Dexmedetomidine Dailymed
Generic: dexmedetomidine hydrochloride is used for the treatment of Pain Psychomotor Agitation
Go PRO for all pill images
1 Indications And Usage
Dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection is a relatively selective alpha2 -adrenergic agonist indicated for:
- Sedation of non-intubated patients prior to and/or during surgical and other procedures. (
1.2 )1.2 Procedural Sedation
Dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection is indicated for sedation of non-intubated patients prior to and/or during surgical and other procedures.
2 Dosage And Administration
- Individualize and titrate dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection dosing to desired clinical effect. (
2.1 )- Administer dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection using a controlled infusion device. (
2.1 )- Dilute the 200 mcg/2 mL (100 mcg/mL) vial contents in 0.9% sodium chloride solution to achieve required concentration (4 mcg/mL) prior to administration. (
2.4 )
For Adult Procedural Sedation: Generally initiate at one mcg/kg over 10 minutes, followed by a maintenance infusion initiated at 0.6 mcg/kg/hour and titrated to achieve desired clinical effect with doses ranging from 0.2 to 1 mcg/kg/hour. (2.2 )
Alternative doses recommended for patients over 65 years of age and awake fiberoptic intubation patients. (2.2 )
2.1 Dosing Guidelines
- Dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection dosing should be individualized and titrated to desired clinical response.
- Dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection is not indicated for infusions lasting longer than 24 hours.
- Dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection should be administered using a controlled infusion device.
2.2 Dosage Information
Table 1: Dosage Information INDICATION DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Initiation of Procedural Sedation For adult patients: a loading infusion of one mcg/kg over 10 minutes. For less invasive procedures such as ophthalmic surgery, a loading infusion of 0.5 mcg/kg given over 10 minutes may be suitable. For awake fiberoptic intubation in adult patients: a loading infusion of one mcg/kg over 10 minutes. For patients over 65 years of age: a loading infusion of 0.5 mcg/kg over 10 minutes [see Use in Specific Populations (8.5)]. For adult patients with impaired hepatic function: a dose reduction should be considered [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Maintenance of Procedural Sedation For adult patients: the maintenance infusion is generally initiated at 0.6 mcg/kg/hour and titrated to achieve desired clinical effect with doses ranging from 0.2 to 1 mcg/kg/hour. The rate of the maintenance infusion should be adjusted to achieve the targeted level of sedation. For awake fiberoptic intubation in adult patients: a maintenance infusion of 0.7 mcg/kg/hour is recommended until the endotracheal tube is secured. For patients over 65 years of age: a dose reduction should be considered [see Use in Specific Populations (8.5)]. For adult patients with impaired hepatic function: a dose reduction should be considered [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. 2.3 Dosage Adjustment
].
Due to possible pharmacodynamic interactions, a reduction in dosage of dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection or other concomitant anesthetics, sedatives, hypnotics or opioids may be required when co-administered [see Drug Interactions (7.1)
Dosage reductions may need to be considered for adult patients with hepatic impairment, and geriatric patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7), Use in Specific Populations (8.6), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
2.4 Preparation of Solution
Strict aseptic technique must always be maintained during handling of dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection.
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit.
Dexmedetomidine Hydrochloride Injection, 200 mcg/2 mL (100 mcg/mL)
Dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection must be diluted with 0.9% sodium chloride injection to achieve required concentration (4 mcg/mL) prior to administration. Preparation of solutions is the same, whether for the loading dose or maintenance infusion.
To prepare the infusion, withdraw 2 mL of dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection and add to 48 mL of 0.9% sodium chloride injection to a total of 50 mL. Shake gently to mix well.
2.5 Administration with Other Fluids
Dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection infusion should not be co-administered through the same intravenous catheter with blood or plasma because physical compatibility has not been established.
Dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection has been shown to be incompatible when administered with the following drugs: amphotericin B, diazepam.
Dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection has been shown to be compatible when administered with the following intravenous fluids:
- 0.9% sodium chloride in water
- 5% dextrose in water
- 20% mannitol
- Lactated Ringer's solution
- 100 mg/mL magnesium sulfate solution
- 0.3% potassium chloride solution
2.6 Compatibility with Natural Rubber
Compatibility studies have demonstrated the potential for absorption of dexmedetomidine hydrochloride to some types of natural rubber. Although dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection is dosed to effect, it is advisable to use administration components made with synthetic or coated natural rubber gaskets.
3 Dosage Forms And Strengths
Dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection, 200 mcg/2 mL dexmedetomidine (100 mcg/mL) in a glass vial. To be used after dilution.
Dexmedetomidine Hydrochloride Injection, 200 mcg/2 mL (100 mcg/mL) in a glass vial. To be used after dilution. (3 )
4 Contraindications
None
None (4 )
5 Warnings And Precautions
- Monitoring: Continuously monitor patients while receiving dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection. (
5.1 )- Bradycardia and sinus arrest: Have occurred in young healthy volunteers with high vagal tone or with different routes of administration, e.g., rapid intravenous or bolus administration. (
5.2 )- Hypotension and bradycardia: May necessitate medical intervention. May be more pronounced in patients with hypovolemia, diabetes mellitus, or chronic hypertension, and in the elderly. Use with caution in patients with advanced heart block or severe ventricular dysfunction. (
5.2 )- Co-administration with other vasodilators or negative chronotropic agents: Use with caution due to additive pharmacodynamic effects. (
5.2 )- Transient hypertension: Observed primarily during the loading dose. Consider reduction in loading infusion rate. (
5.3 )- Arousability: Patients can become aroused/alert with stimulation; this alone should not be considered as lack of efficacy. (
5.4 )- Prolonged exposure to dexmedetomidine beyond 24 hours may be associated with tolerance and tachyphylaxis and a dose-related increase in adverse events. (
5.6 )5.1 Drug Administration
Dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection should be administered only by persons skilled in the management of patients in the operating room setting. Due to the known pharmacological effects of dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection, patients should be continuously monitored while receiving dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection.
5.2 Hypotension, Bradycardia, and Sinus Arrest
Clinically significant episodes of bradycardia and sinus arrest have been reported with dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection administration in young, healthy adult volunteers with high vagal tone or with different routes of administration including rapid intravenous or bolus administration.
Reports of hypotension and bradycardia have been associated with dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection infusion. Some of these cases have resulted in fatalities. If medical intervention is required, treatment may include decreasing or stopping the infusion of dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection, increasing the rate of intravenous fluid administration, elevation of the lower extremities, and use of pressor agents. Because dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection has the potential to augment bradycardia induced by vagal stimuli, clinicians should be prepared to intervene. The intravenous administration of anticholinergic agents (e.g., glycopyrrolate, atropine) should be considered to modify vagal tone. In clinical trials, glycopyrrolate or atropine were effective in the treatment of most episodes of dexmedetomidine hydrochloride-induced bradycardia. However, in some patients with significant cardiovascular dysfunction, more advanced resuscitative measures were required.
Caution should be exercised when administering dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection to patients with advanced heart block and/or severe ventricular dysfunction. Because dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection decreases sympathetic nervous system activity, hypotension and/or bradycardia may be expected to be more pronounced in patients with hypovolemia, diabetes mellitus, or chronic hypertension and in elderly patients.
In clinical trials where other vasodilators or negative chronotropic agents were co-administered with dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection an additive pharmacodynamic effect was not observed. Nonetheless, caution should be used when such agents are administered concomitantly with dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection.
5.3 Transient Hypertension
Transient hypertension has been observed primarily during the loading dose in association with the initial peripheral vasoconstrictive effects of dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection. Treatment of the transient hypertension has generally not been necessary, although reduction of the loading infusion rate may be desirable.
5.4 Arousability
Some patients receiving dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection have been observed to be arousable and alert when stimulated. This alone should not be considered as evidence of lack of efficacy in the absence of other clinical signs and symptoms.
5.5 Withdrawal
Procedural Sedation
In adult subjects, withdrawal symptoms were not seen after discontinuation of short term infusions of dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection (< 6 hours).
5.6 Tolerance and Tachyphylaxis
Use of dexmedetomidine beyond 24 hours has been associated with tolerance and tachyphylaxis and a dose related increase in adverse reactions [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
5.7 Hepatic Impairment
Since dexmedetomidine clearance decreases with severity of hepatic impairment, dose reduction should be considered in patients with impaired hepatic function [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
6 Adverse Reactions
- The most common adverse reactions (incidence greater than 2%) are hypotension, bradycardia, and dry mouth. (
6.1 )
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Akorn Operating Company LLC at 1-800-932-5676 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
6.1 Clinical Studies Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reactions rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Use of dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection has been associated with the following serious adverse reactions:
- Hypotension, bradycardia and sinus arrest [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Transient hypertension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
Most common treatment-emergent adverse reactions, occurring in greater than 2% of patients in procedural sedation studies include hypotension, bradycardia and dry mouth.
Procedural Sedation
Adverse reaction information is derived from the two trials for procedural sedation [see Clinical Studies (14.2)] in which 318 adult patients received dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection. The mean total dose was 1.6 mcg/kg (range: 0.5 to 6.7), mean dose per hour was 1.3 mcg/kg/hr (range: 0.3 to 6.1) and the mean duration of infusion of 1.5 hours (range: 0.1 to 6.2). The population was between 18 to 93 years of age, ASA I-IV, 30% ≥ 65 years of age, 52% male and 61% Caucasian.
Treatment-emergent adverse reactions occurring at an incidence of > 2% are provided in Table 6. The most frequent adverse reactions were hypotension, bradycardia, and dry mouth [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. Pre-specified criteria for the vital signs to be reported as adverse reactions are footnoted below the table. The decrease in respiratory rate and hypoxia was similar between dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection and comparator groups in both studies.
Table 6: Adverse Reactions With an Incidence > 2% - Procedural Sedation Population * Hypotension was defined in absolute and relative terms as Systolic blood pressure of
< 80 mmHg or ≤ 30% lower than pre-study drug infusion value, or Diastolic blood pressure of < 50 mmHg.
† Respiratory depression was defined in absolute and relative terms as respiratory rate (RR)
< 8 beats per minute or > 25% decrease from baseline.
‡ Bradycardia was defined in absolute and relative terms as < 40 beats per minute or
≤ 30% lower than pre-study drug infusion value.
§ Hypertension was defined in absolute and relative terms as Systolic blood pressure
> 180 mmHg or ≥ 30% higher than pre-study drug infusion value or Diastolic blood pressure of > 100 mmHg.
¶ Tachycardia was defined in absolute and relative terms as > 120 beats per minute or
≥ 30% greater than pre-study drug infusion value.
# Hypoxia was defined in absolute and relative terms as SpO2 C 90% or 10% decrease from baseline.
Adverse Event Dexmedetomidine Hydrochloride Injection N = 318 (%) Placebo N = 113 (%) Hypotension* 54% 30% Respiratory Depression† 37% 32% Bradycardia‡ 14% 4% Hypertension§ 13% 24% Tachycardia¶ 5% 17% Nausea 3% 2% Dry Mouth 3% 1% Hypoxia# 2% 3% Bradypnea 2% 4% 6.2 Post-Marketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post approval use of dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Hypotension and bradycardia were the most common adverse reactions associated with the use of dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection during post approval use of the drug.
Table 7: Adverse Reactions Experienced During Post-approval Use of Dexmedetomidine Hydrochloride Injection System Organ Class Preferred Term Blood and Lymphatic System Disorders Anemia Cardiac Disorders Arrhythmia, atrial fibrillation, atrioventricular block, bradycardia, cardiac arrest, cardiac disorder, extrasystoles, myocardial infarction, supraventricular tachycardia, tachycardia, ventricular arrhythmia, ventricular tachycardia Eye Disorders Photopsia, visual impairment Gastrointestinal Disorders Abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions Chills, hyperpyrexia, pain, pyrexia, thirst Hepatobiliary Disorders Hepatic function abnormal, hyperbilirubinemia Investigations Alanine aminotransferase increased, aspartate aminotransferase increased, blood alkaline phosphatase increased, blood urea increased, electrocardiogram T wave inversion, gammaglutamyltransferase increased, electrocardiogram QT prolonged Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders Acidosis, hyperkalemia, hypoglycemia, hypovolemia, hypernatremia Nervous System Disorders Convulsion, dizziness, headache, neuralgia, neuritis, speech disorder Psychiatric Disorders Agitation, confusional state, delirium, hallucination, illusion Renal and Urinary Disorders Oliguria, polyuria Respiratory, Thoracic and Mediastinal Disorders Apnea, bronchospasm, dyspnea, hypercapnia, hypoventilation, hypoxia, pulmonary congestion, respiratory acidosis Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders Hyperhidrosis Surgical and Medical Procedures Light anesthesia Vascular Disorders Blood pressure fluctuation, hemorrhage, hypertension, hypotension
7 Drug Interactions
Anesthetics, sedatives, hypnotics, opioids: Enhancement of pharmacodynamic effects. Reduction in dosage of dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection or the concomitant medication may be required. (7.1 )
7.1 Anesthetics, Sedatives, Hypnotics, Opioids
Co-administration of dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection with anesthetics, sedatives, hypnotics, and opioids is likely to lead to an enhancement of effects. Specific studies have confirmed these effects with sevoflurane, isoflurane, propofol, alfentanil, and midazolam. No pharmacokinetic interactions between dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection and isoflurane, propofol, alfentanil and midazolam have been demonstrated. However, due to possible pharmacodynamic interactions, when co-administered with dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection, a reduction in dosage of dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection or the concomitant anesthetic, sedative, hypnotic or opioid may be required.
7.2 Neuromuscular Blockers
In one study of ten healthy adult volunteers, administration of dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection for 45 minutes at a plasma concentration of one ng/mL resulted in no clinically meaningful increases in the magnitude of neuromuscular blockade associated with rocuronium administration.
8 Use In Specific Populations
- Geriatric patients: Dose reduction should be considered. (
2.2 ,2.3 ,5.1 ,8.5 )- Hepatic impairment: Dose reduction should be considered. (
2.1 ,2.2 ,2.3 ,5.7 ,8.6 )- Pregnancy: Based on animal data, may cause fetal harm. (
8.1 )- Nursing Mothers: Caution should be exercised when administered to a nursing woman. (
8.3 )8.1 Pregnancy
TERATOGENIC EFFECTS SECTION
Teratogenic Effects. Pregnancy Category C
There are no adequate and well controlled studies of dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection use in pregnant women. In an in vitro human placenta study, placental transfer of dexmedetomidine occurred. In a study in the pregnant rat, placental transfer of dexmedetomidine was observed when radiolabeled dexmedetomidine was administered subcutaneously. Thus, fetal exposure should be expected in humans, and dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefits justify the potential risk to the fetus.
Teratogenic effects were not observed in rats following subcutaneous administration of dexmedetomidine during the period of fetal organogenesis (from gestation day 5 to 16) with doses up to 200 mcg/kg (representing a dose approximately equal to the maximum recommended human intravenous dose based on body surface area) or in rabbits following intravenous administration of dexmedetomidine during the period of fetal organogenesis (from gestation day 6 to 18) with doses up to 96 mcg/kg (representing approximately half the human exposure at the maximum recommended dose based on plasma area under the time-curve comparison). However, fetal toxicity, as evidenced by increased post-implantation losses and reduced live pups, was observed in rats at a subcutaneous dose of 200 mcg/kg. The no-effect dose in rats was 20 mcg/kg (representing a dose less than the maximum recommended human intravenous dose based on a body surface area comparison). In another reproductive toxicity study when dexmedetomidine was administered subcutaneously to pregnant rats at 8 and 32 mcg/kg (representing a dose less than the maximum recommended human intravenous dose based on a body surface area comparison) from gestation day 16 through weaning, lower offspring weights were observed. Additionally, when offspring of the 32 mcg/kg group were allowed to mate, elevated fetal and embryocidal toxicity and delayed motor development was observed in second generation offspring.
8.2 Labor and Delivery
The safety of dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection during labor and delivery has not been studied.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether dexmedetomidine hydrochloride is excreted in human milk. Radio-labeled dexmedetomidine administered subcutaneously to lactating female rats was excreted in milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection is administered to a nursing woman.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and efficacy have not been established for Procedural Sedation in pediatric patients. Additional information describing clinical studies in a different indication in which efficacy was not demonstrated in pediatric patients is approved for Hospira's dexmedetomidine injection. However, due to Hospira's marketing exclusivity rights, this drug product is not labeled with that pediatric information. The use of dexmedetomidine for procedural sedation in pediatric patients has not been evaluated.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Procedural Sedation
A total of 131 patients in the clinical studies were 65 years of age and over. A total of 47 patients were 75 years of age and over. Hypotension occurred in a higher incidence in dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection-treated patients 65 years or older (72%) and 75 years or older (74%) as compared to patients < 65 years (47%). A reduced loading dose of 0.5 mcg/kg given over 10 minutes is recommended and a reduction in the maintenance infusion should be considered for patients greater than 65 years of age.
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
Since dexmedetomidine clearance decreases with increasing severity of hepatic impairment, dose reduction should be considered in patients with impaired hepatic function [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
9 Drug Abuse And Dependence
9.1 Controlled Substance
Dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection (dexmedetomidine hydrochloride) is not a controlled substance.
9.3 Dependence
The dependence potential of dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection has not been studied in humans. However, since studies in rodents and primates have demonstrated that dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection exhibits pharmacologic actions similar to those of clonidine, it is possible that dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection may produce a clonidine-like withdrawal syndrome upon abrupt discontinuation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
10 Overdosage
The tolerability of dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection was studied in one study in which healthy adult subjects were administered doses at and above the recommended dose of 0.2 to 0.7 mcg/kg/hr. The maximum blood concentration achieved in this study was approximately 13 times the upper boundary of the therapeutic range. The most notable effects observed in two subjects who achieved the highest doses were first degree atrioventricular block and second degree heart block. No hemodynamic compromise was noted with the atrioventricular block and the heart block resolved spontaneously within one minute.
One patient who received a loading bolus dose of undiluted dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection (19.4 mcg/kg), had cardiac arrest from which he was successfully resuscitated.
11 Description
Dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection is a sterile, nonpyrogenic solution suitable for intravenous infusion following dilution. Dexmedetomidine hydrochloride is the S-enantiomer of medetomidine and is chemically described as (+)-4-(S)-[1-(2,3-dimethylphenyl)ethyl]-1H-imidazole monohydrochloride. Dexmedetomidine hydrochloride has a molecular weight of 236.7 and the empirical formula is C13H16N2• HCl and the structural formula is:
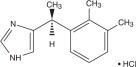
Dexmedetomidine hydrochloride is a white or almost white powder that is freely soluble in water and has a pKa of 7.1. Its partition coefficient in-octanol: water at pH 7.4 is 2.89. Dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection is supplied as a clear, colorless, isotonic solution with a pH of 4.5 to 7.0. Each mL contains 118 mcg of dexmedetomidine hydrochloride equivalent to 100 mcg (0.1 mg) of dexmedetomidine and 9 mg of sodium chloride in water for injection and is to be used after dilution. The solution is preservative-free and contains no additives or chemical stabilizers.
12 Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection is a relatively selective alpha2-adrenergic agonist with sedative properties. Alpha2 selectivity is observed in animals following slow intravenous infusion of low and medium doses (10 to 300 mcg/kg). Both alpha1 and alpha2 activity is observed following slow intravenous infusion of high doses (≥ 1000 mcg/kg) or with rapid intravenous administration.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
In a study in healthy volunteers (N = 10), respiratory rate and oxygen saturation remained within normal limits and there was no evidence of respiratory depression when dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection was administered by intravenous infusion at doses within the recommended dose range (0.2 to 0.7 mcg/kg/hr).
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Following intravenous administration, dexmedetomidine exhibits the following pharmacokinetic parameters: a rapid distribution phase with a distribution half-life (t1/2) of approximately 6 minutes; a terminal elimination half-life (t1/2) of approximately 2 hours; and steady-state volume of distribution (Vss) of approximately 118 liters. Clearance is estimated to be approximately 39 L/h. The mean body weight associated with this clearance estimate was 72 kg.
Dexmedetomidine exhibits linear pharmacokinetics in the dosage range of 0.2 to 0.7 mcg/kg/hr when administered by intravenous infusion for up to 24 hours. Table 8 shows the main pharmacokinetic parameters when dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection was infused (after appropriate loading doses) at maintenance infusion rates of 0.17 mcg/kg/hr (target plasma concentration of 0.3 ng/mL) for 12 and 24 hours, 0.33 mcg/kg/hr (target plasma concentration of 0.6 ng/mL) for 24 hours, and 0.70 mcg/kg/hr (target plasma concentration of 1.25 ng/mL) for 24 hours.
Table 8: Mean ± SD Pharmacokinetic Parameters * Presented as harmonic mean and pseudo standard deviation.
† Mean Css = Average steady-state concentration of dexmedetomidine. The mean Css was calculated based on post-dose sampling from 2.5 to 9 hours samples for 12 hour infusion and post-dose sampling from 2.5 to 18 hours for 24 hour infusions.
Parameter Loading Infusion (min)/Total Infusion Duration (hrs) 10 min/12 hrs 10 min/24 hrs 10 min/24 hrs 35 min/24 hrs Dexmedetomidine Target Plasma Concentration (ng/mL) and Dose (mcg/kg/hr) 0.3/0.17 0.3/0.17 0.6/0.33 1.25/0.70 t 1/2 *, hour 1.78 ± 0.30 2.22 ± 0.59 2.23 ± 0.21 2.50 ± 0.61 CL, liter/hour 46.3 ± 8.3 43.1 ± 6.5 35.3 ± 6.8 36.5 ± 7.5 V ss , liter 88.7 ± 22.9 102.4 ± 20.3 93.6 ± 17.0 99.6 ± 17.8 Avg C ss † , ng/mL 0.27 ± 0.05 0.27 ± 0.05 0.67 ± 0.10 1.37 ± 0.20
The loading doses for each of the above indicated groups were 0.5, 0.5, 1 and 2.2 mcg/kg, respectively.
Dexmedetomidine pharmacokinetic parameters after dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection maintenance doses of 0.2 to 1.4 mcg/kg/hr for > 24 hours were similar to the PK parameters after dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection maintenance dosing for < 24 hours in other studies. The values for clearance (CL), volume of distribution (V), and t1/2 were 39.4 L/hr, 152 L, and 2.67 hours, respectively.
Distribution
The steady-state volume of distribution (Vss) of dexmedetomidine was approximately 118 liters. Dexmedetomidine protein binding was assessed in the plasma of normal healthy male and female subjects. The average protein binding was 94% and was constant across the different plasma concentrations tested. Protein binding was similar in males and females. The fraction of dexmedetomidine that was bound to plasma proteins was significantly decreased in subjects with hepatic impairment compared to healthy subjects.
The potential for protein binding displacement of dexmedetomidine by fentanyl, ketorolac, theophylline, digoxin and lidocaine was explored in vitro, and negligible changes in the plasma protein binding of dexmedetomidine were observed. The potential for protein binding displacement of phenytoin, warfarin, ibuprofen, propranolol, theophylline and digoxin by dexmedetomidine was explored in vitro and none of these compounds appeared to be significantly displaced by dexmedetomidine.
Metabolism
Dexmedetomidine undergoes almost complete biotransformation with very little unchanged dexmedetomidine excreted in urine and feces. Biotransformation involves both direct glucuronidation as well as cytochrome P450 mediated metabolism. The major metabolic pathways of dexmedetomidine are: direct N-glucuronidation to inactive metabolites; aliphatic hydroxylation (mediated primarily by CYP2A6 with a minor role of CYP1A2, CYP2E1, CYP2D6, and CYP2C19) of dexmedetomidine to generate 3-hydroxy-dexmedetomidine, the glucuronide of 3-hydroxy-dexmedetomidine, and 3-carboxy-dexmedetomidine; and N-methylation of dexmedetomidine to generate 3-hydroxy N-methyl-dexmedetomidine, 3-carboxy N-methyl-dexmedetomidine, and dexmedetomidine-N-methyl O-glucuronide.
Elimination
The terminal elimination half-life (t1/2) of dexmedetomidine is approximately 2 hours and clearance is estimated to be approximately 39 L/h. A mass balance study demonstrated that after nine days an average of 95% of the radioactivity, following intravenous administration of radiolabeled dexmedetomidine, was recovered in the urine and 4% in the feces. No unchanged dexmedetomidine was detected in the urine. Approximately 85% of the radioactivity recovered in the urine was excreted within 24 hours after the infusion. Fractionation of the radioactivity excreted in urine demonstrated that products of N-glucuronidation accounted for approximately 34% of the cumulative urinary excretion. In addition, aliphatic hydroxylation of parent drug to form 3-hydroxy-dexmedetomidine, the glucuronide of 3-hydroxy-dexmedetomidine, and 3-carboxylic acid-dexmedetomidine together represented approximately 14% of the dose in urine. N-methylation of dexmedetomidine to form 3-hydroxy N-methyl dexmedetomidine, 3-carboxy N-methyl dexmedetomidine, and N methyl O glucuronide dexmedetomidine accounted for approximately 18% of the dose in urine. The N Methyl metabolite itself was a minor circulating component and was undetected in urine. Approximately 28% of the urinary metabolites have not been identified.
Gender
There was no observed difference in dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection pharmacokinetics due to gender.
Geriatrics
The pharmacokinetic profile of dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection was not altered by age. There were no differences in the pharmacokinetics of dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection in young (18 to 40 years), middle age (41 to 65 years), and elderly (> 65 years) subjects.
Hepatic Impairment
In subjects with varying degrees of hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class A, B, or C), clearance values for dexmedetomidine were lower than in healthy subjects. The mean clearance values for patients with mild, moderate, and severe hepatic impairment were 74%, 64% and 53% of those observed in the normal healthy subjects, respectively. Mean clearances for free drug were 59%, 51% and 32% of those observed in the normal healthy subjects, respectively.
Although dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection is dosed to effect, it may be necessary to consider dose reduction in subjects with hepatic impairment [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
Renal Impairment
Dexmedetomidine pharmacokinetics (Cmax, Tmax, AUC, t1/2, CL, and Vss) were not significantly different in patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance: < 30 mL/min) compared to healthy subjects.
Drug Interactions
In vitro studies: In vitro studies in human liver microsomes demonstrated no evidence of cytochrome P450 mediated drug interactions that are likely to be of clinical relevance.
13 Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Animal carcinogenicity studies have not been performed with dexmedetomidine.
Dexmedetomidine was not mutagenic in vitro, in either the bacterial reverse mutation assay (E. coli and Salmonella typhimurium) or the mammalian cell forward mutation assay (mouse lymphoma). Dexmedetomidine was clastogenic in the in vitro human lymphocyte chromosome aberration test with, but not without, rat S9 metabolic activation. In contrast, dexmedetomidine was not clastogenic in the in vitro human lymphocyte chromosome aberration test with or without human S9 metabolic activation. Although dexmedetomidine was clastogenic in an in vivo mouse micronucleus test in NMRI mice, there was no evidence of clastogenicity in CD-1 mice.
Fertility in male or female rats was not affected after daily subcutaneous injections of dexmedetomidine at doses up to 54 mcg/kg (less than the maximum recommended human intravenous dose on a mcg/m2 basis) administered from 10 weeks prior to mating in males, and 3 weeks prior to mating and during mating in females.
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
There were no differences in the adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)-stimulated cortisol response in dogs following a single dose of dexmedetomidine compared to saline control. However, after continuous subcutaneous infusions of dexmedetomidine at 3 mcg/kg/hr and 10 mcg/kg/hr for one week in dogs (exposures estimated to be within the clinical range), the ACTH-stimulated cortisol response was diminished by approximately 27% and 40%, respectively, compared to saline-treated control animals indicating a dose-dependent adrenal suppression.
14 Clinical Studies
The safety and efficacy of dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection has been evaluated in two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled multicenter clinical trials in 431 patients.
14.2 Procedural Sedation
The safety and efficacy of dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection for sedation of non-intubated patients prior to and/or during surgical and other procedures was evaluated in two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled multicenter clinical trials. Study 1 evaluated the sedative properties of dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection in patients having a variety of elective surgeries/procedures performed under monitored anesthesia care. Study 2 evaluated dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection in patients undergoing awake fiberoptic intubation prior to a surgical or diagnostic procedure.
In Study 1, the sedative properties of dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection were evaluated by comparing the percent of patients not requiring rescue midazolam to achieve a specified level of sedation using the standardized Observer's Assessment of Alertness/Sedation Scale (see Table 12).
Table 12: Observer's Assessment of Alertness/Sedation Assessment Categories Responsiveness Speech Facial Expression Eyes Composite Score Responds readily to name spoken in normal tone Normal Normal Clear, no ptosis 5 (alert) Lethargic response to name spoken in normal tone Mild slowing or thickening Mild relaxation Glazed or mild ptosis (less than half the eye) 4 Responds only after name is called loudly and/or repeatedly Slurring or prominent slowing Marked relaxation (slack jaw) Glazed and marked ptosis (half the eye or more) 3 Responds only after mild prodding or shaking Few recognizable words — — 2 Does not respond to mild prodding or shaking — — — 1 (deep sleep)
Patients were randomized to receive a loading infusion of either dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection 1 mcg/kg, dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection 0.5 mcg/kg, or placebo (normal saline) given over 10 minutes and followed by a maintenance infusion started at 0.6 mcg/kg/hr. The maintenance infusion of study drug could be titrated from 0.2 mcg/kg/hr to 1 mcg/kg/hr to achieve the targeted sedation score (Observer's Assessment of Alertness/Sedation Scale ≤ 4). Patients were allowed to receive rescue midazolam as needed to achieve and/or maintain an Observer's Assessment of Alertness/Sedation Scale ≤ 4. After achieving the desired level of sedation, a local or regional anesthetic block was performed. Demographic characteristics were similar between the dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection and comparator groups. Efficacy results showed that dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection was more effective than the comparator group when used to sedate non-intubated patients requiring monitored anesthesia care during surgical and other procedures (see Table 13).
In Study 2, the sedative properties of dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection were evaluated by comparing the percent of patients requiring rescue midazolam to achieve or maintain a specified level of sedation using the Ramsay Sedation Scale score ≥ 2 (see Table 9).
Table 9: Ramsay Level of Sedation Scale Clinical Score Level of Sedation Achieved 6 Asleep, no response 5 Asleep, sluggish response to light glabellar tap or loud auditory stimulus 4 Asleep, but with brisk response to light glabellar tap or loud auditory stimulus 3 Patient responds to commands 2 Patient cooperative, oriented, and tranquil 1 Patient anxious, agitated, or restless
Patients were randomized to receive a loading infusion of dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection 1 mcg/kg or placebo (normal saline) given over 10 minutes and followed by a fixed maintenance infusion of 0.7 mcg/kg/hr. After achieving the desired level of sedation, topicalization of the airway occurred. Patients were allowed to receive rescue midazolam as needed to achieve and/or maintain a Ramsay Sedation Scale ≥ 2. Demographic characteristics were similar between the dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection and comparator groups. For efficacy results see Table 13.
Table 13: Key Efficacy Results of Procedural Sedation Studies * Based on ITT population defined as all randomized and treated patients.
† Normal approximation to the binomial with continuity correction.
Study Loading Infusion Treatment Arm Number of Patients Enrolled* % Not Requiring Midazolam Rescue Confidence † Interval on the Difference vs. Placebo Mean (SD) Total Dose (mg) of Rescue Midazolam Required Confidence † Intervals of the Mean Rescue Dose Study 1 Dexmedetomidinehydrochloride injection0.5 mcg/kg 134 40 37 (27, 48) 1.4 (1.7) -2.7(-3.4, -2.0) Dexmedetomidinehydrochloride injection1 mcg/kg 129 54 51 (40, 62) 0.9 (1.5) -3.1(-3.8, -2.5) placebo 63 3 — 4.1 (3.0) — Study 2 Dexmedetomidinehydrochloride injection1 mcg/kg 55 53 39 (20, 57) 1.1 (1.5) -1.8(-2.7, -0.9) placebo 50 14 — 2.9 (3.0) —
16 How Supplied/storage And Handling
Dexmedetomidine Hydrochloride Injection, 200 mcg/2 mL (100 mcg/mL), is a sterile, nonpyrogenic, clear, colorless solution. It is available in a 2 mL clear glass vial. Vials are intended for single use only.
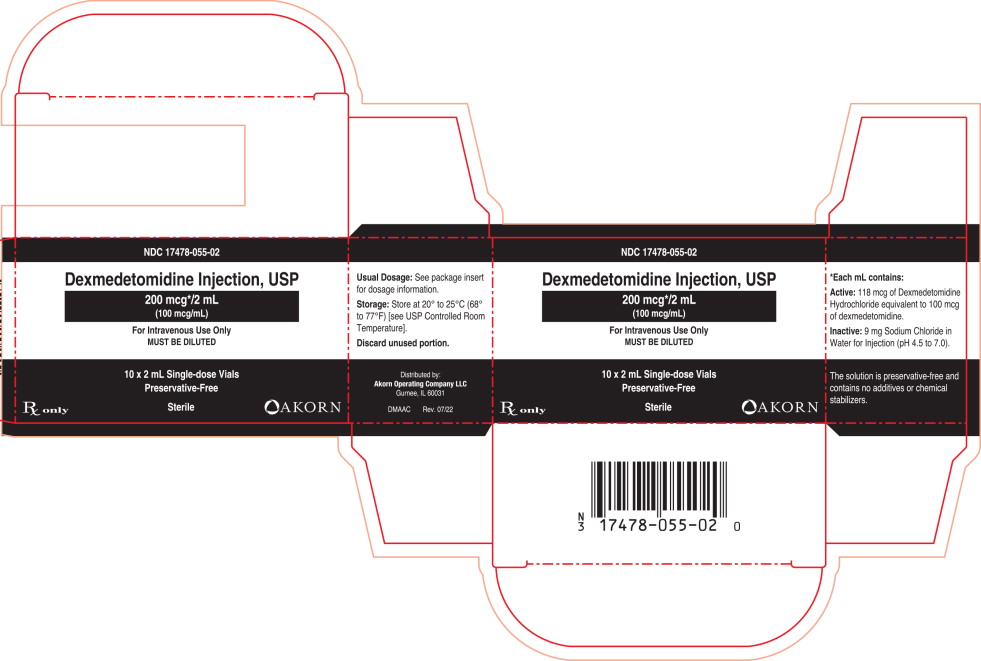
NDC 17478-055-02 2 mL single-dose vial in box of 10
STORAGE AND HANDLING SECTION
Storage: Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Discard unused portion.
17 Patient Counseling Information
Dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection is indicated for short-term intravenous sedation. Dosage must be individualized and titrated to the desired clinical effect. Blood pressure, heart rate and oxygen levels will be monitored both continuously during the infusion of dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection and as clinically appropriate after discontinuation.
- When dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection is infused for more than 6 hours, patients should be informed to report nervousness, agitation, and headaches that may occur for up to 48 hours.
- Additionally, patients should be informed to report symptoms that may occur within 48 hours after the administration of dexmedetomidine hydrochloride injection such as: weakness, confusion, excessive sweating, weight loss, abdominal pain, salt cravings, diarrhea, constipation, dizziness or light-headedness.
AKORNDistributed by: Akorn Operating Company LLC Gurnee, IL 60031DM00N Rev. 07/22
Package Label.principal Display Panel
Principal Display Panel Text for Container Label:
NDC 17478-055-02
Dexmedetomidine
Injection, USP
200 mcg/2 mL
(100 mcg/mL)
Dexmedetomidine
MUST BE DILUTED
For Intravenous Use Only
2 mL Single-dose Vial
Discard unused portion.
Rx only

Package Label.principal Display Panel
Principal Display Panel Text for Carton Label:
NDC 17478-055-02
Dexmedetomidine Injection, USP
200 mcg*/2 mL
(100 mcg/mL)
For Intravenous Use Only
MUST BE DILUTED
10 x 2 mL Single-dose Vials
Preservative-Free
Sterile
Rx only Akorn logo
DISCLAIMER:
"This tool does not provide medical advice, and is for informational and educational purposes only, and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, treatment or diagnosis. Call your doctor to receive medical advice. If you think you may have a medical emergency, please dial 911."
"Do not rely on openFDA to make decisions regarding medical care. While we make every effort to ensure that data is accurate, you should assume all results are unvalidated. We may limit or otherwise restrict your access to the API in line with our Terms of Service."
"This product uses publicly available data from the U.S. National Library of Medicine (NLM), National Institutes of Health, Department of Health and Human Services; NLM is not responsible for the product and does not endorse or recommend this or any other product."
PillSync may earn a commission via links on our site