LULICONAZOLE Dailymed
Generic: luliconazole is used for the treatment of Tinea
Go PRO for all pill images
1 Indications And Usage
Luliconazole Cream, 1% is indicated for the topical treatment of interdigital tinea pedis, tinea cruris, and tinea corporis caused by the organisms Trichophyton rubrum and Epidermophyton floccosum.
Luliconazole Cream, 1% is an azole antifungal indicated for the topical treatment of interdigital tinea pedis, tinea cruris, and tinea corporis caused by the organisms Trichophyton rubrum and Epidermophyton floccosum. (1 )
2 Dosage And Administration
For topical use only. Luliconazole Cream, 1% is not for ophthalmic, oral, or intravaginal use.
- •When treating interdigital tinea pedis, a thin layer of Luliconazole Cream, 1% should be applied to the affected area and approximately 1 inch of the immediate surrounding area(s) once daily for 2 weeks.
- •When treating tinea cruris or tinea corporis, Luliconazole Cream, 1% should be applied to the affected area and approximately 1 inch of the immediate surrounding area(s) once daily for 1 week.
- •For topical use only. Not for ophthalmic, oral, or intravaginal use. (
2 )- •Interdigital Tinea Pedis: Luliconazole Cream, 1% should be applied to the affected and immediate surrounding area(s) once a day for 2 weeks. (
2 )- •Tinea Cruris and Tinea Corporis: Luliconazole Cream, 1% should be applied to the affected skin and immediate surrounding area(s) once a day for 1 week. (
2 )
3 Dosage Forms And Strengths
Cream, 1%. Each gram of Luliconazole Cream, 1% contains 10 mg of luliconazole in a white cream base.
Cream, 1% (3 )
4 Contraindications
None.
None. (4 )
6 Adverse Reactions
The most common adverse reactions observed in clinical trials were application site reactions, which occurred in less than 1% of subjects. (6.1 )
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Oceanside Pharmaceuticals at 1-800-321-4576 or FDA at
- 1-800-FDA-1088 or
www.fda.gov/medwatch. 6.1Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
In three Phase 3 clinical trials, 616 subjects were exposed to Luliconazole Cream, 1%: 305 with interdigital tinea pedis and 311 subjects with tinea cruris. Subjects with interdigital tinea pedis or tinea cruris applied Luliconazole Cream, 1% or vehicle cream once daily for 14 days or 7 days, respectively, to affected and adjacent areas. During clinical trials with Luliconazole Cream, 1%, the most common adverse reactions were application site reactions which occurred in less than 1% of subjects in both the Luliconazole and vehicle arms. Most adverse reactions were mild in severity.
A post-approval clinical trial was conducted in 75 subjects age 2 to <18 years old with tinea corporis. The adverse reactions in the Luliconazole Cream, 1% treated population were similar to the vehicle treated population.
6.2Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during postmarketing use of luliconazole cream, 1%: contact dermatitis and cellulitis. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
7 Drug Interactions
An in vivo study in adult subjects with moderate to severe interdigital tinea pedis and tinea cruris showed that Luliconazole Cream, 1% is mostly a weak inhibitor of CYP2C19. In a separate trial in adolescent subjects with tinea cruris, in vivo blood levels of Luliconazole Cream, 1%, were seen to approach those levels sufficient to show moderate inhibition of CYP2C19 [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8 Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
TERATOGENIC EFFECTS SECTION
Risk Summary
There are no available data with Luliconazole Cream, 1% use in pregnant women to inform a drug-associated risk for major birth defects and miscarriage. In animal reproduction studies with pregnant rats and rabbits, there were no adverse developmental effects observed with subcutaneous administration of luliconazole during organogenesis at doses up to 3 and 24 times, respectively, the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) [see Data].
The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4% and 15 to 20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
The animal multiples of human exposure calculations were based on daily dose body surface area (BSA) comparisons (mg/m2) for the reproductive toxicology studies described in this section and in Section 13.1. The maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) was set at 8 g 1% cream per day (1.33 mg/kg/day for a 60 kg individual, which is equivalent to 49.2 mg/m2/day).
Systemic embryofetal development studies were conducted in rats and rabbits. Subcutaneous doses of 1, 5 and 25 mg/kg/day luliconazole were administered during the period of organogenesis (gestational days 7-17) to pregnant female rats. No treatment-related effects on maternal toxicity or malformations were noted at 25 mg/kg/day (3 times the MRHD based on BSA comparisons). Increased incidences of skeletal variation (14th rib) were noted at 25 mg/kg/day. No treatment-related effects on skeletal variation were noted at 5 mg/kg/day (0.6 times the MRHD based on BSA comparisons).
Subcutaneous doses of 4, 20 and 100 mg/kg/day luliconazole were administered during the period of organogenesis (gestational days 6-18) to pregnant female rabbits. No treatment-related effects on maternal toxicity, embryofetal toxicity or malformations were noted at 100 mg/kg/day (24 times the MRHD based on BSA comparisons).
In a pre- and postnatal development study in rats, subcutaneous doses of 1, 5 and 25 mg/kg/day luliconazole were administered from the beginning of organogenesis (gestation day 7) through the end of lactation (lactation day 20). In the presence of maternal toxicity, embryofetal toxicity (increased prenatal pup mortality, reduced live litter sizes and increased postnatal pup mortality) was noted at 25 mg/kg/day.
No embryofetal toxicity was noted at 5 mg/kg/day (0.6 times the MRHD based on BSA comparisons). No treatment effects on postnatal development were noted at 25 mg/kg/day (3 times the MRHD based on BSA comparisons).
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There is no information available on the presence of luliconazole in human milk, the effects of the drug on the breastfed infant, or the effects of the drug on milk production after topical application of Luliconazole Cream, 1% to women who are breastfeeding. Luliconazole Cream, 1% has low systemic absorption. The lack of clinical data during lactation precludes a clear determination of the risk of Luliconazole Cream, 1% to an infant during lactation. Therefore, the developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for Luliconazole Cream, 1% and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from Luliconazole Cream, 1% or from the underlying maternal condition.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of Luliconazole Cream, 1% in pediatric patients 12 to <18 years of age with tinea pedis and tinea cruris have been established by evidence from well-controlled trials in adult and pediatric subjects and a pharmacokinetic (PK) study in pediatric subjects [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) and Clinical Studies (14)].
The safety and effectiveness of Luliconazole Cream, 1% in pediatric patients 2 to <18 years of age with tinea corporis have been established by evidence from a well-controlled trial in pediatric subjects [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) and Clinical Studies (14)].
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the total number of subjects in clinical studies of Luliconazole Cream, 1%, 8% were 65 and over, while 1.4% were 75 and over. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these subjects and younger subjects, and other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients, but greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out.
11 Description
Luliconazole Cream, 1% contains 1% luliconazole, an azole antifungal agent, in a white cream for topical application.
Luliconazole is (2E)-2-[(4R)-4-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-1,3-dithiolan-2-ylidene]-2-imidazol-1-ylacetonitrile. Its structural formula is:
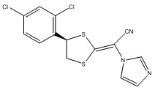
The molecular formula is C14H9Cl2N3S2 with a molecular weight of 354.28. Luliconazole is the R enantiomer and contains one chiral center. The double bond adjacent to the dithiolane group is in the E configuration.
Luliconazole Cream, 1% contains 10 mg of luliconazole per gram of cream in a vehicle consisting of benzyl alcohol, butylated hydroxytoluene, cetostearyl alcohol, isopropyl myristate, medium-chain triglycerides, methylparaben, polysorbate 60, propylene glycol, purified water, and sorbitan monostearate.
12 Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Luliconazole Cream, 1% is an azole antifungal [see Microbiology (12.4)].
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
At therapeutic doses, Luliconazole Cream, 1% is not expected to prolong QTc to any clinically relevant extent.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Luliconazole is the R enantiomer of a chiral molecule. The potential for interconversion between R and S enantiomers in humans has not been assessed. Information on the pharmacokinetics of luliconazole presented below refers to both R enantiomer and S enantiomer, if any, combined.
Luliconazole is >99% protein bound in plasma.
In a PK trial, 12 subjects with moderate to severe tinea pedis and 8 subjects with moderate to severe tinea cruris applied a mean daily amount of approximately 3.5 grams of Luliconazole Cream, 1% to the affected and surrounding areas once daily for 15 days. Plasma concentrations of luliconazole on Day 15 were measurable in all subjects and fluctuated little during the 24-hour interval. In subjects with tinea pedis, the mean ± SD of the maximum concentration (Cmax) was 0.40 ± 0.76 ng/mL after the first dose and 0.93 ± 1.23 ng/mL after the final dose. The mean time to reach Cmax (Tmax) was 16.9 ± 9.39 hours after the first dose and 5.8 ± 7.61 hours after the final dose. Exposure to luliconazole, as expressed by area under the concentration time curve (AUC0–24), was 6.88 ± 14.50 ng*hr/mL after the first dose and 18.74 ± 27.05 ng*hr/mL after the final dose. In subjects with tinea cruris, the mean ± SD Cmax was 4.91 ± 2.51 ng/mL after the first dose and 7.36 ± 2.66 ng/mL after the final dose. The mean Tmax was 21.0 ± 5.55 hours after the first dose and 6.5 ± 8.25 hours after the final dose. Exposure to luliconazole, as expressed by AUC0–24, was 85.1 ± 43.69 ng*hr/mL after the first dose and 121.74 ± 53.36 ng*hr/mL after the final dose.
PK data of luliconazole measured in adolescent subjects (12 to <18 years of age) with moderate to severe interdigital tinea pedis or moderate to severe tinea cruris as well as in subjects 2 to <18 years of age with tinea corporis are described in Specific Populations below.
Specific Populations
PK of luliconazole was assessed in 30 adolescent subjects 12 to <18 years of age with moderate to severe interdigital tinea pedis (N=15) or moderate to severe tinea cruris (N=15). Subjects with tinea pedis applied approximately 3 grams of Luliconazole Cream, 1% once daily to the affected area and adjacent skin for 15 days, while subjects with tinea cruris applied Luliconazole Cream, 1% once daily to the affected and adjacent skin for 8 days.
Generally, the systemic exposure of luliconazole was greater in the subjects with tinea cruris than tinea pedis. In subjects with tinea pedis, the systemic concentrations of luliconazole were quantifiable in all the subjects on Day 8 and Day 15. The mean ± SD Cmax was 1.80 ± 1.86 ng/mL after the first dose on Day 1, and 3.93 ± 1.67 ng/mL and 3.27 ± 1.71 ng/mL on Days 8 and 15, respectively. The mean ± SD AUC0-24 was 20.47 ± 14.47 ng*hr/mL after the first dose on Day 1, and 64.94 ± 32.47 ng*hr/mL and 60.38 ± 37.92 ng*hr/mL on Days 8 and Day 15, respectively. Like in adult subjects, the mean plasma concentrations of luliconazole in adolescent subjects on Days 8 and 15 were similar and fluctuated little during a 24-hour interval.
In subjects with moderate to severe tinea cruris, the systemic concentrations of luliconazole were quantifiable in all the subjects on Day 8. The mean ± SD Cmax was 9.80 ± 5.94 ng/mL after the first dose (Day 1) and 15.40 ± 13.62 ng/mL after the last dose (Day 8). The mean ± SD AUC0-24 was 157.07 ± 92.18 ng*hr/mL and 266.06 ± 236.07 ng*hr/mL, after the first dose (Day 1) and the last dose (Day 8).
In subjects with tinea corporis, the systemic concentrations of luliconazole were assessed at pre-dose and at 6 hours post-dose on the last day of treatment following once daily treatment with Luliconazole Cream, 1% for 7 days. The systemic concentrations were quantifiable in all the 12 subjects and the mean ± SD daily dose of Luliconazole Cream, 1% was 2.84 ± 1.82 g. The mean ± SD concentrations of luliconazole at 15 minutes prior to dosing and at 6 hours post-dose on Day 7 were 4.63 ± 2.93 ng/mL and 4.84 ± 3.33 ng/mL, respectively.
Drug Interactions
Results of in vitro studies indicated that therapeutic doses of Luliconazole Cream, 1% did not inhibit cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzymes 1A2, 2C9 and 2D6, but can inhibit the activity of CYP2B6, 2C8, 2C19, and 3A4. The most sensitive enzyme, CYP2C19, was further evaluated in an in vivo study using omeprazole as a probe substrate in adult subjects with moderate to severe interdigital tinea pedis and tinea cruris. The results showed that Luliconazole Cream, 1% applied at a daily amount of approximately 4 grams increased the omeprazole systemic exposure (AUC) by approximately 30% compared to the exposure of omeprazole administered alone. Luliconazole Cream, 1% is considered a weak inhibitor of CYP2C19.
For tinea cruris, extrapolation from both in vitro inhibition studies and in vivo data in adults to the adolescent subjects showed that in some subjects, levels of luliconazole can approach or exceed those required to be a moderate inhibitor of CYP2C19.
Results of in vitro studies indicated that therapeutic doses of Luliconazole Cream, 1% did not induce CYP1A2, 2B6, and 3A4.
12.4 Microbiology
Luliconazole is an antifungal that belongs to the azole class. Although the exact mechanism of action against dermatophytes is unknown, luliconazole appears to inhibit ergosterol synthesis by inhibiting the enzyme lanosterol demethylase. Inhibition of this enzyme’s activity by azoles results in decreased amounts of ergosterol, a constituent of fungal cell membranes, and a corresponding accumulation of lanosterol.
To date, a mechanism of resistance to luliconazole has not been described.
Luliconazole Cream, 1% has been shown to be active against most isolates of the following fungi, both in vitro and in clinical infections as described in the INDICATIONS AND USAGE section:
- Trichophyton rubrum
- Epidermophyton floccosum
13 Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Long-term studies to evaluate the carcinogenic potential of Luliconazole Cream, 1% have not been conducted.
Luliconazole revealed no evidence of mutagenic or clastogenic potential based on the results of two in vitro genotoxicity tests (Ames assay and Chinese hamster lung cell chromosomal aberration assay) and one in vivo genotoxicity test (mouse bone marrow micronucleus test).
In a fertility study in rats, subcutaneous doses of 1, 5 and 25 mg/kg/day luliconazole were administered prior to and during mating and through early pregnancy. Treatment-related effects on reproductive function were noted in females (decreased live embryos and decreased corpus luteum) at 5 and 25 mg/kg/day and males (decreased sperm counts) at 25 mg/kg/day. No treatment-related effects on fertility or reproductive function were noted at 1 mg/kg/day (0.1× MRHD based on BSA comparisons).
14 Clinical Studies
14.1Interdigital Tinea Pedis
The safety and efficacy of Luliconazole Cream, 1% was evaluated in two randomized, double-blind, vehicle-controlled, multi-center clinical trials in 423 subjects with a clinical and culture-confirmed diagnosis of interdigital tinea pedis. Subjects were randomized to receive Luliconazole Cream, 1% or vehicle. Subjects applied either Luliconazole Cream, 1% or vehicle cream to the entire area of the forefeet including all interdigital web spaces and approximately 2.5 cm (1 in) of the surrounding area of the foot once daily for 14 days.
The mean age of the study population was 41 years (range 13 to 78 years); 82% were male; 53% were White and 40% were Black or African American. Signs and symptoms of tinea pedis (erythema, scaling, and pruritus), KOH exam and dermatophyte culture were assessed at baseline, end-of-treatment (Day 14), 2 and 4 weeks post-treatment.
Overall treatment success was defined as complete clearance (clinical cure and mycological cure) at 4 weeks post-treatment. Luliconazole Cream, 1% demonstrated complete clearance in subjects with interdigital tinea pedis. Treatment outcomes at 4 weeks post-treatment are summarized in Table 1.
Table 1: Efficacy Results at 4 Weeks Post-treatment – Interdigital Tinea Pedis Study 1 Study 2 Luliconazole Cream, 1% N=106 n (%) Vehicle Cream N=103 n (%) Luliconazole Cream, 1% N=107 n (%) Vehicle Cream N=107 n (%)
Complete ClearanceProportion of subjects who achieved both clinical cure and mycological cure
28 (26%)
2 (2%)
15 (14%)
3 (3%)
Effective TreatmentNegative KOH and culture and at most mild erythema and/or scaling and no pruritus
51 (48%)
10 (10%)
35 (33%)
16 (15%)
Clinical CureAbsence of erythema, scaling and pruritus
31 (29%)
8 (8%)
16 (15%)
4 (4%)
Mycological CureNegative KOH and negative fungal culture
66 (62%)
18 (18%)
60 (56%)
29 (27%)
14.2Tinea Cruris
The safety and efficacy of Luliconazole Cream, 1% was evaluated in a randomized, double-blind, vehicle-controlled, multi-center clinical trial in 256 subjects with a clinical and culture-confirmed diagnosis of tinea cruris. Subjects were randomized to receive Luliconazole Cream, 1% or vehicle. Subjects applied either Luliconazole Cream, 1% or vehicle cream to the affected area and approximately 2.5 cm (1 in) of the surrounding area once daily for 7 days.
The mean age of the study population was 40 years (range 14 to 88 years); 83% were male; 58% were White and 34% were Black or African American. Signs and symptoms of tinea cruris (erythema, scaling, and pruritus), positive KOH exam and dermatophyte culture were assessed at baseline, end-of-treatment (Day 7), 2 and 3 weeks post-treatment.
Overall treatment success was defined as complete clearance (clinical cure and mycological cure) at 3 weeks post-treatment. Luliconazole Cream, 1% demonstrated complete clearance in subjects with tinea cruris. Treatment outcomes at 3 weeks post-treatment are summarized in Table 2.
Table 2: Efficacy Results at 3 Weeks Post-treatment - Tinea Cruris Luliconazole Cream, 1% N=165 n (%) Vehicle Cream N=91 n (%)
Complete ClearanceProportion of subjects who achieved both clinical cure and mycological cure
35 (21%)
4 (4%)
Effective TreatmentNegative KOH and culture and at most mild erythema and/or scaling and no pruritus
71 (43%)
17 (19%)
Clinical CureAbsence of erythema, scaling and pruritus
40 (24%)
6 (7%)
Mycological CureNegative KOH and negative fungal culture
129 (78%)
41 (45%)
14.3Tinea Corporis
The safety and efficacy of Luliconazole Cream, 1% was evaluated in a randomized, double-blind, vehicle-controlled, multi-center clinical trial in 75 subjects age 2 to <18 years old with a clinical and culture-confirmed diagnosis of tinea corporis. Subjects were randomized to receive Luliconazole Cream, 1% or vehicle cream. Subjects applied either Luliconazole Cream, 1% or vehicle cream to the affected area and approximately 2.5 cm (1 in) of the surrounding skin once daily for 7 days.
The mean age of the study population was 8 years; 72% were male; 36% were White and 64% were Black or African American. Signs and symptoms of tinea cruris (erythema, scaling, and pruritus), positive KOH exam and dermatophyte culture were assessed at baseline, end-of-treatment (Day 7), 2 and 3 weeks post-treatment.
Treatment outcomes at 3 weeks post-treatment are summarized in Table 3.
Table 3: Efficacy Results at 3 Weeks Post-treatment - Tinea Corporis
Luliconazole Cream, 1%
N=51
n (%)
Vehicle Cream
N=14
n (%)
Complete ClearanceProportion of subjects who achieved both clinical cure and mycological cure
36 (71%)
5 (36%)
Effective TreatmentNegative KOH and culture and at most mild erythema and/or scaling and no pruritus
39 (77%)
8 (57%)
Clinical CureAbsence of erythema, scaling and pruritus
41 (80%)
6 (43%)
Mycological CureNegative KOH and negative fungal culture
41 (80%)
8 (57%)
16 How Supplied/storage And Handling
Luliconazole Cream, 1% is a white cream supplied in tubes as follows:
60 g NDC 68682-850-60
STORAGE AND HANDLING SECTION
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F); excursions permitted from 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
17 Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
- •Inform patients that Luliconazole Cream, 1% is for topical use only. Luliconazole Cream, 1% is not intended for intravaginal or ophthalmic use.
Distributed by: Oceanside Pharmaceuticals, a division ofBausch Health US, LLCBridgewater, NJ 08807 USA
Manufactured by: Bausch Health Companies Inc.Laval, Quebec H7L 4A8, CanadaU.S. Patent Numbers: 8,980,931; 9,012,484; 9,199,977 and 9,453,006
© 2020 Bausch Health Companies Inc. or its affiliates
9616403
Spl Patient Package Insert Section
are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if Luliconazole Cream will harm your unborn baby. are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if Luliconazole Cream passes into your breast milk.
Tell your doctor about all of the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
Use Luliconazole Cream exactly as your doctor tells you to use it.If you have athlete's foot between the toes, apply a thin layer of Luliconazole Cream to the affected skin areas and to about 1 inch of the surrounding skin 1 time a day for 2 weeks. If you have jock itch or ringworm, apply Luliconazole Cream to the affected skin areas and to about 1 inch of the surrounding skin 1 time a day for 1 week. Wash your hands after you apply Luliconazole Cream.Store Luliconazole Cream at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
Keep Luliconazole Cream and all medicines out of the reach of children.
PATIENT INFORMATION Luliconazole Cream, 1%
Important information: Luliconazole Cream is for use on skin only. Do not get Luliconazole Cream near or in your eyes, mouth or vagina.
What is Luliconazole Cream?
Luliconazole Cream is a prescription medicine used on the skin (topical) to treat fungal infections in people with athlete's foot that is between the toes, jock itch, and ringworm.
Before using Luliconazole Cream, tell your doctor about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
• •
How should I use Luliconazole Cream?
• • • •
What are the possible side effects of Luliconazole Cream?
Luliconazole Cream may cause skin reactions at the treatment site. Skin irritation may happen with Luliconazole Cream. Tell your doctor if you have any skin reactions on the areas of your skin treated with Luliconazole Cream.
These are not all the possible side effects of Luliconazole Cream.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store Luliconazole Cream?
•
General information about the safe and effective use of Luliconazole Cream
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those uled in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use Luliconazole Cream for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give Luliconazole Cream to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. You can ask your pharmacist or doctor for information about Luliconazole Cream that is written for health professionals.
What are the ingredients in Luliconazole Cream?
Active ingredient: luliconazole
Inactive ingredients: benzyl alcohol, butylated hydroxytoluene, cetostearyl alcohol, isopropyl myristate, medium-chain triglycerides, methylparaben, polysorbate 60, propylene glycol, purified water, sorbitan monostearate.
Distributed by:
Oceanside Pharmaceuticals, a division of
Bausch Health US, LLC
Bridgewater, NJ 08807 USA
Manufactured by:
Bausch Health Companies Inc.
Laval, Quebec H7L 4A8, Canada
U.S. Patent Numbers: 8,980,931; 9,012,484;
9,199,977 and 9,453,006
© 2020 Bausch Health Companies Inc. or its affiliates
For more information, call 1-800-321-4576.
This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Revised:04/2020
9616403
Click Or Tap Here To Enter Text.
NDC 68682-850-60 Rx only
LULICONAZOLE CREAM 1%
For Topical Use Only Not for ophthalmic, oral, or intravaginal use Keep Out of Reach of Children
Net. Wt. 60 g
OCEANSIDE PHARMACEUTICALS

DISCLAIMER:
"This tool does not provide medical advice, and is for informational and educational purposes only, and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, treatment or diagnosis. Call your doctor to receive medical advice. If you think you may have a medical emergency, please dial 911."
"Do not rely on openFDA to make decisions regarding medical care. While we make every effort to ensure that data is accurate, you should assume all results are unvalidated. We may limit or otherwise restrict your access to the API in line with our Terms of Service."
"This product uses publicly available data from the U.S. National Library of Medicine (NLM), National Institutes of Health, Department of Health and Human Services; NLM is not responsible for the product and does not endorse or recommend this or any other product."
PillSync may earn a commission via links on our site