Midazolam Hydrochloride Dailymed
Generic: midazolam hydrochloride is used for the treatment of Anxiety Disorders Infant, Premature Pregnancy Psychomotor Agitation Status Epilepticus Glaucoma, Angle-Closure
Boxed Warning
Warnings
Boxed Warning
Warnings
Personnel and Equipment for Monitoring and Resuscitation
Risks from Concomitant Use With Opioids
Risk of Respiratory Adverse Events
Individualization of Dosage
Other Adverse Events
Concomitant Use of Central Nervous System Depressants
Debilitation and Comorbid Considerations
Risk of Intra-arterial Injection
Return to Full Cognitive Function
Neonatal Sedation and Withdrawal Syndrome
Pediatric Neurotoxicity
Go PRO for all pill images
Preservative-Free
For intravenous or intramuscular use.
Rx only
Warnings
Personnel and Equipment for Monitoring and Resuscitation
Adults and Pediatrics: Intravenous midazolam has been associated with respiratory depression and respiratory arrest, especially when used for sedation in noncritical care settings. In some cases, where this was not recognized promptly and treated effectively, death or hypoxic encephalopathy has resulted. Intravenous midazolam should be used only in hospital or ambulatory care settings, including physicians' and dental offices, that provide for continuous monitoring of respiratory and cardiac function, e.g., pulse oximetry. Immediate availability of resuscitative drugs and age- and size-appropriate equipment for bag/valve/mask ventilation and intubation, and personnel trained in their use and skilled in airway management should be assured (see WARNINGS ). For deeply sedated pediatric patients, a dedicated individual, other than the practitioner performing the procedure, should monitor the patient throughout the procedure.
Risks From Concomitant Use With Opioids
Concomitant use of benzodiazepines and opioids may result in profound sedation, respiratory depression, coma, and death. Monitor patients for respiratory depression and sedation (see WARNINGS and PRECAUTIONS; Drug Interactions ).
Individualization of Dosage
Midazolam must never be used without individualization of dosage. The initial intravenous dose for sedation in adult patients may be as little as 1 mg, but should not exceed 2.5 mg in a normal healthy adult. Lower doses are necessary for older (over 60 years) or debilitated patients and in patients receiving concomitant narcotics or other central nervous system (CNS) depressants. The initial dose and all subsequent doses should always be titrated slowly; administer over at least 2 minutes and allow an additional 2 or more minutes to fully evaluate the sedative effect. The use of the 1 mg/mL formulation or dilution of the 1 mg/mL or 5 mg/mL formulation is recommended to facilitate slower injection. Doses of sedative medications in pediatric patients must be calculated on a mg/kg basis, and initial doses and all subsequent doses should always be titrated slowly. The initial pediatric dose of midazolam for sedation/anxiolysis/amnesia is age, procedure, and route dependent (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION for complete dosing information).
Neonates: Midazolam should not be administered by rapid injection in the neonatal population. Severe hypotension and seizures have been reported following rapid intravenous administration, particularly with concomitant use of fentanyl (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION for complete information).
Description
Midazolam hydrochloride injection is a water-soluble benzodiazepine available as a sterile, nonpyrogenic parenteral dosage form for intravenous or intramuscular injection. Each mL contains midazolam hydrochloride equivalent to 1 mg or 5 mg midazolam compounded with 0.8% sodium chloride. The pH is adjusted to approximately 3 with hydrochloric acid and, if necessary, sodium hydroxide.
Midazolam is a white to light yellow crystalline compound, insoluble in water. The hydrochloride salt of midazolam, which is formed in situ, is soluble in aqueous solutions. Chemically, midazolam HCl is 8-chloro-6-(2-fluorophenyl)-1-methyl-4H-imidazo[1,5-a][1,4]benzodiazepine hydrochloride. Midazolam hydrochloride has the empirical formula C18H13ClFN3∙HCl, a calculated molecular weight of 362.25 and the following structural formula:

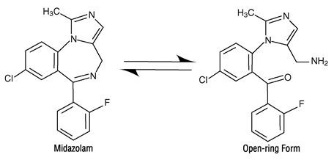
Under the acidic conditions required to solubilize midazolam in the product, midazolam is present as an equilibrium mixture (shown below) of the closed-ring form shown above and an open-ring structure formed by the acid-catalyzed ring opening of the 4,5-double bond of the diazepine ring. The amount of open-ring form is dependent upon the pH of the solution. At the specified pH of the product, the solution may contain up to about 25% of the open-ring compound. At the physiologic conditions under which the product is absorbed (pH of 5 to 8) into the systemic circulation, any open-ring form present reverts to the physiologically active, lipophilic, closed-ring form (midazolam) and is absorbed as such.
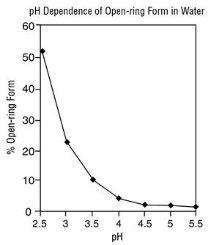
The following chart plots the percentage of midazolam present as the open-ring form as a function of pH in aqueous solutions. As indicated in the graph, the amount of open-ring compound present in solution is sensitive to changes in pH over the pH range specified for the product: 3.0 to 4.0 for the 1 mg/mL concentration and 3.0 to 3.6 for the 5 mg/mL concentration. Above pH 5, at least 99% of the mixture is present in the closed-ring form.
Clinical Pharmacology
Midazolam is a short-acting benzodiazepine central nervous system (CNS) depressant.
Pharmacodynamics:
The effects of midazolam on the CNS are dependent on the dose administered, the route of administration, and the presence or absence of other medications. Onset time of sedative effects after intramuscular administration in adults is 15 minutes, with peak sedation occurring 30 to 60 minutes following injection. In one adult study, when tested the following day, 73% of the patients who received midazolam intramuscularly had no recall of memory cards shown 30 minutes following drug administration; 40% had no recall of the memory cards shown 60 minutes following drug administration. Onset time of sedative effects in the pediatric population begins within 5 minutes and peaks at 15 to 30 minutes depending upon the dose administered. In pediatric patients, up to 85% had no recall of pictures shown after receiving intramuscular midazolam compared with 5% of the placebo controls.
Sedation in adult and pediatric patients is achieved within 3 to 5 minutes after intravenous injection; the time of onset is affected by total dose administered and the concurrent administration of narcotic premedication. Seventy-one percent of the adult patients in endoscopy studies had no recall of introduction of the endoscope; 82% of the patients had no recall of withdrawal of the endoscope. In one study of pediatric patients undergoing lumbar puncture or bone marrow aspiration, 88% of patients had impaired recall vs 9% of the placebo controls. In another pediatric oncology study, 91% of midazolam treated patients were amnestic compared with 35% of patients who had received fentanyl alone.
When midazolam is given intravenous as an anesthetic induction agent, induction of anesthesia occurs in approximately 1.5 minutes when narcotic premedication has been administered and in 2 to 2.5 minutes without narcotic premedication or other sedative premedication. Some impairment in a test of memory was noted in 90% of the patients studied. A dose response study of pediatric patients premedicated with 1 mg/kg intramuscular meperidine found that only 4 out of 6 pediatric patients who received 600 mcg/kg intravenous midazolam lost consciousness, with eye closing at 108 ± 140 seconds. This group was compared with pediatric patients who were given thiopental 5 mg/kg intravenous; 6 out of 6 closed their eyes at 20 ± 3.2 seconds. Midazolam did not dependably induce anesthesia at this dose despite concomitant opioid administration in pediatric patients.
Midazolam, used as directed, does not delay awakening from general anesthesia in adults. Gross tests of recovery after awakening (orientation, ability to stand and walk, suitability for discharge from the recovery room, return to baseline Trieger competency) usually indicate recovery within 2 hours but recovery may take up to 6 hours in some cases. When compared with patients who received thiopental, patients who received midazolam generally recovered at a slightly slower rate. Recovery from anesthesia or sedation for procedures in pediatric patients depends on the dose of midazolam administered, coadministration of other medications causing CNS depression and duration of the procedure.
In patients without intracranial lesions, induction of general anesthesia with intravenous midazolam is associated with a moderate decrease in cerebrospinal fluid pressure (lumbar puncture measurements), similar to that observed following intravenous thiopental. Preliminary data in neurosurgical patients with normal intracranial pressure but decreased compliance (subarachnoid screw measurements) show comparable elevations of intracranial pressure with midazolam and with thiopental during intubation. No similar studies have been reported in pediatric patients.
The usual recommended intramuscular premedicating doses of midazolam do not depress the ventilatory response to carbon dioxide stimulation to a clinically significant extent in adults. Intravenous induction doses of midazolam depress the ventilatory response to carbon dioxide stimulation for 15 minutes or more beyond the duration of ventilatory depression following administration of thiopental in adults. Impairment of ventilatory response to carbon dioxide is more marked in adult patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Sedation with intravenous midazolam does not adversely affect the mechanics of respiration (resistance, static recoil, most lung volume measurements); total lung capacity and peak expiratory flow decrease significantly but static compliance and maximum expiratory flow at 50% of awake total lung capacity (Vmax) increase. In one study of pediatric patients under general anesthesia, intramuscular midazolam (100 mcg/kg or 200 mcg/kg) was shown to depress the response to carbon dioxide in a dose-related manner.
In cardiac hemodynamic studies in adults, intravenous induction of general anesthesia with midazolam was associated with a slight to moderate decrease in mean arterial pressure, cardiac output, stroke volume and systemic vascular resistance. Slow heart rates (less than 65/minute), particularly in patients taking propranolol for angina, tended to rise slightly; faster heart rates (e.g., 85/minute) tended to slow slightly. In pediatric patients, a comparison of intravenous midazolam (500 mcg/kg) with propofol (2.5 mg/kg) revealed a mean 15% decrease in systolic blood pressure in patients who had received intravenous midazolam vs a mean 25% decrease in systolic blood pressure following propofol.
Pharmacokinetics
Midazolam's activity is primarily due to the parent drug. Elimination of the parent drug takes place via hepatic metabolism of midazolam to hydroxylated metabolites that are conjugated and excreted in the urine. Six single-dose pharmacokinetic studies involving healthy adults yield pharmacokinetic parameters for midazolam in the following ranges: volume of distribution (Vd), 1.0 to 3.1 L/kg; elimination half-life, 1.8 to 6.4 hours (mean approximately 3 hours); total clearance (Cl), 0.25 to 0.54 L/hr/kg. In a parallel group study, there was no difference in the clearance, in subjects administered 0.15 mg/kg (n=4) and 0.3 mg/kg (n=4) intravenous doses indicating linear kinetics. The clearance was successively reduced by approximately 30% at doses of 0.45 mg/kg (n=4) and 0.6 mg/kg (n=5) indicating non-linear kinetics in this dose range.
Absorption: The absolute bioavailability of the intramuscular route was greater than 90% in a cross-over study in which healthy subjects (n=17) were administered a 7.5 mg intravenous or intramuscular dose. The mean peak concentration (Cmax) and time to peak (Tmax) following the intramuscular dose was 90 ng/mL (20% CV) and 0.5 hour (50% CV). Cmax for the 1-hydroxy metabolite following the intramuscular dose was 8 ng/mL (Tmax=1.0 hour).
Following intramuscular administration, Cmax for midazolam and its 1-hydroxy metabolite were approximately one-half of those achieved after intravenous injection.
Distribution: The volume of distribution (Vd) determined from six single-dose pharmacokinetic studies involving healthy adults ranged from 1.0 to 3.1 L/kg. Female gender, old age, and obesity are associated with increased values of midazolam Vd. In humans, midazolam has been shown to cross the placenta and enter into fetal circulation and has been detected in human milk and CSF (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY, Special Populations ).
In adults and pediatric patients older than 1 year, midazolam is approximately 97% bound to plasma protein, principally albumin and that for 1-hydroxy metabolite is about 89%.
studies with human liver microsomes indicate that the biotransformation of midazolam is mediated by cytochrome P450-3A4. This cytochrome also appears to be present in gastrointestinal tract mucosa as well as liver. Sixty to seventy percent of the biotransformation products is 1-hydroxy-midazolam (also termed alpha-hydroxy-midazolam) while 4-hydroxy-midazolam constitutes 5% or less. Small amounts of a dihydroxy derivative have also been detected but not quantified. The principal urinary excretion products are glucuronide conjugates of the hydroxylated derivatives.
Metabolism: In vitro
Drugs that inhibit the activity of cytochrome P450-3A4 may inhibit midazolam clearance and elevate steady-state midazolam concentrations.
Studies of the intravenous administration of 1-hydroxy-midazolam in humans suggest that 1-hydroxy-midazolam is at least as potent as the parent compound and may contribute to the net pharmacologic activity of midazolam. In vitro studies have demonstrated that the affinities of 1- and 4-hydroxy-midazolam for the benzodiazepine receptor are approximately 20% and 7%, respectively, relative to midazolam.
Excretion: Clearance of midazolam is reduced in association with old age, congestive heart failure, liver disease (cirrhosis) or conditions which diminish cardiac output and hepatic blood flow.
The principal urinary excretion product is 1-hydroxy-midazolam in the form of a glucuronide conjugate; smaller amounts of the glucuronide conjugates of 4-hydroxy- and dihydroxy-midazolam are detected as well. The amount of midazolam excreted unchanged in the urine after a single intravenous dose is less than 0.5% (n=5). Following a single intravenous infusion in 5 healthy volunteers, 45% to 57% of the dose was excreted in the urine as 1-hydroxymethyl midazolam conjugate.
Pharmacokinetics-Continuous Infusion: The pharmacokinetic profile of midazolam following continuous infusion, based on 282 adult subjects, has been shown to be similar to that following single-dose administration for subjects of comparable age, gender, body habitus and health status. However, midazolam can accumulate in peripheral tissues with continuous infusion. The effects of accumulation are greater after long-term infusions than after short-term infusions. The effects of accumulation can be reduced by maintaining the lowest midazolam infusion rate that produces satisfactory sedation.
Infrequent hypotensive episodes have occurred during continuous infusion; however, neither the time to onset nor the duration of the episode appeared to be related to plasma concentrations of midazolam or alpha-hydroxy-midazolam. Further, there does not appear to be an increased chance of occurrence of a hypotensive episode with increased loading doses.
Patients with renal impairment may have longer elimination half-lives for midazolam (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY, Special Populations, Renal Failure ).
Changes in the pharmacokinetic profile of midazolam due to drug interactions, physiological variables, etc., may result in changes in the plasma concentration-time profile and pharmacological response to midazolam in these patients. For example, patients with acute renal failure appear to have a longer elimination half-life for midazolam and may experience delayed recovery (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY, Special Populations, Renal Failure ). In other groups, the relationship between prolonged half-life and duration of effect has not been established.
Pediatrics and Neonates: In pediatric patients aged 1 year and older, the pharmacokinetic properties following a single dose of midazolam reported in 10 separate studies of midazolam are similar to those in adults. Weight-normalized clearance is similar or higher (0.19 to 0.80 L/hr/kg) than in adults and the terminal elimination half-life (0.78 to 3.3 hours) is similar to or shorter than in adults. The pharmacokinetic properties during and following continuous intravenous infusion in pediatric patients in the operating room as an adjunct to general anesthesia and in the intensive care environment are similar to those in adults.
In seriously ill neonates, however, the terminal elimination half-life of midazolam is substantially prolonged (6.5 to 12.0 hours) and the clearance reduced (0.07 to 0.12 L/hr/kg) compared to healthy adults or other groups of pediatric patients. It cannot be determined if these differences are due to age, immature organ function or metabolic pathways, underlying illness or debility.
Obese: In a study comparing normals (n=20) and obese patients (n=20) the mean half-life was greater in the obese group (5.9 vs 2.3 hours). This was due to an increase of approximately 50% in the Vd corrected for total body weight. The clearance was not significantly different between groups.
Geriatric: In three parallel group studies, the pharmacokinetics of midazolam administered intravenously or intramuscularly were compared in young (mean age 29, n=52) and healthy elderly subjects (mean age 73, n=53). Plasma half-life was approximately two-fold higher in the elderly. The mean Vd based on total body weight increased consistently between 15% to 100% in the elderly. The mean Cl decreased approximately 25% in the elderly in two studies and was similar to that of the younger patients in the other.
Congestive Heart Failure: In patients suffering from congestive heart failure, there appeared to be a two-fold increase in the elimination half-life, a 25% decrease in the plasma clearance and a 40% increase in the volume of distribution of midazolam.
Hepatic Impairment: Midazolam pharmacokinetics were studied after an intravenous single dose (0.075 mg/kg) was administered to 7 patients with biopsy proven alcoholic cirrhosis and 8 control patients. The mean half-life of midazolam increased 2.5-fold in the alcoholic patients. Clearance was reduced by 50% and the Vd increased by 20%. In another study in 21 male patients with cirrhosis, without ascites and with normal kidney function as determined by creatinine clearance, no changes in the pharmacokinetics of midazolam or 1-hydroxy-midazolam were observed when compared to healthy individuals.
Renal Impairment: Patients with renal impairment may have longer elimination half-lives for midazolam and its metabolites which may result in slower recovery.
Midazolam and 1-hydroxy-midazolam pharmacokinetics in 6 ICU patients who developed acute renal failure (ARF) were compared with a normal renal function control group. Midazolam was administered as an infusion (5 to 15 mg/hr). Midazolam clearance was reduced (1.9 vs 2.8 mL/min/kg) and the half-life was prolonged (7.6 vs 13 hours) in the ARF patients. The renal clearance of the 1-hydroxy-midazolam glucuronide was prolonged in the ARF group (4 vs 136 mL/min) and the half-life was prolonged (12 vs >25 hours). Plasma levels accumulated in all ARF patients to about ten times that of the parent drug. The relationship between accumulating metabolite levels and prolonged sedation is unclear.
In a study of chronic renal failure patients (n=15) receiving a single intravenous dose, there was a two-fold increase in the clearance and volume of distribution but the half-life remained unchanged. Metabolite levels were not studied.
Plasma Concentration-Effect Relationship: Concentration-effect relationships (after an intravenous dose) have been demonstrated for a variety of pharmacodynamic measures (eg, reaction time, eye movement, sedation) and are associated with extensive intersubject variability. Logistic regression analysis of sedation scores and steady-state plasma concentration indicated that at plasma concentrations greater than 100 ng/mL there was at least a 50% probability that patients would be sedated, but respond to verbal commands (sedation score=3). At 200 ng/mL there was at least a 50% probability that patients would be asleep, but respond to glabellar tap (sedation score=4).
Drug Interactions: For information concerning pharmacokinetic drug interactions with midazolam (see PRECAUTIONS).
Indications And Usage
Midazolam injection is indicated:
- •
intramuscularly or intravenously for preoperative sedation/anxiolysis/amnesia; - •intravenously as an agent for sedation/anxiolysis/amnesia prior to or during diagnostic, therapeutic or endoscopic procedures, such as bronchoscopy, gastroscopy, cystoscopy, coronary angiography, cardiac catheterization, oncology procedures, radiologic procedures, suture of lacerations and other procedures either alone or in combination with other CNS depressants;
- •intravenously for induction of general anesthesia, before administration of other anesthetic agents. With the use of narcotic premedication, induction of anesthesia can be attained within a relatively narrow dose range and in a short period of time. Intravenous midazolam can also be used as a component of intravenous supplementation of nitrous oxide and oxygen (balanced anesthesia);
- •continuous intravenous infusion for sedation of intubated and mechanically ventilated patients as a component of anesthesia or during treatment in a critical care setting.
Contraindications
Injectable midazolam is contraindicated in patients with a known hypersensitivity to the drug. Benzodiazepines are contraindicated in patients with acute narrow-angle glaucoma. Benzodiazepines may be used in patients with open-angle glaucoma only if they are receiving appropriate therapy. Measurements of intraocular pressure in patients without eye disease show a moderate lowering following induction with midazolam; patients with glaucoma have not been studied.
Warnings
Personnel and Equipment for Monitoring and Resuscitation
Prior to the intravenous administration of midazolam in any dose, the immediate availability of oxygen, resuscitative drugs, age- and size-appropriate equipment for bag/valve/mask ventilation and intubation, and skilled personnel for the maintenance of a patent airway and support of ventilation should be ensured. Patients should be continuously monitored for early signs of hypoventilation, airway obstruction, or apnea, with means readily available (e.g., pulse oximetry). Hypoventilation, airway obstruction, and apnea can lead to hypoxia and/or cardiac arrest unless effective countermeasures are taken immediately. The immediate availability of specific reversal agents (flumazenil) is highly recommended. Vital signs should continue to be monitored during the recovery period. Because intravenous midazolam can depress respiration (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY ), especially when used concomitantly with opioid agonists and other sedatives (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION ), it should be used for sedation/anxiolysis/amnesia only in the presence of personnel skilled in early detection of hypoventilation, maintaining a patent airway and supporting ventilation. When used for sedation/anxiolysis/amnesia, midazolam should always be titrated slowly in adult or pediatric patients. Adverse hemodynamic events have been reported in pediatric patients with cardiovascular instability; rapid intravenous administration should also be avoided in this population (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION for complete information).
Risks from Concomitant Use With Opioids
Concomitant use of benzodiazepines, including midazolam, and opioids may result in profound sedation, respiratory depression, coma, and death. If a decision is made to use midazolam concomitantly with opioids, monitor patients closely for respiratory depression and sedation (see PRECAUTIONS; Drug Interactions ).
Risk of Respiratory Adverse Events
Serious cardiorespiratory adverse events have occurred after administration of midazolam. These have included respiratory depression, airway obstruction, oxygen desaturation, apnea, respiratory arrest and/or cardiac arrest, sometimes resulting in death or permanent neurologic injury. There have also been rare reports of hypotensive episodes requiring treatment during or after diagnostic or surgical manipulations particularly in adult or pediatric patients with hemodynamic instability. Hypotension occurred more frequently in the sedation studies in patients premedicated with a narcotic.
Individualization of Dosage
Midazolam must never be used without individualization of dosage particularly when used with other medications capable of producing central nervous system depression.
See DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION for complete information.
Other Adverse Events
Reactions such as agitation, involuntary movements (including tonic/clonic movements and muscle tremor), hyperactivity and combativeness have been reported in both adult and pediatric patients. These reactions may be due to inadequate or excessive dosing or improper administration of midazolam; however, consideration should be given to the possibility of cerebral hypoxia or true paradoxical reactions. Should such reactions occur, the response to each dose of midazolam and all other drugs, including local anesthetics, should be evaluated before proceeding. Reversal of such responses with flumazenil has been reported in pediatric patients.
Concomitant Use of Central Nervous System Depressants
Concomitant use of barbiturates, alcohol or other central nervous system depressants may increase the risk of hypoventilation, airway obstruction, desaturation, or apnea and may contribute to profound and/or prolonged drug effect. Narcotic premedication also depresses the ventilatory response to carbon dioxide stimulation.
Debilitation and Comorbid Considerations
Higher risk adult and pediatric surgical patients, elderly patients and debilitated adult and pediatric patients require lower dosages, whether or not concomitant sedating medications have been administered. Adult or pediatric patients with COPD are unusually sensitive to the respiratory depressant effect of midazolam. Pediatric and adult patients undergoing procedures involving the upper airway such as upper endoscopy or dental care, are particularly vulnerable to episodes of desaturation and hypoventilation due to partial airway obstruction. Adult and pediatric patients with chronic renal failure and patients with congestive heart failure eliminate midazolam more slowly (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY ). Because elderly patients frequently have inefficient function of one or more organ systems and because dosage requirements have been shown to decrease with age, reduced initial dosage of midazolam is recommended, and the possibility of profound and/or prolonged effect should be considered. Injectable midazolam should not be administered to adult or pediatric patients in shock or coma, or in acute alcohol intoxication with depression of vital signs. Particular care should be exercised in the use of intravenous midazolam in adult or pediatric patients with uncompensated acute illnesses, such as severe fluid or electrolyte disturbances.
Risk of Intra-arterial Injection
There have been limited reports of intra-arterial injection of midazolam. Adverse events have included local reactions, as well as isolated reports of seizure activity in which no clear causal relationship was established. Precautions against unintended intra-arterial injection should be taken. Extravasation should also be avoided.
The safety and efficacy of midazolam following nonintravenous and nonintramuscular routes of administration have not been established. Midazolam should only be administered intramuscularly or intravenously.
Return to Full Cognitive Function
Midazolam is associated with a high incidence of partial or complete impairment of recall for the next several hours. The decision as to when patients who have received injectable midazolam, particularly on an outpatient basis, may again engage in activities requiring complete mental alertness, operate hazardous machinery or drive a motor vehicle must be individualized. Gross tests of recovery from the effects of midazolam (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY ) cannot be relied upon to predict reaction time under stress. It is recommended that no patient operate hazardous machinery or a motor vehicle until the effects of the drug, such as drowsiness, have subsided or until 1 full day after anesthesia and surgery, whichever is longer. For pediatric patients, particular care should be taken to assure safe ambulation.
Neonatal Sedation and Withdrawal Syndrome
Use of midazolam late in pregnancy can result in sedation (respiratory depression, lethargy, hypotonia) and/or withdrawal symptoms (hyperreflexia, irritability, restlessness, tremors, inconsolable crying, and feeding difficulties) in the neonate (see PRECAUTIONS: Pregnancy ). Monitor neonates exposed to midazolam during pregnancy or labor for signs of sedation and monitor neonates exposed to midazolam during pregnancy for signs of withdrawal; manage these neonates accordingly.
Pediatric Neurotoxicity
Published animal studies demonstrate that the administration of anesthetic and sedation drugs that block NMDA receptors and/or potentiate GABA activity increase neuronal apoptosis in the developing brain and result in long-term cognitive deficits when used for longer than 3 hours. The clinical significance of these findings is not clear. However, based on the available data, the window of vulnerability to these changes is believed to correlate with exposures in the third trimester of gestation through the first several months of life, but may extend out to approximately three years of age in humans (see PRECAUTIONS, Pregnancy and Pediatric Use and ANIMAL TOXICOLOGY AND/OR PHARMACOLOGY ).
Some published studies in children suggest that similar deficits may occur after repeated or prolonged exposures to anesthetic agents early in life and may result in adverse cognitive or behavioral effects. These studies have substantial limitations, and it is not clear if the observed effects are due to the anesthetic/sedation drug administration or other factors such as the surgery or underlying illness.
Anesthetic and sedation drugs are a necessary part of the care of children needing surgery, other procedures, or tests that cannot be delayed, and no specific medications have been shown to be safer than any other. Decisions regarding the timing of any elective procedures requiring anesthesia should take into consideration the benefits of the procedure weighed against the potential risks.
Precautions
GENERAL PRECAUTIONS SECTION
General: Intravenous doses of midazolam should be decreased for elderly and for debilitated patients (see WARNINGS and DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION ). These patients will also probably take longer to recover completely after midazolam administration for the induction of anesthesia.
Midazolam does not protect against the increase in intracranial pressure or against the heart rate rise and/or blood pressure rise associated with endotracheal intubation under light general anesthesia.
The efficacy and safety of midazolam in clinical use are functions of the dose administered, the clinical status of the individual patient, and the use of concomitant medications capable of depressing the CNS. Anticipated effects range from mild sedation to deep levels of sedation virtually equivalent to a state of general anesthesia where the patient may require external support of vital functions. Care must be taken to individualize and carefully titrate the dose of midazolam to the patient's underlying medical/surgical conditions, administer to the desired effect being certain to wait an adequate time for peak CNS effects of both midazolam and concomitant medications, and have the personnel and size-appropriate equipment and facilities available for monitoring and intervention (see Boxed WARNING , WARNINGS and DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION ). Practitioners administering midazolam must have the skills necessary to manage reasonably foreseeable adverse effects, particularly skills in airway management. For information regarding withdrawal (see DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE ).
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS SECTION
Information for Patients: To assure safe and effective use of benzodiazepines, the following information and instructions should be communicated to the patient when appropriate:
- 1.Inform your physician about any alcohol consumption and medicine you are now taking, especially blood pressure medication and antibiotics, including drugs you buy without a prescription. Alcohol has an increased effect when consumed with benzodiazepines; therefore, caution should be exercised regarding simultaneous ingestion of alcohol during benzodiazepine treatment.
- 2.Inform your physician if you are pregnant or are planning to become pregnant.
- 3.Inform your physician if you are nursing.
- 4.Patients should be informed of the pharmacological effects of midazolam, such as sedation and amnesia, which in some patients may be profound. The decision as to when patients who have received injectable midazolam, particularly on an outpatient basis, may again engage in activities requiring complete mental alertness, operate hazardous machinery or drive a motor vehicle must be individualized.
- 5.Patients receiving continuous infusion of midazolam in critical care settings over an extended period of time, may experience symptoms of withdrawal following abrupt discontinuation.
- 6.Effect of anesthetic and sedation drugs on early brain development: Studies conducted in young animals and children suggest repeated or prolonged use of general anesthetic or sedation drugs in children younger than 3 years may have negative effects on their developing brains. Discuss with parents and caregivers the benefits, risks, and timing and duration of surgery or procedures requiring anesthetic and sedation drugs.
Advise pregnant females that use of midazolam late in pregnancy can result in sedation (respiratory depression, lethargy, hypotonia) and/or withdrawal symptoms (hyperreflexia, irritability, restlessness, tremors, inconsolable crying, and feeding difficulties) in newborns (see WARNINGS: Neonatal Sedation and Withdrawal Syndrome and PRECAUTIONS: Pregnancy ). Instruct patients to inform their healthcare provider if they are pregnant.
Instruct patients to notify their healthcare provider if they are breastfeeding or intend to breastfeed. Instruct breastfeeding patients receiving midazolam to monitor infants for excessive sedation, poor feeding, and poor weight gain, and to seek medical attention if they notice these signs. A lactating woman may consider pumping and discarding breastmilk for at least 4 to 8 hours after receiving midazolam for sedation or anesthesia to minimize drug exposure to a breastfed infant (see PRECAUTIONS: Nursing Mothers).
Drug Interactions:
The concomitant use of benzodiazepines and opioids increases the risk of respiratory depression because of actions at different receptor sites in the CNS that control respiration. Benzodiazepines interact at GABAA sites and opioids interact primarily at mu receptors. When benzodiazepines and opioids are combined, the potential for benzodiazepines to significantly worsen opioid-related respiratory depression exists. Monitor patients closely for respiratory depression and sedation.
Other CNS Depressants
The sedative effect of intravenous midazolam is accentuated by any concomitantly administered medication, which depresses the central nervous system, particularly opioids (e.g., morphine, meperidine and fentanyl) and also secobarbital and droperidol. Consequently, the dosage of midazolam should be adjusted according to the type and amount of concomitant medications administered and the desired clinical response (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION ).
Caution is advised when midazolam is administered concomitantly with drugs that are known to inhibit the P450-3A4 enzyme system such as cimetidine (not ranitidine), erythromycin, diltiazem, verapamil, ketoconazole and itraconazole. These drug interactions may result in prolonged sedation due to a decrease in plasma clearance of midazolam.
The effect of single oral doses of 800 mg cimetidine and 300 mg ranitidine on steady-state concentrations of oral midazolam was examined in a randomized crossover study (n=8). Cimetidine increased the mean midazolam steady-state concentration from 57 to 71 ng/mL. Ranitidine increased the mean steady-state concentration to 62 ng/mL. No change in choice reaction time or sedation index was detected after dosing with the H2 receptor antagonists.
In a placebo-controlled study, erythromycin administered as a 500 mg dose, three times a day, for 1 week (n=6), reduced the clearance of midazolam following a single 0.5 mg/kg intravenous dose. The half-life was approximately doubled.
Caution is advised when midazolam is administered to patients receiving erythromycin since this may result in a decrease in the plasma clearance of midazolam.
The effects of diltiazem (60 mg three times a day) and verapamil (80 mg three times a day) on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of midazolam were investigated in a three-way crossover study (n=9). The half-life of midazolam increased from 5 to 7 hours when midazolam was taken in conjunction with verapamil or diltiazem. No interaction was observed in healthy subjects between midazolam and nifedipine.
In a placebo-controlled study, where saquinavir or placebo was administered orally as a 1200 mg dose, three times a day, for 5 days (n=12), a 56% reduction in the clearance of midazolam following a single 0.05 mg/kg intravenous dose was observed. The half-life was approximately doubled.
A moderate reduction in induction dosage requirements of thiopental (about 15%) has been noted following use of intramuscular midazolam for premedication in adults.
The intravenous administration of midazolam decreases the minimum alveolar concentration (MAC) of halothane required for general anesthesia. This decrease correlates with the dose of midazolam administered; no similar studies have been carried out in pediatric patients but there is no scientific reason to expect that pediatric patients would respond differently than adults.
Although the possibility of minor interactive effects has not been fully studied, midazolam and pancuronium have been used together in patients without noting clinically significant changes in dosage, onset or duration in adults. Midazolam does not protect against the characteristic circulatory changes noted after administration of succinylcholine or pancuronium and does not protect against the increased intracranial pressure noted following administration of succinylcholine. Midazolam does not cause a clinically significant change in dosage, onset or duration of a single intubating dose of succinylcholine; no similar studies have been carried out in pediatric patients but there is no scientific reason to expect that pediatric patients would respond differently than adults.
No significant adverse interactions with commonly used premedications or drugs used during anesthesia and surgery (including atropine, scopolamine, glycopyrrolate, diazepam, hydroxyzine, d-tubocurarine, succinylcholine and other nondepolarizing muscle relaxants) or topical local anesthetics (including lidocaine, dyclonine HCl and Cetacaine) have been observed in adults or pediatric patients. In neonates, however, severe hypotension has been reported with concomitant administration of fentanyl. This effect has been observed in neonates on an infusion of midazolam who received a rapid injection of fentanyl and in patients on an infusion of fentanyl who have received a rapid injection of midazolam.
DRUG & OR LABORATORY TEST INTERACTIONS SECTION
Drug/Laboratory Test Interactions: Midazolam has not been shown to interfere with results obtained in clinical laboratory tests.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis: Midazolam maleate was administered with diet in mice and rats for 2 years at dosages of 1, 9 and 80 mg/kg/day. In female mice in the highest dose group there was a marked increase in the incidence of hepatic tumors. In high-dose male rats there was a small but statistically significant increase in benign thyroid follicular cell tumors. Dosages of 9 mg/kg/day of midazolam maleate (4 times a human induction dose of 0.35 mg/kg based on body surface area comparison) do not increase the incidence of tumors. The pathogenesis of induction of these tumors is not known. These tumors were found after chronic administration, whereas human use will ordinarily be of single or several doses.
Mutagenesis: Midazolam did not have mutagenic activity in Salmonella typhimurium (5 bacterial strains), Chinese hamster lung cells (V79), human lymphocytes or in the micronucleus test in mice.
Impairment of Fertility: Male rats were treated orally with 1, 4, or 16 mg/kg midazolam beginning 62 days prior to mating with female rats treated with the same doses for 14 days prior to mating to Gestation Day 13 or Lactation Day 21. The high dose produced an equivalent exposure (AUC) as 4 mg/kg intravenous midazolam (1.85 times the human induction dose of 0.35 mg/kg based on body surface area comparison). There were no adverse effects on either male or female fertility noted.
Pregnancy
and PRECAUTIONS: Clinical Considerations ). Available data from published observational studies of pregnant women exposed to benzodiazepines do not report a clear association with benzodiazepines and major birth defects (see Data).
Neonates born to mothers using benzodiazepines late in pregnancy have been reported to experience symptoms of sedation and/or neonatal withdrawal (see WARNINGS: Neonatal Sedation and Withdrawal Syndrome ,
The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated risk of major birth defects and of miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4% and 15 to 20%, respectively.
Benzodiazepines cross the placenta and may produce respiratory depression, hypotonia, and sedation in neonates. Monitor neonates exposed to midazolam injection during pregnancy or labor for signs of sedation, respiratory depression, hypotonia, and feeding problems. Monitor neonates exposed to midazolam injection during pregnancy for signs of withdrawal. Manage these neonates accordingly (see WARNINGS: Neonatal Sedation and Withdrawal Syndrome ).
Published data from observational studies on the use of benzodiazepines during pregnancy do not report a clear association with benzodiazepines and major birth defects.
Although early studies reported an increased risk of congenital malformations with diazepam and chlordiazepoxide, there was no consistent pattern noted. In addition, the majority of more recent case-control and cohort studies of benzodiazepine use during pregnancy, which were adjusted for confounding exposures to alcohol, tobacco and other medications, have not confirmed these findings.
Pregnant rats were treated with midazolam using intravenous doses of 0.2, 1, and 4 mg/kg/day (0.09, 0.46, and 1.85 times the human induction dose of 0.35 mg/kg based on body surface area comparisons) during the period of organogenesis (Gestation Day 7 through 15). Midazolam did not cause adverse effects to the fetus at doses of up to 1.85 times the human induction dose. All doses produced slight to moderate ataxia. The high dose produced a 5% decrease in maternal body weight gain compared to control.
Pregnant rabbits were treated with midazolam using intravenous doses of 0.2, 0.6, and 2 mg/kg/day (0.09, 0.46, and 1.85 times the human induction dose of 0.35 mg/kg based on body surface area comparisons) during the period of organogenesis (Gestation Day 7 to 18). Midazolam did not cause adverse effects to the fetus at doses of up to 1.85 times the human induction dose. The high dose was associated with findings of ataxia and sedation but no evidence of maternal toxicity.
Pregnant rats were administered midazolam using intravenous doses of 0.2, 1, and 4 mg/kg/day (0.09, 0.46, and 1.85 times the human induction dose of 0.35 mg/kg based on body surface area comparisons) during late gestation and through lactation (Gestation Day 15 through Lactation Day 21). All doses produced ataxia. The high dose produced a slight decrease in maternal body weight gain compared to control. There were no clear adverse effects noted in the offspring. The study included no functional assessments of the pups, such as learning and memory testing or reproductive capacity.
In a published study in primates, administration of an anesthetic dose of ketamine for 24 hours on Gestation Day 122 increased neuronal apoptosis in the developing brain of the fetus. In other published studies, administration of either isoflurane or propofol for 5 hours on Gestation Day 120 resulted in increased neuronal and oligodendrocyte apoptosis in the developing brain of the offspring. With respect to brain development, this time period corresponds to the third trimester of gestation in the human. The clinical significance of these findings is not clear; however, studies in juvenile animals suggest neuroapoptosis correlates with long-term cognitive deficits (see WARNINGS, Pediatric Neurotoxicity, PRECAUTIONS, Pediatric Use, and ANIMAL TOXICOLOGY AND/OR PHARMACOLOGY ).
Nursing Mothers
There are reports of sedation, poor feeding and poor weight gain in infants exposed to benzodiazepines through breast milk. Based on data from published studies, midazolam is present in human milk in low levels. There are no data on the effects of midazolam on milk production.
The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for midazolam injection and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from midazolam injection or from the underlying maternal condition.
Infants exposed to midazolam injection through breast milk should be monitored for sedation, poor feeding and poor weight gain. A lactating woman may consider interrupting breastfeeding and pumping and discarding breast milk during treatment for a range of at least 4 to 8 hours after midazolam administration in order to minimize drug exposure to a breastfed infant.
Pediatric Use
The safety and efficacy of midazolam for sedation/anxiolysis/amnesia following single dose intramuscular administration, intravenously by intermittent injections and continuous infusion have been established in pediatric and neonatal patients. For specific safety monitoring and dosage guidelines (see Boxed WARNING , CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY , INDICATIONS AND USAGE , WARNINGS , PRECAUTIONS , ADVERSE REACTIONS , OVERDOSAGE and DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION). UNLIKE ADULT PATIENTS, PEDIATRIC PATIENTS GENERALLY RECEIVE INCREMENTS OF MIDAZOLAM ON A MG/KG BASIS. As a group, pediatric patients generally require higher dosages of midazolam (mg/kg) than do adults. Younger (less than six years) pediatric patients may require higher dosages (mg/kg) than older pediatric patients, and may require closer monitoring. In obese PEDIATRIC PATIENTS, the dose should be calculated based on ideal body weight. When midazolam is given in conjunction with opioids or other sedatives, the potential for respiratory depression, airway obstruction, or hypoventilation is increased. The health care practitioner who uses this medication in pediatric patients should be aware of and follow accepted professional guidelines for pediatric sedation appropriate to their situation.
Midazolam should not be administered by rapid injection in the neonatal population. Severe hypotension and seizures have been reported following rapid intravenous administration, particularly, with concomitant use of fentanyl.
Published juvenile animal studies demonstrate that the administration of anesthetic and sedation drugs, such as Midazolam Injection USP, that either block NMDA receptors or potentiate the activity of GABA during the period of rapid brain growth or synaptogenesis, results in widespread neuronal and oligodendrocyte cell loss in the developing brain and alterations in synaptic morphology and neurogenesis. Based on comparisons across species, the window of vulnerability to these changes is believed to correlate with exposures in the third trimester of gestation through the first several months of life, but may extend out to approximately 3 years of age in humans.
In primates, exposure to 3 hours of ketamine that produced a light surgical plane of anesthesia did not increase neuronal cell loss, however, treatment regimens of 5 hours or longer of isoflurane increased neuronal cell loss. Data from isoflurane-treated rodents and ketamine-treated primates suggest that the neuronal and oligodendrocyte cell losses are associated with prolonged cognitive deficits in learning and memory. The clinical significance of these nonclinical findings is not known, and healthcare providers should balance the benefits of appropriate anesthesia in pregnant women, neonates, and young children who require procedures with the potential risks suggested by the nonclinical data (see WARNINGS, Pediatric Neurotoxicity, PRECAUTIONS, Pregnancy and ANIMAL TOXICOLOGY AND/OR PHARMACOLOGY ).
Geriatric Use
Because geriatric patients may have altered drug distribution and diminished hepatic and/or renal function, reduced doses of midazolam are recommended. Intravenous and intramuscular doses of midazolam should be decreased for elderly and for debilitated patients (see WARNINGS and DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION ) and subjects over 70 years of age may be particularly sensitive. These patients will also probably take longer to recover completely after midazolam administration for the induction of anesthesia. Administration of intramuscular and intravenous midazolam to elderly and/or high risk surgical patients has been associated with rare reports of death under circumstances compatible with cardiorespiratory depression. In most of these cases, the patients also received other central nervous system depressants capable of depressing respiration, especially narcotics (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION ).
Specific dosing and monitoring guidelines for geriatric patients are provided in the DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION section for premedicated patients for sedation/anxiolysis/amnesia following intravenous and intramuscular administration, for induction of anesthesia following intravenous administration and for continuous infusion.
Adverse Reactions
See WARNINGS concerning serious cardiorespiratory events and possible paradoxical reactions. Fluctuations in vital signs were the most frequently seen findings following parenteral administration of midazolam in adults and included decreased tidal volume and/or respiratory rate decrease (23.3% of patients following intravenous and 10.8% of patients following intramuscular administration) and apnea (15.4% of patients following intravenous administration), as well as variations in blood pressure and pulse rate. The majority of serious adverse effects, particularly those associated with oxygenation and ventilation, have been reported when midazolam is administered with other medications capable of depressing the central nervous system. The incidence of such events is higher in patients undergoing procedures involving the airway without the protective effect of an endotracheal tube, (e.g., upper endoscopy and dental procedures).
Adults: The following additional adverse reactions were reported after intramuscular administration:
headache (1.3%)
Local effects at intramuscular Injection site
pain (3.7%)
induration (0.5%)
redness (0.5%)
muscle stiffness (0.3%)
Administration of intramuscular midazolam to elderly and/or higher risk surgical patients has been associated with rare reports of death under circumstances compatible with cardiorespiratory depression. In most of these cases, the patients also received other central nervous system depressants capable of depressing respiration, especially narcotics (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION ).
The following additional adverse reactions were reported subsequent to intravenous administration as a single sedative/anxiolytic/amnestic agent in adult patients:
hiccoughs (3.9%)
Local effects at the intravenous site
nausea (2.8%)
tenderness (5.6%)
vomiting (2.6%)
pain during injection (5.0%)
coughing (1.3%)
redness (2.6%)
"oversedation" (1.6%)
induration (1.7%)
headache (1.5%)
phlebitis (0.4%)
drowsiness (1.2%)
Pediatric Patients: The following adverse events related to the use of intravenous midazolam in pediatric patients were reported in the medical literature: desaturation 4.6%, apnea 2.8%, hypotension 2.7%, paradoxical reactions 2.0%, hiccough 1.2%, seizure-like activity 1.1% and nystagmus 1.1%. The majority of airway-related events occurred in patients receiving other CNS depressing medications and in patients where midazolam was not used as a single sedating agent.
Neonates: For information concerning hypotensive episodes and seizures following the administration of midazolam to neonates (see Boxed WARNING , CONTRAINDICATIONS , WARNINGS and PRECAUTIONS).
Other adverse experiences, observed mainly following intravenous injection as a single sedative/anxiolytic/amnesia agent and occurring at an incidence of <1.0% in adult and pediatric patients, are as follows:
Respiratory: Laryngospasm, bronchospasm, dyspnea, hyperventilation, wheezing, shallow respirations, airway obstruction, tachypnea
Cardiovascular: Bigeminy, premature ventricular contractions, vasovagal episode, bradycardia, tachycardia, nodal rhythm
Gastrointestinal: Acid taste, excessive salivation, retching
CNS/Neuromuscular: Retrograde amnesia, euphoria, hallucination, confusion, argumentativeness, nervousness, anxiety, grogginess, restlessness, emergence delirium or agitation, prolonged emergence from anesthesia, dreaming during emergence, sleep disturbance, insomnia, nightmares, athetoid movements, seizure-like activity, ataxia, dizziness, dysphoria, slurred speech, dysphonia, paresthesia
Special Senses: Blurred vision, diplopia, nystagmus, pinpoint pupils, cyclic movements of eyelids, visual disturbance, difficulty focusing eyes, ears blocked, loss of balance, light-headedness
Integumentary: Hive-like elevation at injection site, swelling or feeling of burning, warmth or coldness at injection site
Hypersensitivity: Allergic reactions including anaphylactoid reactions, hives, rash, pruritus
Miscellaneous: Yawning, lethargy, chills, weakness, toothache, faint feeling, hematoma
Drug Abuse And Dependence
Midazolam Injection contains midazolam a Schedule IV control substance.
Midazolam was actively self-administered in primate models used to assess the positive reinforcing effects of psychoactive drugs.
Midazolam produced physical dependence of a mild to moderate intensity in cynomolgus monkeys after 5 to 10 weeks of administration. Available data concerning the drug abuse and dependence potential of midazolam suggest that its abuse potential is at least equivalent to that of diazepam.
Withdrawal symptoms, similar in character to those noted with barbiturates and alcohol (convulsions, hallucinations, tremor, abdominal and muscle cramps, vomiting and sweating), have occurred following abrupt discontinuation of benzodiazepines, including midazolam. Abdominal distention, nausea, vomiting, and tachycardia are prominent symptoms of withdrawal in infants. The more severe withdrawal symptoms have usually been limited to those patients who had received excessive doses over an extended period of time. Generally milder withdrawal symptoms (e.g., dysphoria and insomnia) have been reported following abrupt discontinuance of benzodiazepines taken continuously at therapeutic levels for several months. Consequently, after extended therapy, abrupt discontinuation should generally be avoided and a gradual dosage tapering schedule followed. There is no consensus in the medical literature regarding tapering schedules; therefore, practitioners are advised to individualize therapy to meet patient's needs. In some case reports, patients who have had severe withdrawal reactions due to abrupt discontinuation of high-dose long-term midazolam, have been successfully weaned off of midazolam over a period of several days.
Overdosage
Clinical Presentation
Overdosage of benzodiazepines is characterized by central nervous system depression ranging from drowsiness to coma. In mild to moderate cases, symptoms can include drowsiness, confusion, dysarthria, lethargy, hypnotic state, diminished reflexes, ataxia, and hypotonia. Rarely, paradoxical or disinhibitory reactions (including agitation, irritability, impulsivity, violent behavior, confusion, restlessness, exclient, and talkativeness) may occur. In severe overdosage cases, patients may develop respiratory depression and coma. Overdosage of benzodiazepines in combination with other CNS depressants (including alcohol and opioids) may be fatal (see WARNINGS: Risks from Concomitant Use With Opioids, and Concomitant Use of Central Nervous System Depressants ). Markedly abnormal (lowered or elevated) blood pressure, heart rate, or respiratory rate raise the concern that additional drugs and/or alcohol are involved in the overdosage.
Management of Overdose
In managing benzodiazepine overdosage, employ general supportive measures, including intravenous fluids and airway maintenance. Flumazenil, a specific benzodiazepine receptor antagonist indicated for the complete or partial reversal of the sedative effects of benzodiazepines in the management of benzodiazepine overdosage, can lead to withdrawal and adverse reactions, including seizures, particularly in the context of mixed overdosage with drugs that increase seizure risk (e.g., tricyclic and tetracyclic antidepressants) and in patients with long-term benzodiazepine use and physical dependency. The risk of withdrawal seizures with flumazenil use may be increased in patients with epilepsy. Flumazenil is contraindicated in patients who have received a benzodiazepine for control of a potentially life-threatening condition (e.g., status epilepticus). If the decision is made to use flumazenil, it should be used as an adjunct to, not as a substitute for, supportive management of benzodiazepine overdosage. See the flumazenil injection Prescribing Information.
Consider contacting a poison center (1-800-222-1222), poisoncontrol.org, or a medical toxicologist for additional overdosage management recommendations.
Dosage And Administration
Midazolam injection is a potent sedative agent that requires slow administration and individualization of dosage. Clinical experience has shown midazolam to be 3 to 4 times as potent per mg as diazepam. BECAUSE SERIOUS AND LIFE-THREATENING CARDIORESPIRATORY ADVERSE EVENTS HAVE BEEN REPORTED, PROVISION FOR MONITORING, DETECTION AND CORRECTION OF THESE REACTIONS MUST BE MADE FOR EVERY PATIENT TO WHOM MIDAZOLAM INJECTION IS ADMINISTERED, REGARDLESS OF AGE OR HEALTH STATUS. Excessive single doses or rapid intravenous administration may result in respiratory depression, airway obstruction and/or arrest. The potential for these latter effects is increased in debilitated patients, those receiving concomitant medications capable of depressing the CNS, and patients without an endotracheal tube but undergoing a procedure involving the upper airway such as endoscopy or dental (see Boxed WARNING and WARNINGS).
Reactions such as agitation, involuntary movements, hyperactivity and combativeness have been reported in adult and pediatric patients. Should such reactions occur, caution should be exercised before continuing administration of midazolam (see WARNINGS ).
Midazolam injection should only be administered intramuscularly or intravenously (see WARNINGS ).
Care should be taken to avoid intra-arterial injection or extravasation (see WARNINGS ).
Midazolam Injection may be mixed in the same syringe with the following frequently used premedications: morphine sulfate, meperidine, atropine sulfate or scopolamine. Midazolam, at a concentration of 0.5 mg/mL, is compatible with 5% dextrose in water and 0.9% sodium chloride for up to 24 hours and with lactated Ringer's solution for up to 4 hours. Both the 1 mg/mL and 5 mg/mL formulations of midazolam may be diluted with 0.9% sodium chloride or 5% dextrose in water.
Monitoring: Patient response to sedative agents, and resultant respiratory status, is variable. Regardless of the intended level of sedation or route of administration, sedation is a continuum; a patient may move easily from light to deep sedation, with potential loss of protective reflexes. This is especially true in pediatric patients. Sedative doses should be individually titrated, taking into account patient age, clinical status and concomitant use of other CNS depressants. Continuous monitoring of respiratory and cardiac function is required (i.e., pulse oximetry).
and size-appropriate equipment and personnel trained in their use and skilled in airway management should be assured (see WARNINGS ).
Adults and Pediatrics: Sedation guidelines recommend a careful presedation history to determine how a patient's underlying medical conditions or concomitant medications might affect their response to sedation/analgesia as well as a physical examination including a focused examination of the airway for abnormalities. Further recommendations include appropriate presedation fasting.
Titration to effect with multiple small doses is essential for safe administration. It should be noted that adequate time to achieve peak central nervous system effect (3 to 5 minutes) for midazolam should be allowed between doses to minimize the potential for oversedation. Sufficient time must elapse between doses of concomitant sedative medications to allow the effect of each dose to be assessed before subsequent drug administration. This is an important consideration for all patients who receive intravenous midazolam.
Immediate availability of resuscitative drugs and age-
Pediatrics: For deeply sedated pediatric patients a dedicated individual, other than the practitioner performing the procedure, should monitor the patient throughout the procedure.
Intravenous access is not thought to be necessary for all pediatric patients sedated for a diagnostic or therapeutic procedure because in some cases the difficulty of gaining intravenous access would defeat the purpose of sedating the child; rather, emphasis should be placed upon having the intravenous equipment available and a practitioner skilled in establishing vascular access in pediatric patients immediately available.
Healthy Adults Below the Age of 60: Titrate slowly to the desired effect, (e.g., the initiation of slurred speech). Some patients may respond to as little as 1 mg. No more than 2.5 mg should be given over a period of at least 2 minutes. Wait an additional 2 or more minutes to fully evaluate the sedative effect. If further titration is necessary, continue to titrate, using small increments, to the appropriate level of sedation. Wait an additional 2 or more minutes after each increment to fully evaluate the sedative effect. A total dose greater than 5 mg is not usually necessary to reach the desired endpoint.If narcotic premedication or other CNS depressants are used, patients will require approximately 30% less midazolam than unpremedicated patients.Patients Age 60 or Older, and Debilitated or Chronically Ill Patients: Because the danger of hypoventilation, airway obstruction, or apnea is greater in elderly patients and those with chronic disease states or decreased pulmonary reserve, and because the peak effect may take longer in these patients, increments should be smaller and the rate of injection slower. Titrate slowly to the desired effect, (e.g., the initiation of slurred speech). Some patients may respond to as little as 1 mg. No more than 1.5 mg should be given over a period of no less than 2 minutes. Wait an additional 2 or more minutes to fully evaluate the sedative effect. If additional titration is necessary, it should be given at a rate of no more than 1 mg over a period of 2 minutes, waiting an additional 2 or more minutes each time to fully evaluate the sedative effect. Total doses greater than 3.5 mg are not usually necessary. If concomitant CNS depressant premedications are used in these patients, they will require at least 50% less midazolam than healthy young unpremedicated patients. Maintenance Dose: Additional doses to maintain the desired level of sedation may be given in increments of 25% of the dose used to first reach the sedative endpoint, but again only by slow titration, especially in the elderly and chronically ill or debilitated patient. These additional doses should be given only after a thorough clinical evaluation clearly indicates the need for additional sedation.
USUAL ADULT DOSAGE
INTRAMUSCULARLY
For preoperative sedation/anxiolysis/amnesia (induction of sleepiness or drowsiness and relief of apprehension and to impair memory of perioperative events). For intramuscular use, midazolam should be injected deep in a large muscle mass.
The recommended premedication dose of midazolam for good risk (ASA Physical Status I & II) adult patients below the age of 60 years is 0.07 to 0.08 mg/kg intramuscular (approximately 5 mg intramuscular) administered up to 1 hour before surgery. The dose must be individualized and reduced when intramuscular midazolam is administered to patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, other higher risk surgical patients, patients 60 or more years of age, and patients who have received concomitant narcotics or other CNS depressants (see ADVERSE REACTIONS ). In a study of patients 60 years or older, who did not receive concomitant administration of narcotics, 2 to 3 mg (0.02 to 0.05 mg/kg) of midazolam produced adequate sedation during the preoperative period. The dose of 1 mg intramuscular midazolam may suffice for some older patients if the anticipated intensity and duration of sedation is less critical. As with any potential respiratory depressant, these patients require observation for signs of cardiorespiratory depression after receiving intramuscular midazolam. Onset is within 15 minutes, peaking at 30 to 60 minutes. It can be administered concomitantly with atropine sulfate or scopolamine and reduced doses of narcotics.
INTRAVENOUSLY
Sedation/anxiolysis/amnesia for procedures (see INDICATIONS AND USAGE ): Narcotic premedication results in less variability in patient response and a reduction in dosage of midazolam. For peroral procedures, the use of an appropriate topical anesthetic is recommended. For bronchoscopic procedures, the use of narcotic premedication is recommended.
When used for sedation/anxiolysis/amnesia for a procedure, dosage must be individualized and titrated. Midazolam should always be titrated slowly; administer over at least 2 minutes and allow an additional 2 or more minutes to fully evaluate the sedative effect. Individual response will vary with age, physical status and concomitant medications, but may also vary independent of these factors (see WARNINGS concerning cardiac/respiratory arrest/airway obstruction/hypoventilation).
Midazolam 1 mg/mL formulation is recommended for sedation/anxiolysis/amnesia for procedures to facilitate slower injection. Both the 1 mg/mL and the 5 mg/mL formulations may be diluted with 0.9% sodium chloride or 5% dextrose in water.
1. 2. 3.
Induction of Anesthesia:
For induction of general anesthesia, before administration of other anesthetic agents.
Individual response to the drug is variable, particularly when a narcotic premedication is not used. The dosage should be titrated to the desired effect according to the patient's age and clinical status. When midazolam is used before other intravenous agents for induction of anesthesia, the initial dose of each agent may be significantly reduced, at times to as low as 25% of the usual initial dose of the individual agents. Unpremedicated Patients: In the absence of premedication, an average adult under the age of 55 years will usually require an initial dose of 0.3 to 0.35 mg/kg for induction, administered over 20 to 30 seconds and allowing 2 minutes for effect. If needed to complete induction, increments of approximately 25% of the patient's initial dose may be used; induction may instead be completed with inhalational anesthetics. In resistant cases, up to 0.6 mg/kg total dose may be used for induction, but such larger doses may prolong recovery. Unpremedicated patients over the age of 55 years usually require less midazolam for induction; an initial dose of 0.3 mg/kg is recommended. Unpremedicated patients with severe systemic disease or other debilitation usually require less midazolam for induction. An initial dose of 0.2 to 0.25 mg/kg will usually suffice; in some cases, as little as 0.15 mg/kg may suffice. Premedicated Patients: When the patient has received sedative or narcotic premedication, particularly narcotic premedication, the range of recommended doses is 0.15 to 0.35 mg/kg. In average adults below the age of 55 years, a dose of 0.25 mg/kg, administered over 20 to 30 seconds and allowing 2 minutes for effect, will usually suffice. The initial dose of 0.2 mg/kg is recommended for good risk (ASA I & II) surgical patients over the age of 55 years. In some patients with severe systemic disease or debilitation, as little as 0.15 mg/kg may suffice. Narcotic premedication frequently used during clinical trials included fentanyl (1.5 to 2 mcg/kg intravenous, administered 5 minutes before induction), morphine (dosage individualized, up to 0.15 mg/kg intramuscular), and meperidine (dosage individualized, up to 1 mg/kg intramuscular). Sedative premedications were hydroxyzine pamoate (100 mg orally) and sodium secobarbital (200 mg orally). Except for intravenous fentanyl, administered 5 minutes before induction, all other premedications should be administered approximately 1 hour prior to the time anticipated for midazolam induction.
Injectable midazolam can also be used during maintenance of anesthesia, for surgical procedures, as a component of balanced anesthesia. Effective narcotic premedication is especially recommended in such cases.
Incremental injections of approximately 25% of the induction dose should be given in response to signs of lightening of anesthesia and repeated as necessary.
CONTINUOUS INFUSION
For continuous infusion, midazolam 5 mg/mL formulation is recommended diluted to a concentration of 0.5 mg/mL with 0.9% sodium chloride or 5% dextrose in water.
Usual Adult Dose: If a loading dose is necessary to rapidly initiate sedation, 0.01 to 0.05 mg/kg (approximately 0.5 to 4 mg for a typical adult) may be given slowly or infused over several minutes. This dose may be repeated at 10 to 15 minute intervals until adequate sedation is achieved. For maintenance of sedation, the usual initial infusion rate is 0.02 to 0.1 mg/kg/hr (1 to 7 mg/hr). Higher loading or maintenance infusion rates may occasionally be required in some patients. The lowest recommended doses should be used in patients with residual effects from anesthetic drugs, or in those concurrently receiving other sedatives or opioids.Individual response to midazolam is variable. The infusion rate should be titrated to the desired level of sedation, taking into account the patient's age, clinical status and current medications. In general, midazolam should be infused at the lowest rate that produces the desired level of sedation. Assessment of sedation should be performed at regular intervals and the midazolam infusion rate adjusted up or down by 25% to 50% of the initial infusion rate so as to assure adequate titration of sedation level. Larger adjustments or even a small incremental dose may be necessary if rapid changes in the level of sedation are indicated. In addition, the infusion rate should be decreased by 10% to 25% every few hours to find the minimum effective infusion rate. Finding the minimum effective infusion rate decreases the potential accumulation of midazolam and provides for the most rapid recovery once the infusion is terminated. Patients who exhibit agitation, hypertension, or tachycardia in response to noxious stimulation, but who are otherwise adequately sedated, may benefit from concurrent administration of an opioid analgesic. Addition of an opioid will generally reduce the minimum effective midazolam infusion rate.
PEDIATRIC PATIENTS
UNLIKE ADULT PATIENTS, PEDIATRIC PATIENTS GENERALLY RECEIVE INCREMENTS OF MIDAZOLAM ON A MG/KG BASIS. As a group, pediatric patients generally require higher dosages of midazolam (mg/kg) than do adults. Younger (less than six years) pediatric patients may require higher dosages (mg/kg) than older pediatric patients, and may require close monitoring (see tables below). In obese PEDIATRIC PATIENTS, the dose should be calculated based on ideal body weight. When midazolam is given in conjunction with opioids or other sedatives, the potential for respiratory depression, airway obstruction, or hypoventilation is increased. For appropriate patient monitoring, see Boxed WARNING , WARNINGS , and DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION, Monitoring . The health care practitioner who uses this medication in pediatric patients should be aware of and follow accepted professional guidelines for pediatric sedation appropriate to their situation.
OBSERVER'S ASSESSMENT OF ALERTNESS/SEDATION (OAA/S)
Assessment Categories
Responsiveness
Speech
Facial Expression
Eyes
Composite Score
Responds readily to name spoken in normal tone
normal
normal
clear, no ptosis
5 (alert)
Lethargic response to name spoken in normal tone
mild slowing or thickening
mild relaxation
glazed or mild ptosis (less than half the eye)
4
Responds only after name is called loudly and/or repeatedly
slurring or prominent slowing
marked relaxation (slack jaw)
glazed and marked ptosis (half the eye or more)
3
Responds only after mild prodding or shaking
few recognizable words
–
–
2
Does not respond to mild prodding or shaking
–
–
–
1 (deep sleep)
Pediatric patients less than 6 months of age: Limited information is available in non-intubated pediatric patients less than 6 months of age. It is uncertain when the patient transfers from neonatal physiology to pediatric physiology, therefore the dosing recommendations are unclear. Pediatric patients less than 6 months of age are particularly vulnerable to airway obstruction and hypoventilation, therefore titration with small increments to clinical effect and careful monitoring are essential.
FREQUENCY OF OBSERVER'S ASSESSMENT OF ALERTNESS/SEDATION COMPOSITE SCORES IN ONE STUDY OF PEDIATRIC PATIENTS UNDERGOING PROCEDURES WITH INTRAVENOUS MIDAZOLAM FOR SEDATION
Age Range (years)
OAA/S Score
n
1 (deep sleep)
2
3
4
5 (alert)
1–2
16
6(38%)
4(25%)
3(19%)
3(19%)
0
>2–5
22
9(41%)
5(23%)
8(36%)
0
0
>5–12
34
1(3%)
6(18%)
22(65%)
5(15%)
0
>12–17
18
0
4(22%)
14(78%)
0
0
Total (1–17)
90
16(18%)
19(21%)
47(52%)
8(9%)
0
Pediatric patients 6 months to 5 years of age: Initial dose 0.05 to 0.1 mg/kg. A total dose up to 0.6 mg/kg may be necessary to reach the desired endpoint but usually does not exceed 6 mg. Prolonged sedation and risk of hypoventilation may be associated with the higher doses. Pediatric patients 6 to 12 years of age: Initial dose 0.025 to 0.05 mg/kg; total dose up to 0.4 mg/kg may be needed to reach the desired endpoint but usually does not exceed 10 mg. Prolonged sedation and risk of hypoventilation may be associated with the higher doses. Pediatric patients 12 to 16 years of age: Should be dosed as adults. Prolonged sedation may be associated with higher doses; some patients in this age range will require higher than recommended adult doses but the total dose usually does not exceed 10 mg. The dose of midazolam must be reduced in patients premedicated with opioid or other sedative agents including midazolam. Higher risk or debilitated patients may require lower dosages whether or not concomitant sedating medications have been administered (see WARNINGS ). To initiate sedation, an intravenous loading dose of 0.05 to 0.2 mg/kg administered over at least 2 to 3 minutes can be used to establish the desired clinical effect IN PATIENTS WHOSE TRACHEA IS INTUBATED. (Midazolam should not be administered as a rapid intravenous dose.) This loading dose may be followed by a continuous intravenous infusion to maintain the effect. An infusion of midazolam injection has been used in patients whose trachea was intubated but who were allowed to breathe spontaneously. Assisted ventilation is recommended for pediatric patients who are receiving other central nervous system depressant medications such as opioids. Based on pharmacokinetic parameters and reported clinical experience, continuous intravenous infusions of midazolam should be initiated at a rate of 0.06 to 0.12 mg/kg/hr (1 to 2 mcg/kg/min). The rate of infusion can be increased or decreased (generally by 25% of the initial or subsequent infusion rate) as required, or supplemental intravenous doses of midazolam can be administered to increase or maintain the desired effect. Frequent assessment at regular intervals using standard pain/sedation scales is recommended. Drug elimination may be delayed in patients receiving erythromycin and/or other P450-3A4 enzyme inhibitors (see PRECAUTIONS, Drug Interactions ) and in patients with liver dysfunction, low cardiac output (especially those requiring inotropic support), and in neonates. Hypotension may be observed in patients who are critically ill, particularly those receiving opioids and/or when midazolam is rapidly administered. When initiating an infusion with midazolam in hemodynamically compromised patients, the usual loading dose of midazolam should be titrated in small increments and the patient monitored for hemodynamic instability, e.g., hypotension. These patients are also vulnerable to the respiratory depressant effects of midazolam and require careful monitoring of respiratory rate and oxygen saturation.
INTRAMUSCULARLY
USUAL PEDIATRIC DOSE (NON-NEONATAL)
For sedation/anxiolysis/amnesia prior to anesthesia or for procedures, intramuscular midazolam can be used to sedate pediatric patients to facilitate less traumatic insertion of an intravenous catheter for titration of additional medication.
Sedation after intramuscular midazolam is age and dose dependent: higher doses may result in deeper and more prolonged sedation. Doses of 0.1 to 0.15 mg/kg are usually effective and do not prolong emergence from general anesthesia. For more anxious patients, doses up to 0.5 mg/kg have been used. Although not systematically studied, the total dose usually does not exceed 10 mg. If midazolam is given with an opioid, the initial dose of each must be reduced.
INTRAVENOUSLY BY INTERMITTENT INJECTION
USUAL PEDIATRIC DOSE (NON-NEONATAL)
For sedation/anxiolysis/amnesia prior to and during procedures or prior to anesthesia.
It should be recognized that the depth of sedation/anxiolysis needed for pediatric patients depends on the type of procedure to be performed. For example, simple light sedation/anxiolysis in the preoperative period is quite different from the deep sedation and analgesia required for an endoscopic procedure in a child. For this reason, there is a broad range of dosage. For all pediatric patients, regardless of the indications for sedation/anxiolysis, it is vital to titrate midazolam and other concomitant medications slowly to the desired clinical effect. The initial dose of midazolam should be administered over 2 to 3 minutes. Since midazolam is water soluble, it takes approximately three times longer than diazepam to achieve peak EEG effects, therefore one must wait an additional 2 to 3 minutes to fully evaluate the sedative effect before initiating a procedure or repeating a dose. If further sedation is necessary, continue to titrate with small increments until the appropriate level of sedation is achieved. If other medications capable of depressing the CNS are coadministered, the peak effect of those concomitant medications must be considered and the dose of midazolam adjusted. The importance of drug titration to effect is vital to the safe sedation/anxiolysis of the pediatric patient. The total dose of midazolam will depend on patient response, the type and duration of the procedure, as well as the type and dose of concomitant medications.
1. 2. 3. 4.
CONTINUOUS INTRAVENOUS INFUSION
USUAL PEDIATRIC DOSE (NON-NEONATAL)
For sedation/anxiolysis/amnesia in critical care settings.
CONTINUOUS INTRAVENOUS INFUSION
USUAL NEONATAL DOSE
For sedation in critical care settings.
Based on pharmacokinetic parameters and reported clinical experience in preterm and term neonates WHOSE TRACHEA WAS INTUBATED, continuous intravenous infusions of midazolam injection should be initiated at a rate of 0.03 mg/kg/hr (0.5 mcg/kg/min) in neonates <32 weeks and 0.06 mg/kg/hr (1 mcg/kg/min) in neonates >32 weeks. Intravenous loading doses should not be used in neonates, rather the infusion may be run more rapidly for the first several hours to establish therapeutic plasma levels. The rate of infusion should be carefully and frequently reassessed, particularly after the first 24 hours so as to administer the lowest possible effective dose and reduce the potential for drug accumulation. Hypotension may be observed in patients who are critically ill and in preterm and term infants, particularly those receiving fentanyl and/or when midazolam is administered rapidly. Due to an increased risk of apnea, extreme caution is advised when sedating preterm and former preterm patients whose trachea is not intubated.
NOTE: Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit.
How Supplied
Package configurations containing preservative-free midazolam hydrochloride equivalent to 1 mg midazolam/mL:
Unit of Sale
Concentration
NDC 55154-4743-5 Overbagged with 5 x 2 mL Single-dose Fliptop Vials
2 mg/2 mL(1 mg/mL)
STORAGE AND HANDLING SECTION
Store at 20 to 25°C (68 to 77°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Discard unused portion.
Animal Toxicology And/or Pharmacology
Published studies in animals demonstrate that the use of anesthetic agents during the period of rapid brain growth or synaptogenesis results in widespread neuronal and oligodendrocyte cell loss in the developing brain and alterations in synaptic morphology and neurogenesis. Based on comparisons across species, the window of vulnerability to these changes is believed to correlate with exposures in the third trimester through the first several months of life, but may extend out to approximately 3 years of age in humans.
In primates, exposure to 3 hours of an anesthetic regimen that produced a light surgical plane of anesthesia did not increase neuronal cell loss, however, treatment regimens of 5 hours or longer increased neuronal cell loss. Data in rodents and in primates suggest that the neuronal and oligodendrocyte cell losses are associated with subtle but prolonged cognitive deficits in learning and memory. The clinical significance of these nonclinical findings is not known, and healthcare providers should balance the benefits of appropriate anesthesia in neonates and young children who require procedures against the potential risks suggested by the nonclinical data (see WARNINGS, Pediatric Neurotoxicity and PRECAUTIONS, Pregnancy and Pediatric Use ).
For more information concerning this drug, please call 1-800-438-1985 or visit www.pfizer.com.
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, please call 1-800-438-1985 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch .

Distributed by Hospira, Inc., Lake Forest, IL 60045 USA
Distributed By:
Cardinal Health
Dublin, OH 43017
LC8836170424
LAB-0849-9.0Revised: 1/2023
Package/label Display Panel
MIDAZOLAM INJECTION, USP
2 mg/2 mL (1 mg/mL)
5 x 2 mL SINGLE-DOSE FLIPTOP VIALS

DISCLAIMER:
"This tool does not provide medical advice, and is for informational and educational purposes only, and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, treatment or diagnosis. Call your doctor to receive medical advice. If you think you may have a medical emergency, please dial 911."
"Do not rely on openFDA to make decisions regarding medical care. While we make every effort to ensure that data is accurate, you should assume all results are unvalidated. We may limit or otherwise restrict your access to the API in line with our Terms of Service."
"This product uses publicly available data from the U.S. National Library of Medicine (NLM), National Institutes of Health, Department of Health and Human Services; NLM is not responsible for the product and does not endorse or recommend this or any other product."
PillSync may earn a commission via links on our site