zaleplon is excreted in breast milk, with the highest excreted amount occurring during a feeding at approximately 1 hour after Sonata administration. Since the small amount of the drug from breast milk may result in potentially important concentrations in infants, and because the effects of zaleplon on a nursing infant are not known, it is recommended that nursing mothers not take Sonata.
Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of Sonata in pediatric patients have not been established.
Geriatric Use
A total of 628 patients in double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group clinical trials who received Sonata were at least 65 years of age; of these, 311 received 5 mg and 317 received 10 mg. In both sleep laboratory and outpatient studies, elderly patients with insomnia responded to a 5 mg dose with a reduced sleep latency, and thus 5 mg is the recommended dose in this population. During short-term treatment (14 night studies) of elderly patients with Sonata, no adverse event with a frequency of at least 1% occurred at a significantly higher rate with either 5 mg or 10 mg Sonata than with placebo.
Adverse Reactions
The premarketing development program for Sonata included zaleplon exposures in patients and/or normal subjects from 2 different groups of studies: approximately 900 normal subjects in clinical pharmacology/pharmacokinetic studies; and approximately 2,900 exposures from patients in placebo-controlled clinical effectiveness studies, corresponding to approximately 450 patient exposure years. The conditions and duration of treatment with Sonata varied greatly and included (in overlapping categories) open-label and double-blind phases of studies, inpatients and outpatients, and short-term or longer-term exposure. Adverse reactions were assessed by collecting adverse events, results of physical examinations, vital signs, weights, laboratory analyses, and ECGs.
Adverse events during exposure were obtained primarily by general inquiry and recorded by clinical investigators using terminology of their own choosing. Consequently, it is not possible to provide a meaningful estimate of the proportion of individuals experiencing adverse events without first grouping similar types of events into a smaller number of standardized event categories. In the tables and tabulations that follow, COSTART terminology has been used to classify reported adverse events.
The stated frequencies of adverse events represent the proportion of individuals who experienced, at least once, a treatment-emergent adverse event of the type uled. An event was considered treatment-emergent if it occurred for the first time or worsened while receiving therapy following baseline evaluation.
Adverse Findings Observed in Short-Term, Placebo-Controlled Trials Adverse Events Associated With Discontinuation of Treatment
In premarketing placebo-controlled, parallel-group phase 2 and phase 3 clinical trials, 3.1% of 744 patients who received placebo and 3.7% of 2,149 patients who received Sonata discontinued treatment because of an adverse clinical event. This difference was not statistically significant. No event that resulted in discontinuation occurred at a rate of greater than or equal to 1%.
Adverse Events Occurring at an Incidence of 1% or More Among Sonata 20 mg-Treated Patients
Table 1 enumerates the incidence of treatment-emergent adverse events for a pool of three 28-night and one 35-night placebo-controlled studies of Sonata at doses of 5 mg or 10 mg and 20 mg. The table includes only those events that occurred in 1% or more of patients treated with Sonata 20 mg and that had a higher incidence in patients treated with Sonata 20 mg than in placebo-treated patients.
The prescriber should be aware that these figures cannot be used to predict the incidence of adverse events in the course of usual medical practice where patient characteristics and other factors differ from those which prevailed in the clinical trials. Similarly, the cited frequencies cannot be compared with figures obtained from other clinical investigations involving different treatments, uses, and investigators. The cited figures, however, do provide the prescribing physician with some basis for estimating the relative contribution of drug and non-drug factors to the adverse event incidence rate in the population studied.
1: Events for which the incidence for Sonata 20 mg-treated patients was at least 1% and greater than the incidence among placebo-treated patients. Incidence greater than 1% has been rounded to the nearest whole number.
Table 1 Incidence (%) of Treatment-Emergent Adverse Events in Long-Term (28 and 35 Nights) Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trials of Sonata1 Body System Placebo Sonata 5 mg or 10 mg Sonata 20 mg    Preferred Term (n = 344) (n = 569) (n = 297) Body as a whole    Abdominal pain 3 6 6    Asthenia 5 5 7    Headache 35 30 42    Malaise less than 1 less than 1 2    Photosensitivity reaction less than 1 less than 1 1 Digestive system    Anorexia less than 1 less than 1 2    Colitis 0 0 1    Nausea 7 6 8 Metabolic and nutritional    Peripheral edema less than 1 less than 1 1 Nervous system    Amnesia 1 2 4    Confusion less than 1 less than 1 1    Depersonalization less than 1 less than 1 2    Dizziness 7 7 9    Hallucinations less than 1 less than 1 1    Hypertonia less than 1 1 1    Hypesthesia less than 1 less than 1 2    Paresthesia 1 3 3    Somnolence 4 5 6    Tremor 1 2 2    Vertigo less than 1 less than 1 1 Respiratory system    Epistaxis less than 1 less than 1 1 Special senses    Abnormal vision less than 1 less than 1 2    Ear pain 0 less than 1 1    Eye pain 2 4 3    Hyperacusis less than 1 1 2    Parosmia less than 1 less than 1 2 Urogenital system    Dysmenorrhea 2 3 4 Other Adverse Events Observed During the Premarketing Evaluation of Sonata
Listed below are COSTART terms that reflect treatment-emergent adverse events as defined in the introduction to the ADVERSE REACTIONS section. These events were reported by patients treated with Sonata (zaleplon) at doses in a range of 5 mg/day to 20 mg/day during premarketing phase 2 and phase 3 clinical trials throughout the United States, Canada, and Europe, including approximately 2,900 patients. All reported events are included except those already uled in Table 1 or elsewhere in labeling, those events for which a drug cause was remote, and those event terms that were so general as to be uninformative. It is important to emphasize that although the events reported occurred during treatment with Sonata, they were not necessarily caused by it.
Events are further categorized by body system and uled in order of decreasing frequency according to the following definitions: frequent adverse events are those occurring on one or more occasions in at least 1/100 patients; infrequent adverse events are those occurring in less than 1/100 patients but at least 1/1,000 patients; rare events are those occurring in fewer than 1/1,000 patients.
Body as a whole - Frequent: back pain, chest pain, fever; Infrequent: chest pain substernal, chills, face edema, generalized edema, hangover effect, neck rigidity.
Cardiovascular system - Frequent: migraine; Infrequent: angina pectoris, bundle branch block, hypertension, hypotension, palpitation, syncope, tachycardia, vasodilatation, ventricular extrasystoles; Rare: bigeminy, cerebral ischemia, cyanosis, pericardial effusion, postural hypotension, pulmonary embolus, sinus bradycardia, thrombophlebitis, ventricular tachycardia.
Digestive system - Frequent: constipation, dry mouth, dyspepsia; Infrequent: eructation, esophagitis, flatulence, gastritis, gastroenteritis, gingivitis, glossitis, increased appetite, melena, mouth ulceration, rectal hemorrhage, stomatitis; Rare: aphthous stomatitis, biliary pain, bruxism, cardiospasm, cheilitis, cholelithiasis, duodenal ulcer, dysphagia, enteritis, gum hemorrhage, increased salivation, intestinal obstruction, abnormal liver function tests, peptic ulcer, tongue discoloration, tongue edema, ulcerative stomatitis.
Endocrine system - Rare: diabetes mellitus, goiter, hypothyroidism.
Hemic and lymphatic system - Infrequent: anemia, ecchymosis, lymphadenopathy; Rare: eosinophilia, leukocytosis, lymphocytosis, purpura.
Metabolic and nutritional - Infrequent: edema, gout, hypercholesteremia, thirst, weight gain; Rare: bilirubinemia, hyperglycemia, hyperuricemia, hypoglycemia, hypoglycemic reaction, ketosis, lactose intolerance, AST (SGOT) increased, ALT (SGPT) increased, weight loss.
Musculoskeletal system - Frequent: arthralgia, arthritis, myalgia; Infrequent: arthrosis, bursitis, joint disorder (mainly swelling, stiffness, and pain), myasthenia, tenosynovitis; Rare: myositis, osteoporosis.
Nervous system - Frequent: anxiety, depression, nervousness, thinking abnormal (mainly difficulty concentrating); Infrequent: abnormal gait, agitation, apathy, ataxia, circumoral paresthesia, emotional lability, euphoria, hyperesthesia, hyperkinesia, hypotonia, incoordination, insomnia, libido decreased, neuralgia, nystagmus; Rare: CNS stimulation, delusions, dysarthria, dystonia, facial paralysis, hostility, hypokinesia, myoclonus, neuropathy, psychomotor retardation, ptosis, reflexes decreased, reflexes increased, sleep talking, sleep walking, slurred speech, stupor, trismus.
Respiratory system - Frequent: bronchitis; Infrequent: asthma, dyspnea, laryngitis, pneumonia, snoring, voice alteration; Rare: apnea, hiccup, hyperventilation, pleural effusion, sputum increased.
Skin and appendages - Frequent: pruritus, rash; Infrequent: acne, alopecia, contact dermatitis, dry skin, eczema, maculopapular rash, skin hypertrophy, sweating, urticaria, vesiculobullous rash; Rare: melanosis, psoriasis, pustular rash, skin discoloration.
Special senses - Frequent: conjunctivitis, taste perversion; Infrequent: diplopia, dry eyes, photophobia, tinnitus, watery eyes; Rare: abnormality of accommodation, blepharitis, cataract specified, corneal erosion, deafness, eye hemorrhage, glaucoma, labyrinthitis, retinal detachment, taste loss, visual field defect.
Urogenital system - Infrequent: bladder pain, breast pain, cystitis, decreased urine stream, dysuria, hematuria, impotence, kidney calculus, kidney pain, menorrhagia, metrorrhagia, urinary frequency, urinary incontinence, urinary urgency, vaginitis; Rare: albuminuria, delayed menstrual period, leukorrhea, menopause, urethritis, urinary retention, vaginal hemorrhage.
Postmarketing Reports
Anaphylactic/anaphylactoid reactions, including severe reactions.
Drug Abuse And Dependence
Controlled Substance Class
Sonata is classified as a Schedule IV controlled substance by federal regulation.
Abuse, Dependence, and Tolerance
Abuse and addiction are separate and distinct from physical dependence and tolerance. Abuse is characterized by misuse of the drug for non-medical purposes, often in combination with other psychoactive substances. Physical dependence is a state of adaption that is manifested by a specific withdrawal syndrome that can be produced by abrupt cessation, rapid dose reduction, decreasing blood level of the drug and/or administration of an antagonist. Tolerance is a state of adaptation in which exposure to a drug induces changes that result in a diminution of one or more of the drug's effects over time. Tolerance may occur to both the desired and undesired effects of drugs and may develop at different rates for different effects.
Addiction is a primary, chronic, neurobiological disease with genetic, psychosocial, and environmental factors influencing its development and manifestations. It is characterized by behaviors that include one or more of the following: impaired control over drug use, compulsive use, continued use despite harm, and craving. Drug addiction is a treatable disease, utilizing a multidisciplinary approach, but relapse is common.
Abuse
Two studies assessed the abuse liability of Sonata at doses of 25 mg, 50 mg, and 75 mg in subjects with known histories of sedative drug abuse. The results of these studies indicate that Sonata has an abuse potential similar to benzodiazepine and benzodiazepine-like hypnotics.
Dependence
The potential for developing physical dependence on Sonata and a subsequent withdrawal syndrome was assessed in controlled studies of 14-, 28-, and 35-night durations and in open-label studies of 6- and 12-month durations by examining for the emergence of rebound insomnia following drug discontinuation. Some patients (mostly those treated with 20 mg) experienced a mild rebound insomnia on the first night following withdrawal that appeared to be resolved by the second night. The use of the Benzodiazepine Withdrawal Symptom Questionnaire and examination of any other withdrawal-emergent events did not detect any other evidence for a withdrawal syndrome following abrupt discontinuation of Sonata therapy in pre-marketing studies.
However, available data cannot provide a reliable estimate of the incidence of dependence during treatment at recommended doses of Sonata. Other sedative/hypnotics have been associated with various signs and symptoms following abrupt discontinuation, ranging from mild dysphoria and insomnia to a withdrawal syndrome that may include abdominal and muscle cramps, vomiting, sweating, tremors, and convulsions. Seizures have been observed in two patients, one of which had a prior seizure, in clinical trials with Sonata. Seizures and death have been seen following the withdrawal of zaleplon from animals at doses many times higher than those proposed for human use. Because individuals with a history of addiction to, or abuse of, drugs or alcohol are at risk of habituation and dependence, they should be under careful surveillance when receiving Sonata or any other hypnotic.
Tolerance
Possible tolerance to the hypnotic effects of Sonata 10 mg and 20 mg was assessed by evaluating time to sleep onset for Sonata compared with placebo in two 28-night placebo-controlled studies and latency to persistent sleep in one 35-night placebo-controlled study where tolerance was evaluated on nights 29 and 30. No development of tolerance to Sonata was observed for time to sleep onset over 4 weeks.
Overdosage
There is limited pre-marketing clinical experience with the effects of an overdosage of Sonata. Two cases of overdose were reported. One was the accidental ingestion by a 2¬Ĺ year old boy of 20 mg to 40 mg of zaleplon. The second was a 20 year old man who took 100 mg zaleplon plus 2.25 mg of triazolam. Both were treated and recovered uneventfully.
Signs and Symptoms
Signs and symptoms of overdose effects of CNS depressants can be expected to present as exaggerations of the pharmacological effects noted in preclinical testing. Overdose is usually manifested by degrees of central nervous system depression ranging from drowsiness to coma. In mild cases, symptoms include drowsiness, mental confusion, and lethargy; in more serious cases, symptoms may include ataxia, hypotonia, hypotension, respiratory depression, rarely coma, and very rarely death.
Recommended Treatment
General symptomatic and supportive measures should be used along with immediate gastric lavage where appropriate. Intravenous fluids should be administered as needed. Animal studies suggest that flumazenil is an antagonist to zaleplon. However, there is no pre-marketing clinical experience with the use of flumazenil as an antidote to a Sonata overdose. As in all cases of drug overdose, respiration, pulse, blood pressure, and other appropriate signs should be monitored and general supportive measures employed. Hypotension and CNS depression should be monitored and treated by appropriate medical intervention.
Poison Control Center
As with the management of all overdosage, the possibility of multiple drug ingestion should be considered. The physician may wish to consider contacting a poison control center for up-to-date information on the management of hypnotic drug product overdosage.
Dosage And Administration
The dose of Sonata should be individualized. The recommended dose of Sonata for most nonelderly adults is 10 mg. For certain low weight individuals, 5 mg may be a sufficient dose. Although the risk of certain adverse events associated with the use of Sonata appears to be dose dependent, the 20 mg dose has been shown to be adequately tolerated and may be considered for the occasional patient who does not benefit from a trial of a lower dose. Doses above 20 mg have not been adequately evaluated and are not recommended.
Sonata should be taken immediately before bedtime or after the patient has gone to bed and has experienced difficulty falling asleep (see PRECAUTIONS. ). Taking Sonata with or immediately after a heavy, high-fat meal results in slower absorption and would be expected to reduce the effect of Sonata on sleep latency (see Pharmacokinetics under CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY ).
Special Populations
Elderly patients and debilitated patients appear to be more sensitive to the effects of hypnotics, and respond to 5 mg of Sonata. The recommended dose for these patients is therefore 5 mg. Doses over 10 mg are not recommended.
Hepatic insufficiency: Patients with mild to moderate hepatic impairment should be treated with Sonata 5 mg because clearance is reduced in this population. Sonata is not recommended for use in patients with severe hepatic impairment.
Renal insufficiency: No dose adjustment is necessary in patients with mild to moderate renal impairment. Sonata has not been adequately studied in patients with severe renal impairment.
An initial dose of 5 mg should be given to patients concomitantly taking cimetidine because zaleplon clearance is reduced in this population (see Drug Interactions under PRECAUTIONS ).
How Supplied
HOW SUPPLIED
Sonata (zaleplon) capsules are supplied as follows:
5 mg: opaque green cap and opaque pale green body with ‚Äú5 mg‚ÄĚ on the cap and ‚ÄúSONATA‚ÄĚ on the body. ¬†¬†¬†NDC 54868-5139-0¬†¬† NDC 54868-5139-1 Bottles of 10Bottles of 30 10 mg: opaque green cap and opaque light green body with ‚Äú10 mg‚ÄĚ on the cap and ‚ÄúSONATA‚ÄĚ on the body. ¬†¬†¬†NDC 54868-4431-1¬†¬† NDC 54868-4431-0¬†¬† NDC 54868-4431-3¬†¬† NDC 54868-4431-2 Bottles of 10Bottles of 30Bottles of 50Bottles of 100
Sonata¬ģ is a registered trademark of Jones Pharma Inc.‚ĄĘ, a wholly owned subsidiary of King Pharmaceuticals¬ģ, Inc.
STORAGE CONDITIONS
Store at controlled room temperature, 20¬įC to 25¬įC (68¬įF to 77¬įF).
Dispense in a light-resistant container as defined in the USP.
Repackaging and Relabeling by:Physicians Total Care, Inc.Tulsa, OK      74146
Information For Patients Taking Sonata
Your doctor has prescribed Sonata to help you sleep. The following information is intended to guide you in the safe use of this medicine. It is not meant to take the place of your doctor's instructions. If you have any questions about Sonata capsules, be sure to ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Sonata is used to treat difficulty in falling asleep. Sonata works very quickly and has its effect during the first part of the night, since it is rapidly eliminated by the body. You should take Sonata immediately before going to bed or after you have gone to bed and are having difficulty falling asleep. If your principal sleep difficulty is awakening prematurely after falling asleep, there is no evidence that Sonata will be helpful to you. For Sonata to help you fall asleep you should not take it with or immediately after a high-fat/heavy meal.
Sonata belongs to a group of medicines known as the ‚Äúhypnotics‚ÄĚ, or simply, sleep medicines. There are many different sleep medicines available to help people sleep better. Sleep problems are usually temporary, requiring treatment for only a short time, usually 1 or 2 days up to 1 or 2 weeks. Some people have chronic sleep problems that may require more prolonged use of sleep medicine. However, you should not use these medicines for long periods without talking with your doctor about the risks and benefits of prolonged use.
Who should not take Sonata
Do not take Sonata if you are hypersensitive to its active substance, zaleplon, or to any of its inactive ingredients, including tartrazine (FD&C Yellow No. 5).
This product contains FD&C Yellow No. 5 (tartrazine) which may cause allergic-type reactions (including bronchial asthma) in certain susceptible persons. Although the overall incidence of FD&C Yellow No. 5 (tartrazine) sensitivity in the general population is low, it is frequently seen in patients who also have aspirin hypersensitivity.
Side Effects
All medicines have side effects. The most common side effects of sleep medicines are:
- Drowsiness
- Dizziness
- Lightheadedness
- Difficulty with coordination
These side effects with Sonata occur most often within an hour after taking it, so it is especially important to take it only when you are about to go to bed or are already in bed.
Severe allergic reactions, sometimes with difficulty in breathing and possibly life threatening, have been reported and may require immediate medical care.
Sleep medicines can make you sleepy during the day. How drowsy you feel depends upon how your body reacts to the medicine, which sleep medicine you are taking, and how large a dose your doctor has prescribed. Daytime drowsiness is best avoided by taking the lowest dose possible that will still help you sleep at night. Your doctor will work with you to find the dose of Sonata that is best for you. Sonata generally does not cause next-day sleepiness but a few people have reported this.
To manage these side effects while you are taking this medicine:
- When you first start taking Sonata or any other sleep medicine, until you know whether the medicine will still have some carryover effect in you the next day, use extreme care while doing anything that requires complete alertness, such as driving a car, operating machinery, or piloting an aircraft. - NEVER drink alcohol while you are being treated with Sonata or any sleep medicine. Alcohol can increase the side effects of Sonata or any other sleep medicine. - Do not take any other medicines without asking your doctor first. This includes medicines you can buy without a prescription. Some medicines can cause drowsiness and are best avoided while taking Sonata. - Always take the exact dose of Sonata prescribed by your doctor. Never change your dose without talking to your doctor first.
Special Concerns
There are some special problems that may occur while taking sleep medicines.
Memory Problems
Sleep medicines may cause a special type of memory loss or ‚Äúamnesia.‚ÄĚ When this occurs, a person may not remember what has happened for several hours after taking the medicine. This is usually not a problem since most people fall asleep after taking the medicine. Memory loss can be a problem, however, when sleep medicines are taken while traveling, such as during an airplane flight and the person wakes up before the effect of the medicine is gone. This has been called ‚Äútraveler's amnesia.‚ÄĚ Memory problems are not common while taking Sonata. In most instances memory problems can be avoided if you take Sonata only when you are able to get 4 or more hours of sleep before you need to be active again. Be sure to talk to your doctor if you think you are having memory problems.
Tolerance
When sleep medicines are used every night for more than a few weeks, they may lose their effectiveness to help you sleep. This is known as ‚Äútolerance.‚ÄĚ Development of tolerance to Sonata has not been observed in outpatient clinical studies of up to 4 weeks in duration; however, it is unknown if the benefits of Sonata in falling asleep more quickly persist beyond 4 weeks. Sleep medicines should, in most cases, be used only for short periods of time, such as 1 or 2 days and generally no longer than 1 or 2 weeks. If your sleep problems continue, consult your doctor, who will determine whether other measures are needed to overcome your sleep problems.
Dependence
Sleep medicines can cause dependence, especially when these medicines are used regularly for longer than a few weeks or at high doses. Some people develop a need to continue taking their medicines. This is known as dependence or ‚Äúaddiction.‚ÄĚ
When people develop dependence, they may have difficulty stopping the sleep medicine. If the medicine is suddenly stopped, the body is not able to function normally and unpleasant symptoms (see Withdrawal ) may occur. They may find they have to keep taking the medicine either at the prescribed dose or at increasing doses just to avoid withdrawal symptoms.
All people taking sleep medicines have some risk of becoming dependent on the medicine. However, people who have been dependent on alcohol or other drugs in the past may have a higher chance of becoming addicted to sleep medicines. This possibility must be considered before using these medicines for more than a few weeks. If you have been addicted to alcohol or drugs in the past, it is important to tell your doctor before starting Sonata or any sleep medicine.
Withdrawal
Withdrawal symptoms may occur when sleep medicines are stopped suddenly after being used daily for a long time. In some cases, these symptoms can occur even if the medicine has been used for only a week or two. In mild cases, withdrawal symptoms may include unpleasant feelings. In more severe cases, abdominal and muscle cramps, vomiting, sweating, shakiness, and rarely, seizures may occur. These more severe withdrawal symptoms are very uncommon. Although withdrawal symptoms have not been observed in the relatively limited controlled trials experience with Sonata, there is, nevertheless, the risk of such events in association with the use of any sleep medicines.
Another problem that may occur when sleep medicines are stopped is known as ‚Äúrebound insomnia.‚ÄĚ This means that a person may have more trouble sleeping the first few nights after the medicine is stopped than before starting the medicine. If you should experience rebound insomnia, do not get discouraged. This problem usually goes away on its own after 1 or 2 nights.
If you have been taking Sonata or any other sleep medicine for more than 1 or 2 weeks, do not stop taking it on your own. Always follow your doctor's directions.
Changes In Behavior and Thinking
Some people using sleep medicines have experienced unusual changes in their thinking and/or behavior. These effects are not common. However, they have included:
- more outgoing or aggressive behavior than normal - loss of personal identity - confusion - strange behavior - agitation - hallucinations - worsening of depression - suicidal thoughts
How often these effects occur depends on several factors, such as a person's general health, the use of other medicines, and which sleep medicine is being used. Clinical experience with Sonata (zaleplon) suggests that it is uncommonly associated with these behavior changes.
It is also important to realize that it is rarely clear whether these behavior changes are caused by the medicine, an illness, or occur on their own. In fact, sleep problems that do not improve may be due to illnesses that were present before the medicine was used. If you or your family notice any changes in your behavior, or if you have any unusual or disturbing thoughts, call your doctor immediately.
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
Sleep medicines may cause sedation or other potential effects in the unborn baby when used during the last weeks of pregnancy. Therefore, Sonata is not recommended for use during pregnancy. Be sure to tell your doctor if you are pregnant, if you are planning to become pregnant, or if you become pregnant while taking Sonata.
In addition, a very small amount of Sonata may be present in breast milk after use of the medication. The effects of very small amounts of Sonata on an infant are not known; therefore, as with all other hypnotics, it is recommended that you not take Sonata if you are breastfeeding a baby.
Safe Use of Sleeping Medicines
To ensure the safe and effective use of Sonata or any other sleep medicine, you should observe the following cautions:
- Sonata is a prescription medicine and should be used ONLY as directed by your doctor. Follow your doctor's instructions about how to take, when to take, and how long to take Sonata.
- Never use Sonata or any other sleep medicine for longer than directed by your doctor.
- If you notice any unusual and/or disturbing thoughts or behavior during treatment with Sonata or any other sleep medicine, contact your doctor.
- Tell your doctor about any medicines you may be taking, including medicines you may buy without a prescription. You should also tell your doctor if you drink alcohol. DO NOT use alcohol while taking Sonata or any other sleep medicine.
- Do not take Sonata unless you are able to get 4 or more hours of sleep before you must be active again.
- Do not increase the prescribed dose of Sonata or any other sleep medicine unless instructed by your doctor.
- When you first start taking Sonata or any other sleep medicine, until you know whether the medicine will still have some carryover effect in you the next day, use extreme care while doing anything that requires complete alertness, such as driving a car, operating machinery, or piloting an aircraft.
- Be aware that you may have more sleeping problems the first night or two after stopping any sleep medicine.
- Be sure to tell your doctor if you are pregnant, if you are planning to become pregnant, if you become pregnant, or are breastfeeding a baby while taking Sonata.
- As with all prescription medicines, never share Sonata or any other sleep medicine with anyone else. Always store Sonata or any other sleep medicine in the original container and out of reach of children.
- Be sure to tell your physician if you suffer from depression.
- Sonata works very quickly. You should only take Sonata immediately before going to bed or after you have gone to bed and are having difficulty falling asleep.
- For Sonata to work best, you should not take Sonata with or immediately after a high-fat/heavy meal.
- Some people should start with the lowest dose (5 mg) of Sonata; these include the elderly (ie, ages 65 and over) and people with liver disease.
Prescribing Information as of March 2006.
Distributed by: King Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Bristol, TN 37620Manufactured by: Wyeth Pharmaceuticals Inc., Philadelphia, PA 19101
Principal Display Panel
Sonata (zaleplon) capsules
5 mg

10 mg

DISCLAIMER:
"This tool does not provide medical advice, and is for informational and educational purposes only, and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, treatment or diagnosis. Call your doctor to receive medical advice. If you think you may have a medical emergency, please dial 911."
"Do not rely on openFDA to make decisions regarding medical care. While we make every effort to ensure that data is accurate, you should assume all results are unvalidated. We may limit or otherwise restrict your access to the API in line with our Terms of Service."
"This product uses publicly available data from the U.S. National Library of Medicine (NLM), National Institutes of Health, Department of Health and Human Services; NLM is not responsible for the product and does not endorse or recommend this or any other product."
PillSync may earn a commission via links on our site


