Olopatadine Hydrochloride Dailymed
Generic: olopatadine hydrochloride is used for the treatment of Conjunctivitis, Allergic
Go PRO for all pill images
1 Indications And Usage
Olopatadine hydrochloride (HCl) nasal spray is indicated for the relief of the symptoms of seasonal allergic rhinitis in adults and pediatric patients 6 years of age and older.
Olopatadine hydrochloride (HCl) nasal spray is an H1 receptor antagonist indicated for the relief of the symptoms of seasonal allergic rhinitis in adults and pediatric patients 6 years of age and older(1) .
2 Dosage And Administration
For nasal use only. Recommended dosages:
- Adults and Adolescents ≥ 12 Years: Two sprays per nostril (665 mcg per spray) twice daily
(2.1) .- Pediatric Patients 6 to 11 Years: One spray per nostril (665 mcg per spray) twice daily
(2.2) .- Priming Information: Prime olopatadine HCl nasal spray before initial use and when olopatadine HCl nasal spray has not been used for more than 7 days
(2.3) .2.1 Adults and Adolescents Twelve Years of Age and Older
The recommended dosage is two sprays per nostril twice daily.
2.2 Pediatric Patients Six to Eleven Years of Age
The recommended dosage is one spray per nostril twice daily.
2.3 Administration Information
Administer olopatadine HCl nasal spray by the nasal route only.
Priming: Before initial use, prime olopatadine HCl nasal spray by releasing 5 sprays or until a fine mist appears. The correct amount of medication cannot be assured before the initial priming.
Re-priming (as needed): When olopatadine HCl nasal spray has not been used for more than 7 days, re-prime by releasing 2 sprays. Avoid spraying olopatadine HCl nasal spray into the eyes.
Discard Instructions: Discard nasal device after 240 sprays (enough for 30 days of dosing) have been used even though the bottle is not completely empty. The correct amount of medication cannot be assured after 240 sprays have been used.
3 Dosage Forms And Strengths
Olopatadine HCl nasal spray, 665 mcg is a clear, colorless solution packaged in a white plastic bottle fitted with a metered-dose spray pump, a white colored dust cover and white safety clip. Each spray (100 microliters) delivers 665 mcg of olopatadine hydrochloride, USP.
Nasal spray: 665 mcg of olopatadine hydrochloride, USP in each spray(3) .
4 Contraindications
None.
None(4) .
5 Warnings And Precautions
- Epistaxis, Nasal Ulceration, and Nasal Septal Perforation: Monitor patients periodically for signs of adverse effects on the nasal mucosa. Discontinue if ulcerations or perforations occur. Avoid use in patients with nasal disease other than allergic rhinitis
(5.1) .- Avoid engaging in hazardous occupations requiring complete mental alertness and coordination, such as driving or operating machinery when taking olopatadine HCl
(5.2) .- Avoid concurrent use of alcohol or other central nervous system depressants with olopatadine HCl
(5.2) .5.1 Local Nasal Effects
Epistaxis and Nasal Ulceration
In placebo-controlled clinical trials (vehicle nasal spray) of 2 weeks to 12 months duration, epistaxis and nasal ulcerations were reported [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Nasal Septal Perforation
Three placebo-controlled long term (12 months) safety trials (vehicle nasal spray) were conducted. In the first safety trial, patients were treated with an investigational formulation of olopatadine HCl containing povidone (not the commercially marketed formulation) or a vehicle nasal spray containing povidone. Nasal septal perforations were reported in one patient treated with the investigational formulation of olopatadine HCl and 2 patients treated with the vehicle nasal spray. In the second safety trial with olopatadine HCl, which does not contain povidone, there were no reports of nasal septal perforation. In the third safety trial, one patient exposed to the 3.7 pH vehicle nasal spray (containing no povidone) reported a nasal septal perforation [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Before starting olopatadine HCl, conduct a nasal examination to ensure that patients are free of nasal disease other than allergic rhinitis. Perform nasal examinations periodically for signs of adverse effects on the nasal mucosa and consider stopping olopatadine HCl if patients develop nasal ulcerations.
5.2 Somnolence and Impaired Mental Alertness
In clinical trials, the occurrence of somnolence has been reported in some patients taking olopatadine HCl [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Patients should be cautioned against engaging in hazardous occupations requiring complete mental alertness and motor coordination, such as driving or operating machinery after administration of olopatadine HCl. Concurrent use of olopatadine HCl with alcohol or other central nervous system depressants should be avoided because additional reductions in alertness and additional impairment of central nervous system performance may occur.
6 Adverse Reactions
The most clinically significant adverse reactions described in other sections of labeling include:
- Epistaxis, Nasal Ulceration, and Nasal Septal Perforation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Somnolence and Impaired Mental Alertness [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
The most common (> 1%) adverse reactions, included bitter taste, headache, epistaxis, pharyngolaryngeal pain, post-nasal drip, cough, and urinary tract infection in patients 12 years of age and older and epistaxis, headache, upper respiratory tract infection, bitter taste, pyrexia, and rash in patients 6 to 11 years of age(6.1) .
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Amneal Pharmaceuticals, at 1-877-835-5472 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The safety data described below reflect exposure to olopatadine HCl in 2,770 patients with seasonal or perennial allergic rhinitis in 10 controlled clinical trials of 2 weeks to 12 months duration. Olopatadine HCl is not indicated for use in patients with perennial allergic rhinitis.
The safety data from adults and adolescents are based upon 6 placebo-controlled clinical trials (3.7 pH vehicle nasal spray or 7.0 pH vehicle nasal spray) in which 1,834 patients with seasonal or perennial allergic rhinitis (652 males and 1,182 females) 12 years of age and older were treated with olopatadine HCl two sprays per nostril twice daily. There were 1,180 patients (olopatadine HCl, 587; vehicle nasal spray, 593) that participated in 3 efficacy and safety trials of 2 weeks duration. There were 2,840 patients (olopatadine HCl, 1,247; 3.7 pH vehicle nasal spray, 1,251; 7.0 pH vehicle nasal spray, 342) that participated in 3 long-term clinical trials of 1-year duration. The racial distribution of adult and adolescent patients receiving olopatadine HCl was 77% white, 9% black, and 14% other. The incidence of discontinuation due to adverse reactions in these controlled clinical trials was comparable for olopatadine HCl and vehicle nasal spray. Overall, 4.7% of the 1,834 adult and adolescent patients across all 6 studies treated with olopatadine HCl, 3.5% of the 1,844 patients treated with 3.7 pH vehicle nasal spray discontinued due to adverse reactions, and 2.9% of the 342 patients treated with 7.0 pH vehicle nasal spray discontinued due to adverse reactions.
The safety data from pediatric patients 6 to 11 years of age are based upon 3 clinical trials in which 870 children with seasonal allergic rhinitis (376 females and 494 males) were treated with olopatadine HCl one or two sprays per nostril twice daily for 2 weeks. The racial distribution of pediatric patients receiving olopatadine HCl was 68.6% white, 16.6% black, and 14.8% other. The incidence of discontinuation due to adverse reactions in these controlled clinical trials was comparable for olopatadine HCl and vehicle nasal spray. Overall, 1.4% of the 870 pediatric patients across all 3 studies treated with olopatadine HCl and 1.3% of the 872 pediatric patients treated with vehicle nasal spray discontinued due to adverse reactions.
Adults and Adolescents 12 Years of Age and Older in Short-Term (2 week) Trials
There were 1,180 patients 12 years of age and older (olopatadine HCl, 587; vehicle nasal spray, 593) that participated in 3 efficacy and safety trials of 2 weeks duration. Table 1 presents the most common adverse reactions (0.9% or greater in patients treated with olopatadine HCl) that occurred more frequently in patients treated with olopatadine HCl compared with vehicle nasal spray in the 3 clinical trials of 2 weeks duration.
Table 1: Adverse Reactions Occurring at an Incidence of 0.9% or Greater in Controlled Clinical Trials of 2 Weeks Duration With Olopatadine HCl in Adolescent and Adult Patients 12 Years of Age and Older With Seasonal Allergic Rhinitis
Adverse Reaction
Adult and Adolescent Patients 12 Years and Older
Olopatadine HCl N = 587
Vehicle Nasal Spray N = 593
Bitter taste
75 (12.8%)
5 (0.8%)
Headache
26 (4.4%)
24 (4.0%)
Epistaxis
19 (3.2%)
10 (1.7%)
Pharyngolaryngeal Pain
13 (2.2%)
8 (1.3%)
Post-nasal drip
9 (1.5%)
5 (0.8%)
Cough
8 (1.4%)
3 (0.5%)
Urinary tract infection
7 (1.2%)
3 (0.5%)
CPK elevation
5 (0.9%)
2 (0.3%)
Dry mouth
5 (0.9%)
1 (0.2%)
Fatigue
5 (0.9%)
4 (0.7%)
Influenza
5 (0.9%)
1 (0.2%)
Nasopharyngitis
5 (0.9%)
4 (0.7%)
Somnolence
5 (0.9%)
2 (0.3%)
Throat irritation
5 (0.9%)
0 (0.0%)
There were no differences in the incidence of adverse reactions based on gender or race. Clinical trials did not include sufficient numbers of patients 65 years of age and older to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects.
Pediatric Patients 6 to 11 Years of Age
There were 1,742 pediatric patients 6 to 11 years of age (olopatadine nasal spray, 870; vehicle nasal spray, 872) with seasonal allergic rhinitis that participated in 3 clinical trials of 2 weeks duration. Two of the studies used the investigational formulation of olopatadine nasal spray, and one of the studies used olopatadine HCl. One study evaluated the safety of olopatadine HCl at doses of one and two sprays per nostril twice daily in 1,188 patients, in which 298 were exposed to olopatadine HCl 1 spray, 296 were exposed to olopatadine HCl 2 sprays, 297 were exposed to vehicle 1 spray, and 297 were exposed to vehicle 2 sprays twice daily for 2 weeks. Table 2 presents the most common adverse reactions (greater than 1.0% in pediatric patients 6 to 11 years of age treated with olopatadine HCl one spray per nostril) that occurred more frequently with olopatadine HCl compared with vehicle nasal spray.
Table 2. Adverse Reactions Occurring at an Incidence of Greater Than 1.0% in a Controlled Clinical Trial of 2 Weeks Duration With Olopatadine HCl in Pediatric Patients 6 to 11 Years of Age With Seasonal Allergic Rhinitis
Adverse Reaction
Pediatric Patients 6 to 11 Years of Age
Olopatadine HCl One Spray per Nostril N = 298
Vehicle Nasal Spray One Spray per Nostril N = 297
Epistaxis
17 (5.7%)
11 (3.7%)
Headache
13 (4.4%)
11 (3.7%)
Upper respiratory tract infection
8 (2.6%)
0
Bitter taste
3 (1.0%)
0
Pyrexia
4 (1.3%)
3 (1.0%)
Rash
4 (1.3%)
0
There were no differences in the incidence of adverse reactions based on gender, race, or ethnicity.
Long-Term (12 month) Safety Trials
In a 12-month, placebo-controlled, safety trial (vehicle nasal spray), 890 patients 12 years of age and older with perennial allergic rhinitis were randomized to treatment with olopatadine HCl two sprays per nostril twice daily (445 patients) or vehicle nasal spray (445 patients). In the olopatadine HCl and vehicle nasal spray groups, 72% and 74% of patients, respectively, completed the trial. Overall, 7% and 5%, respectively, discontinued study participation due to an adverse reaction. The most frequently reported adverse reaction was epistaxis, which occurred in 25% of patients treated with olopatadine HCl and 28% in patients treated with vehicle nasal spray. Epistaxis resulted in discontinuation of 0.9% of patients treated with olopatadine HCl and 0.2% of patients treated with vehicle nasal spray. Nasal ulcerations occurred in 10% of patients treated with olopatadine HCl and 9% of patients treated with vehicle nasal spray. Nasal ulcerations resulted in discontinuation of 0.4% of patients treated with olopatadine HCl and 0.2% patients treated with vehicle nasal spray. There were no patients with nasal septal perforation in either treatment group. Somnolence was reported in 1 patient treated with olopatadine HCl and 1 patient treated with vehicle nasal spray. Weight increase was reported in 6 patients treated with olopatadine HCl and 1 patient treated with vehicle nasal spray. Depression or worsening of depression occurred in 9 patients treated with olopatadine HCl and in 5 patients treated with vehicle nasal spray. Three patients, 2 of whom had preexisting histories of depression, who received olopatadine HCl were hospitalized for depression compared to none who received vehicle nasal spray.
In a second 12-month, placebo-controlled, safety trial (vehicle nasal spray), 459 patients 12 years of age and older with perennial allergic rhinitis were treated with two sprays per nostril of an investigational formulation of olopatadine HCl containing povidone (not the commercially marketed formulation) and 465 patients were treated with 2 sprays of a vehicle nasal spray containing povidone. Nasal septal perforations were reported in one patient treated with the investigational formulation of olopatadine HCl and 2 patients treated with the vehicle nasal spray. Epistaxis was reported in 19% of patients treated with the investigational formulation of olopatadine HCl and 12% of patients treated with vehicle nasal spray. Somnolence was reported in 3 patients treated with the investigational formulation of olopatadine HCl compared to 1 patient treated with vehicle nasal spray. Fatigue was reported in 5 patients treated with the investigational formulation of olopatadine HCl compared to 1 patient treated with vehicle nasal spray.
In a third 3-arm, 12-month placebo-controlled, safety trial (vehicle nasal spray), conducted post approval, 1,026 patients 12 years of age and older with perennial allergic rhinitis were randomized to treatment with olopatadine HCl (343 patients), a 3.7 pH vehicle nasal spray (341 patients), or a 7.0 pH vehicle nasal spray (342 patients). All treatments were administered as two sprays per nostril, twice daily. Overall, 5% of olopatadine HCl patients, 2% of 3.7 pH vehicle patients and 3% of 7.0 pH vehicle patients discontinued due to adverse reactions. The most frequently reported adverse reaction was epistaxis, which occurred in 24% of patients treated with olopatadine HCl, 20% of patients treated with 3.7 pH vehicle nasal spray, and 23% of patients treated with 7.0 pH vehicle nasal spray. Epistaxis resulted in the discontinuation of 2 patients treated with olopatadine HCl and 1 patient treated with 7.0 pH vehicle nasal spray. Nasal septal perforation was reported for one patient treated with the 3.7 pH vehicle nasal spray. Nasal ulcerations occurred in 9% of patients treated with olopatadine HCl, 8% of patients treated with 3.7 pH vehicle nasal spray, and 9% of patients treated with 7.0 pH vehicle nasal spray. Nasal ulceration resulted in the discontinuation of 1 patient treated with olopatadine HCl. Hyposmia and anosmia were each reported by one patient treated with olopatadine HCl. Neither somnolence nor weight loss was reported. Depression occurred in 3 patients treated with olopatadine HCl, 2 patients treated with 3.7 pH vehicle nasal spray, and 3 patients treated with 7.0 pH vehicle nasal spray.
There were no long-term clinical trials in children below 12 years of age.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
During the post approval use of olopatadine HCl, the following adverse reactions have been identified. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure. The most common adverse reactions reported include dizziness, dysgeusia, epistaxis, headache, nasal discomfort, oropharyngeal pain, and somnolence. Additionally, hyposmia and anosmia have been reported with the use of olopatadine HCl.
7 Drug Interactions
Formal drug-drug interaction studies were not conducted for olopatadine HCl. Drug interactions with inhibitors of liver enzymes are not anticipated because olopatadine is eliminated predominantly by renal excretion. Drug interactions involving P450 inhibition and plasma protein binding are also not expected [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8 Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Published data from postmarketing experience with antihistamines, with similar mechanism of action to olopatadine HCl, have not identified a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes.
However, there are no published human data specific to olopatadine HCl. In animal reproductive studies, oral administration of olopatadine hydrochloride to pregnant rats and rabbits caused a decrease in the number of live fetuses at maternal doses approximately 110 and 1,460 times the maximum recommended human daily intranasal dose (MRHDID) on a mg/m2 basis, respectively (see Data ).
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4%, and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Animal Data
In an oral embryo-fetal development study, pregnant rabbits were dosed throughout the period of organogenesis at doses up to 400 mg/kg/day. A decrease in the number of live fetuses was observed at 400 mg/kg/day (1,460 times the MRHDID, on a mg/m2 basis).
In an oral embryo-fetal development study, pregnant rats were dosed throughout the period of organogenesis at doses up to 600 mg/kg/day. Maternal toxicity, producing death and reduced maternal body weight gain was observed at 600 mg/kg/day (approximately 1,100 times the MRHDID on a mg/m2 basis). Olopatadine produced cleft palate at 60 mg/kg/day (approximately 110 times the MRHDID on a mg/m2 basis) and decreased embryo-fetal viability and reduced fetal weight in rats at 600 mg/kg/day (approximately 1,100 times the MRHDID on a mg/m2 basis).
In peri-/postnatal toxicity studies, pregnant rats received oral doses of olopatadine up to 600 mg/kg/day during late gestation and throughout the lactation period. Olopatadine produced decreased neonatal survival at 60 mg/kg/day (approximately 110 times the MRHDID on a mg/m2 basis) and reduced body weight gain in pups at 4 mg/kg/day (approximately 7 times the MRHDID on a mg/m2 basis). These effects appeared attributable to exposure of pups via the milk as demonstrated in a cross-fostered study in which pups of untreated dams cross-fostered to dams treated with 60 mg/kg/day olopatadine orally during the lactation period exhibited decreased body weight gain.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of olopatadine in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. Although orally administered olopatadine is present in rat milk, there is no information about nasally administered olopatadine.
It is not known whether topical nasal administration could result in sufficient systemic absorption to produce detectable quantities in human breast milk.
The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for olopatadine HCl and any potential adverse effects on the breast fed infant from olopatadine HCl or from the underlying maternal condition.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of olopatadine HCl for the relief of symptoms of seasonal allergic rhinitis have been established in pediatric patients aged 6 years and older.
The safety and effectiveness of olopatadine HCl in pediatric patients 6 to 11 years of age are supported by 3 vehicle-controlled 2-week studies in 870 patients [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Doses studied included one and two sprays per nostril twice daily. One of these studies evaluated the safety of olopatadine HCl at doses of one and two sprays per nostril twice daily in 1,188 patients, of which 298 patients were exposed to olopatadine HCl 1 spray, and 297 patients were exposed to vehicle 1 spray. In this study, the incidence of epistaxis with olopatadine HCl use was 5.7% [see Adverse Reactions (6.1), Clinical Studies (14)].
The safety and effectiveness of olopatadine HCl in pediatric patients aged 12 years and older are supported by 3 randomized, double blind, parallel group, multicenter, placebo-controlled clinical trials of 2 weeks duration in adult and adolescent patients [see Clinical Studies (14)]. In these studies, the incidence of epistaxis with olopatadine HCl use in 587 patients was 3.2% [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
The safety and effectiveness of olopatadine HCl have not been established in pediatric patients under 6 years of age.
The safety of olopatadine HCl at a dose of one spray per nostril twice daily was evaluated in one 2-week vehicle-controlled study in 132 pediatric patients 2 to 5 years of age with allergic rhinitis. In this trial, 66 patients were exposed to olopatadine HCl. The most common (greater than 1.0%) adverse reactions reported were diarrhea (9.1%), epistaxis (6.1%), rhinorrhea (4.5%), bitter taste (3.0%), and wheezing (3.0%). Diarrhea was reported more frequently (9.1%) in patients 2 to 5 years of age than 6 to 11 year old age group (< 1%).
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of olopatadine HCl did not include sufficient numbers of patients aged 65 years and older to determine whether they respond differently from younger patients. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
10 Overdosage
Symptoms of antihistamine overdose may include drowsiness in both adults and children. Agitation and restlessness followed by drowsiness may also occur in children. There is no known specific antidote to olopatadine HCl. Should overdose occur, symptomatic or supportive treatment is recommended, taking into account any concomitantly ingested medications.
For additional information about overdose treatment, call a poison control center (1-800-222-1222).
11 Description
Olopatadine HCl nasal spray, 665 mcg is a metered-spray solution for nasal administration. Olopatadine hydrochloride USP, the active component of olopatadine HCl nasal spray, 665 mcg, is a white, water-soluble crystalline powder. The chemical name for olopatadine hydrochloride, USP is (Z)-11-[3-(dimethylamino)propylidene]-6,11-dihydrodibenz [b,e]oxepin-2-acetic acid hydrochloride. It has a molecular weight of 373.88 g/mol, and its molecular formula is C21H23NO3•HCl with the following chemical structure:
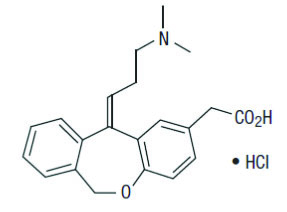
Olopatadine HCl nasal spray, 665 mcg contains 0.6% w/v olopatadine (base) in a nonsterile aqueous solution with pH of approximately 3.7. After initial priming (5 sprays), each metered spray from the nasal applicator delivers 100 microliters of the aqueous solution containing 665 mcg of olopatadine hydrochloride USP, which is equivalent to 600 mcg of olopatadine (base) [see Dosage Forms and Strengths (3)]. Olopatadine HCl nasal spray also contains benzalkonium chloride (0.01%), dibasic sodium phosphate (anhydrous), edetate disodium, sodium chloride, hydrochloric acid and/or sodium hydroxide (to adjust pH), and purified water.
12 Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Olopatadine is a histamine H1 receptor antagonist. The antihistaminic activity of olopatadine has been documented in isolated tissues, animal models, and humans.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Cardiac Electrophysiology
In a placebo-controlled cardiovascular safety study, 32 healthy volunteers received 20 mg oral solution of olopatadine twice daily for 14 days (8-fold greater daily dose than the recommended daily nasal dose). The mean QTcF (QT corrected by Fridericia’s correction method for heart rate) change from baseline was -2.7 msec and -3.8 msec for olopatadine, and placebo, respectively. In this study, 8 subjects treated with olopatadine had a QTcF change from baseline of 30 to 60 msec, 1 subject had a QTcF change from baseline greater than 60 msec, and no subjects had QTcF values greater than 500 msec. Eight subjects treated with placebo had a QTcF change from baseline of 30 to 60 msec, no subjects had a QTcF change from baseline greater than 60 msec, and no subjects had QTcF values greater than 500 msec. In a 12-month study in 429 perennial allergic rhinitis patients treated with olopatadine HCl two sprays per nostril twice daily, no evidence of any effect of olopatadine hydrochloride on QT prolongation was observed.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetic properties of olopatadine were studied after administration by the nasal, oral, intravenous, and topical ocular routes. Olopatadine exhibited linear pharmacokinetics across the routes studied over a large dose range.
Absorption
Healthy Subjects: Olopatadine was absorbed with individual peak plasma concentrations observed between 30 minutes and 1 hour after twice daily intranasal administration of olopatadine HCl. The mean (± SD) steady-state peak plasma concentration (Cmax) of olopatadine was 16.0 ± 8.99 ng/mL. Systemic exposure as indexed by area under the curve (AUC0-12) averaged 66.0 ± 26.8 ng·h/mL. The average absolute bioavailability of intranasal olopatadine is 57%. The mean accumulation ratio following multiple intranasal administration of olopatadine HCl was about 1.3.
Seasonal Allergic Rhinitis Patients: Systemic exposure of olopatadine in seasonal allergic rhinitis (SAR) patients after twice daily intranasal administration of olopatadine HCl was comparable to that observed in healthy subjects. Olopatadine was absorbed with peak plasma concentrations observed between 15 minutes and 2 hours. The mean steady-state Cmax was 23.3 ± 6.2 ng/mL and AUC0-12 averaged 78.0 ± 13.9 ng·h/mL.
Distribution
The protein binding of olopatadine was moderate at approximately 55% in human serum, and independent of drug concentration over the range of 0.1 to 1,000 ng/mL. Olopatadine was bound predominately to human serum albumin.
Elimination
The plasma elimination half-life of olopatadine is 8 to 12 hours. Olopatadine is mainly eliminated through urinary excretion. Approximately 70% of a [14C] olopatadine hydrochloride oral dose was recovered in urine with 17% in the feces. Of the drug-related material recovered within the first 24 hours in the urine, 86% was unchanged olopatadine with the balance comprised of olopatadine N-oxide and N-desmethyl olopatadine.
Metabolism
Olopatadine is not extensively metabolized. Based on plasma metabolite profiles following oral administration of [14C] olopatadine, at least six minor metabolites circulate in human plasma. Olopatadine accounts for 77% of peak plasma total radioactivity and all metabolites amounted to < 6% combined. Two of these have been identified as the olopatadine N-oxide and N-desmethyl olopatadine. In in vitro studies with cDNA-expressed human cytochrome P450 isoenzymes (CYP) and flavin-containing monooxygenases (FMO), N-desmethyl olopatadine (Ml) formation was catalyzed mainly by CYP3A4, while olopatadine N-oxide (M3) was primarily catalyzed by FMO1 and FMO3. Olopatadine at concentrations up to 33,900 ng/mL did not inhibit the in vitro metabolism of specific substrates for CYP1A2, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, CYP2E1, and CYP3A4. The potential for olopatadine and its metabolites to act as inducers of CYP enzymes has not been evaluated.
Specific Populations
Patients with Hepatic Impairment
No specific pharmacokinetic study examining the effect of hepatic impairment was conducted. Since metabolism of olopatadine is a minor route of elimination, no adjustment of the dosing regimen of olopatadine HCl is warranted in patients with hepatic impairment.
Patients with Renal Impairment
The mean Cmax values for olopatadine following single nasal doses were not markedly different between healthy subjects (18.1 ng/mL) and patients with mild, moderate, and severe renal impairment (range 15.5 to 21.6 ng/mL). The mean plasma AUC0-12 was 2-fold higher in patients with severe impairment (creatinine clearance < 30 mL/min/1.73 m2). In these patients, peak steady-state plasma concentrations of olopatadine are approximately 10-fold lower than those observed after higher 20 mg oral doses, twice daily, which were well-tolerated. These findings indicate that no adjustment of the dosing regimen of olopatadine HCl is warranted in patients with renal impairment.
Male and Female Patients
The mean systemic exposure (Cmax and AUC0-12) in female SAR patients following multiple administration of olopatadine was 40% and 27% higher, respectively than those values observed in male SAR patients.
Racial or Ethnic Groups
The effects of race on olopatadine pharmacokinetics have not been adequately investigated.
Pediatric Patients 6 to 11 Years of Age
The systemic pharmacokinetics of olopatadine, olopatadine N-oxide and N-desmethyl olopatadine in patients 6 through 11 years of age were characterized using data from 42 pediatric patients administered olopatadine HCl, one spray per nostril twice daily for a minimum of 14 days. The mean Cmax (15.4 ± 7.3 ng/mL) of olopatadine was approximately 2-fold less than was comparable to that observed in adults (78.0 ± 13.9 ng·h/mL). The Cmax and AUC0-12 of olopatadine N-oxide were comparable to that observed in adults. The Cmax and AUC0-12 of N-desmethyl olopatadine are approximately 18% and 37% higher than that observed in adults, respectively.
Pediatric Patients 2 to 5 Years of Age
The systemic pharmacokinetics of olopatadine, olopatadine N-oxide, and N-desmethyl olopatadine were characterized using population pharmacokinetic methods applied to sparse data (approximately 5 samples per patient) obtained from 66 pediatric patients (2 to less than 6 years of age) administered one-half the recommended adult dose (one spray per nostril) of olopatadine HCl twice daily for a minimum of 14 days. The mean Cmax and AUC0-12 of olopatadine were 13.4 ± 4.6 ng/mL and 75.0 ± 26.4 ng·hr/mL respectively. The mean Cmax and AUC0-12 of olopatadine N-oxide and N-desmethyl olopatadine were similar to that of patients 6 to 11 years of age.
Drug Interaction Studies
Drug interactions with inhibitors of liver enzymes are not anticipated because olopatadine is eliminated predominantly by renal excretion. Olopatadine did not inhibit the in vitro metabolism of specific substrates for CYP1A2, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, CYP2E1, and CYP3A4. Based on these data, drug interactions involving P450 inhibition are not expected. Due to the modest protein binding of olopatadine (55%), drug interactions through displacement from plasma proteins are also not expected.
13 Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenicity
Olopatadine demonstrated no tumorigenic potential in mice at oral doses up to 500 mg/kg/day (approximately 460 times the MRHDID on a mg/m2 basis) for 78 weeks or in rats at oral doses up to 200 mg/kg/day (approximately 370 times the MRHDID on a mg/m2 basis) for 104 weeks.
Mutagenesis
No mutagenic potential was observed when olopatadine was tested in an in vitro bacterial reverse mutation (Ames) test, an in vitro mammalian chromosome aberration assay or an in vivo mouse micronucleus test.
Impairment of Fertility
Olopatadine administered at an oral dose of 400 mg/kg/day, (approximately 730 times the MRHDID for adults on an mg/m2 basis) produced toxicity in male and female rats, and resulted in a decrease in the fertility index and reduced implantation rate. No effects on reproductive function were observed at 50 mg/kg/day (approximately 90 times the MRHDID on a mg/m2 basis).
14 Clinical Studies
Adult and Adolescent Patients 12 Years of Age and Older
The efficacy and safety of olopatadine HCl were evaluated in 3 randomized, double blind, parallel group, multicenter, placebo-controlled clinical trials (vehicle nasal spray) of 2 weeks duration in adult and adolescent patients, 12 years of age and older with symptoms of seasonal allergic rhinitis. The 3 clinical trials were conducted in the United States and included 1,598 patients (556 males, and 1042 females) 12 years of age and older. In these 3 trials, 587 patients were treated with olopatadine HCl 0.6%, 418 patients were treated with olopatadine HCl 0.4%, and 593 patients were treated with vehicle nasal spray. Assessment of efficacy was based on patient recording of 4 individual nasal symptoms (nasal congestion, rhinorrhea, itchy nose, and sneezing) on a 0 to 3 categorical severity scale (0 = absent, 1 = mild, 2 = moderate, 3 = severe) as reflective or instantaneous scores. Reflective scoring required patients to record symptom severity over the previous 12 hours; the instantaneous scoring required patients to record symptom severity at the time of recording. The primary efficacy endpoint was the difference from placebo in the percent change from baseline in the average of morning and evening reflective total nasal symptom score (rTNSS) averaged for the 2-week treatment period. In all 3 trials, patients treated with olopatadine HCl, two sprays per nostril, twice-daily, exhibited statistically significantly greater decreases in rTNSS compared to vehicle nasal spray. Results for the rTNSS from 2 representative trials are shown in Table 3.
Table 3: Mean Reflective Total Nasal Symptom Score (rTNSS) in Adult and Adolescent Patients With Seasonal Allergic Rhinitis
Study No.
Treatment
N
Baseline
Change From Baseline
Difference From Placebo
Estimate
95% CI
p-value
Study 1
Olopatadine HCl Nasal Spray 0.6%
183
8.71
-3.63
-0.96
(-1.42, -0.51)
< 0.0001
Olopatadine HCl Nasal Spray 0.4%
188
8.90
-3.38
-0.71
(-1.17, -0.26)
0.0023
Vehicle Nasal Spray
191
8.75
-2.67
Study 2
Olopatadine HCl Nasal Spray 0.6%
220
9.17
-2.90
-0.98
(-1.37, -0.59)
< 0.0001
Olopatadine HCl Nasal Spray 0.4%
228
9.26
-2.63
-0.72
(-1.11, -0.33)
0.0003
Vehicle Nasal Spray
223
9.07
-1.92
Abbreviation: CI, confidence interval.
Itchy eyes and watery eyes were evaluated as secondary endpoints but eye redness was not evaluated. In 2 of the studies, patients treated with olopatadine HCl had significantly greater decreases in reflective symptom scores for itchy eyes and watery eyes, compared to vehicle nasal spray.
In the 2-week seasonal allergy trials, onset of action was also evaluated by instantaneous TNSS assessments twice-daily after the first dose of study medication. In these trials, onset of action was seen after 1 day of dosing. Onset of action was evaluated in 3 environmental exposure unit studies with single doses of olopatadine HCl. In these studies, patients with seasonal allergic rhinitis were exposed to high levels of pollen in the environmental exposure unit and then treated with either olopatadine HCl or vehicle nasal spray, two sprays in each nostril, after which they self-reported their allergy symptoms hourly as instantaneous scores for the subsequent 12 hours. Olopatadine HCl 0.6% was found to have an onset of action of 30 minutes after dosing in the environmental exposure unit.
Pediatric Patients 6 to 11 Years of Age
There were 3 clinical trials of 2 weeks duration with olopatadine nasal spray in patients 6 to 11 years of age with seasonal allergic rhinitis. Efficacy of olopatadine HCl was evaluated in 2 of the 3 trials. One of the 2 trials that showed efficacy was a randomized, double blind, parallel group, multicenter, placebo (vehicle nasal spray)-controlled clinical trial of 2 weeks duration, including 1,188 children ages 6 to < 12 years with seasonal allergic rhinitis. Assessment of efficacy was based on patient/caregiver recording of 4 individual nasal symptoms (nasal congestion, rhinorrhea, itchy nose, and sneezing) on a 0 to 3 categorical severity scale (0 = absent, 1 = mild, 2 = moderate, 3 = severe) as reflective or instantaneous scores. Reflective scoring captured symptom severity over the previous 12 hours; the instantaneous scoring captured symptom severity at the time of recording. The primary efficacy endpoint was the difference from placebo in the percent change from baseline in the average of patient/caregiver-reported morning and evening reflective total nasal symptom score (rTNSS) averaged for the 2-week treatment period. Patients treated with olopatadine HCl, one or two sprays per nostril twice daily, had statistically significantly greater decreases in rTNSS compared to vehicle nasal spray. Results for rTNSS are shown in Table 4.
Table 4: Mean Reflective Total Nasal Symptom Score in Pediatric Patients 6 to 11 Years of Age With Seasonal Allergic Rhinitis
Treatment
N
Baseline
Change From Baseline
Difference from Placebo
Estimate
95% CI
p-value
Olopatadine HCl Nasal Spray 0.6%, one spray per nostril twice daily
294
8.99
-2.24
-0.55
(-0.90, -0.19)
0.0015
Vehicle Nasal Spray, one spray per nostril twice daily
294
9.09
-1.70
Abbreviation: CI, confidence interval.
Itchy eyes and watery eyes were evaluated as secondary endpoints in the same study but eye redness was not evaluated. Patients treated with olopatadine HCl had significantly greater decreases in reflective symptom scores for itchy eyes and watery eyes, compared to vehicle nasal spray.
16 How Supplied/storage And Handling
How Supplied
Olopatadine HCl nasal spray, 665 mcg is supplied in a white plastic bottle with nasal applicator, fitted with a metered-dose manual spray pump, a white colored dust cover and white safety clip in a box of 1 (NDC 65162-890-23). Each trade size bottle contains 30.5 g of clear, colorless liquid and will provide 240 metered sprays. After priming [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)], each spray delivers a fine mist containing 665 mcg of olopatadine hydrochloride, USP in 100 microliters of formulation through the nozzle.
Net content 30.5 g, 240 sprays: NDC 65162-890-23 (trade size)
Storage
Store olopatadine HCl nasal spray at room temperature between 4°C to 25°C (39°F to 77°F).
17 Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information and Instructions for Use).
Local Nasal Effects and Other Common Adverse Reactions
Inform patients that treatment with olopatadine HCl may lead to adverse reactions, which include epistaxis and nasal ulcerations [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. Other common adverse reactions reported with use of olopatadine HCl include bitter taste, headache, and pharyngolaryngeal pain [see Adverse Reactions (6)].
Somnolence and Impaired Mental Alertness
Somnolence has been reported in some patients taking olopatadine HCl. Caution patients against engaging in hazardous occupations requiring complete mental alertness and motor coordination, such as driving or operating machinery after administration of olopatadine HCl [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Concurrent Use of Alcohol and Other Central Nervous System Depressants
Advise patients that concurrent use of olopatadine HCl with alcohol or other central nervous system depressants should be avoided because additional reductions in alertness and additional impairment of central nervous system performance may occur [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Keep Spray Out of Eyes
Inform patients to avoid spraying olopatadine HCl in their eyes [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
Distributed by: Amneal Pharmaceuticals LLC Bridgewater, NJ 08807
Rev. 04-2021-01
Patient Information
Olopatadine Hydrochloride (oh” loe pat’ a deen hye” droe klor’ ide) Nasal Spray, for intranasal use
What is olopatadine HCl nasal spray?
Olopatadine HCl nasal spray is a prescription nasal spray that contains an antihistamine. Olopatadine HCl nasal spray is used to treat seasonal allergy symptoms in adults and children 6 years of age and older. It is not known if olopatadine HCl nasal spray is safe and effective in children under 6 years of age.
Before using olopatadine HCl nasal spray, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
- have nose problems, such as nose bleeds, or sores in the nose.
- are pregnant or planning to become pregnant. It is not known if olopatadine HCl nasal spray will harm your unborn baby.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if olopatadine HCl passes into your breast milk. You and your healthcare provider should decide if you will use olopatadine HCl nasal spray if you plan to breastfeed.
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
Olopatadine HCl nasal spray and other medicines may affect each other and cause side effects.
Know the medicines you take. Keep a ul of your medicines and show it to your healthcare provider or pharmacist when you get a new medicine.
How should I use olopatadine HCl nasal spray?
- See the “Instructions for Use” at the end of this Patient Information leaflet for information about the right way to use olopatadine HCl nasal spray.
- Olopatadine HCl nasal spray is for use in your nose only. Do not spray it in your eyes or mouth.
- Use olopatadine HCl nasal spray exactly as your healthcare provider tells you to use it.
- Do not use more than your healthcare provider tells you.
- If you use too much olopatadine HCl nasal spray, call your healthcare provider or pharmacist right away.
- Throw away olopatadine HCl nasal spray after 240 sprays (about 30 days) after the first priming. Even though the bottle may not be completely empty, you may not get the correct dose of medicine if you continue to use it.
What should I avoid while using olopatadine HCl nasal spray?
- Olopatadine HCl nasal spray can cause sleepiness or drowsiness. Do not drive, operate machinery, or do anything that needs you to be alert until you know how olopatadine HCl nasal spray affects you.
- Do not drink alcohol or take any medicines that may cause you to feel sleepy while using olopatadine HCl nasal spray. It may make your sleepiness worse.
What are the possible side effects of olopatadine HCl nasal spray?
Olopatadine HCl nasal spray may cause serious side effects, including:
- ·nosebleeds.
- sores in the nose.
- hole in the cartilage between the nose (nasal septum perforation). A whistling sound when you breathe may be a symptom of nasal septum perforation.
- sleepiness or drowsiness.
The most common side effects of olopatadine HCl nasal spray in people 12 years of age and older include:
- bad or bitter taste
- headache
- throat pain
- ·nose congestion
- cough
- urinary tract infection
The most common side effects of olopatadine HCl nasal spray in people 6 to 11 years of age include:
- headache
- upper respiratory tract infection
- bad or bitter taste
- fever
- rash
Tell your healthcare provider if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away.
These are not all of the possible side effects of olopatadine HCl nasal spray. For more information, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store olopatadine HCl nasal spray?
- Store olopatadine HCl nasal spray at room temperature between 39°F to 77°F (4°C to 25°C).
- Do not use your olopatadine HCl nasal spray after the expiration date on the label or box.
Keep olopatadine HCl nasal spray and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about olopatadine HCl nasal spray.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for conditions that are not mentioned in the Patient Information leaflet. Do not use olopatadine HCl nasal spray for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give olopatadine HCl nasal spray to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them. You can ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for information about olopatadine HCl nasal spray that is written for health professionals.
What are the ingredients in olopatadine HCl nasal spray?
Active ingredient: olopatadine hydrochloride, USP 665 micrograms per spray.
Inactive ingredients: benzalkonium chloride 0.01%, dibasic sodium phosphate (anhydrous), edetate disodium, sodium chloride, hydrochloric acid and/or sodium hydroxide (to adjust pH), and purified water.
Distributed by: Amneal Pharmaceuticals LLC Bridgewater, NJ 08807
Rev. 04-2021-01
For more information, go to www.amneal.com or call 1-877-835-5472.
This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Instructions For Use
Olopatadine Hydrochloride (oh” loe pat’ a deen hye” droe klor’ ide) Nasal Spray, for intranasal use
This Instructions for Use contains information on how to use olopatadine HCl nasal spray.
Read this Instructions for Use that comes with olopatadine HCl nasal spray before you start using it and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking with your healthcare provider about your medical condition or treatment.
Olopatadine HCl nasal spray is for use in your nose only. Do not spray olopatadine HCl nasal spray in your eyes or mouth.
Important information you need to know before using olopatadine HCl nasal spray
- Use olopatadine HCl nasal spray exactly how your healthcare provider tells you to use it.
- Your olopatadine HCl nasal spray bottle must be shaken and primed before you use it for the first time and when you have not used it for more than 7 days.
- Throw away olopatadine HCl nasal spray after 240 sprays after the first priming. Even though the bottle may not be completely empty, you may not get the correct dose of medicine if you continue to use it.
Using olopatadine HCl nasal spray
Step 1. Remove the white plastic overcap and the white safety clip just under the “shoulders” of the pump (see Figure A).
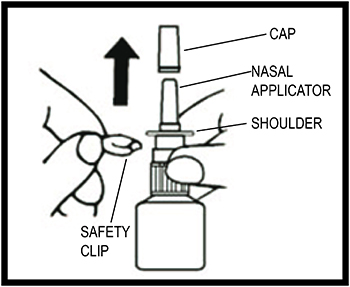
Figure A
Step 2. Hold the bottle and press down on the shoulders of the nasal applicator with your forefinger and middle finger.
- Support the bottom of the bottle with your thumb (see Figure B). Prime the bottle by pressing and releasing the shoulders of the bottle down firmly 5 times or until you see a fine mist come out of the nasal applicator.
- Now your pump is primed and ready to use.
- If you do not use olopatadine HCl nasal spray for more than 7 days, you will need to prime the bottle again by pressing and releasing the shoulders of the bottle down firmly 2 times or until you see a fine mist come out of the nasal applicator.
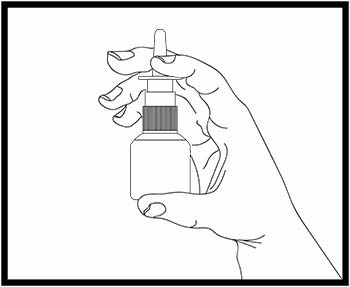
Figure B
Step 3. Gently blow your nose to clear your nostrils. Hold 1 nostril closed with a finger. Tilt your head down (chin toward chest) and insert the nasal applicator into a nostril. Hold the bottle upright with the nasal applicator tip pointing away from the center of the nose (see Figure C).
Step 4. Breathe in gently through your nose. While breathing in, press firmly and quickly on the nasal applicator shoulders to release the spray into your nostril (see Figure C).
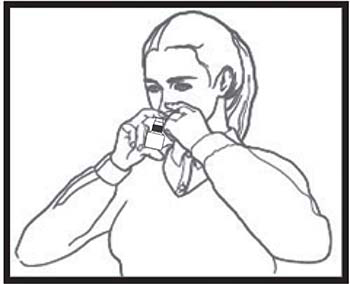
Figure C
Step 5. Breathe out through your mouth. Do not tilt your head back or blow your nose right after using olopatadine HCl nasal spray. This may cause you to get a bitter taste in your mouth.
Step 6. Repeat Steps 3 through 5 above to deliver a spray in your other nostril.
Step 7. If your healthcare provider tells you to use 2 sprays in each nostril, repeat Steps 3 through 5 for the second spray in each nostril.
Step 8. Wipe the nasal applicator with a clean tissue and replace the plastic cap (see Figure D).
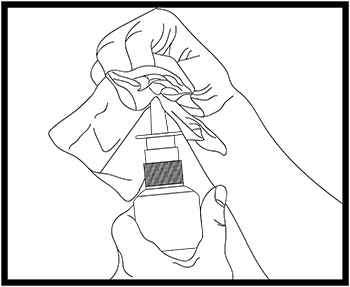
Figure D
Cleaning the olopatadine HCl nasal spray nasal applicator
Step 9. To clean the nasal applicator, remove the plastic cap (see Figure E).
If the nasal applicator becomes clogged, do not try to clear it using a pointed object.
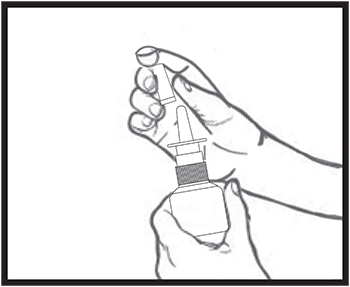
Figure E
Step 10. Gently pull the nasal applicator up to remove it from the bottle (see Figure F).
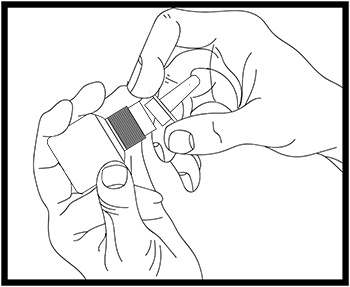
Figure F
Step 11. With the nasal applicator pointing downwards, wash it by running warm tap water into the nasal applicator for about 1 minute (see Figure G).
Step 12. Shake the nasal applicator to remove any water and put the nasal applicator back on the bottle.
Step 13. Prime the bottle again by pressing the shoulders of the bottle down firmly and releasing the shoulders 2 times or until you see a fine mist come out of the white nasal applicator. Repeat Steps 11 and 12 above if the nasal applicator is still clogged.
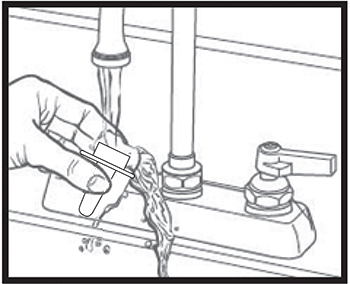
Figure G
How should I store olopatadine HCl nasal spray?
- Store olopatadine HCl nasal spray at room temperature between 39°F to 77°F (4°C to 25°C).
- Do not use olopatadine HCl nasal spray after the expiration date on the label or box.
Keep olopatadine HCl nasal spray and all medicines out of the reach of children.
For more information about olopatadine HCl nasal spray, call 1-877-835-5472.
Distributed by: Amneal Pharmaceuticals LLC Bridgewater, NJ 08807
Rev. 04-2021-01
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Principal Display Panel
DISCLAIMER:
"This tool does not provide medical advice, and is for informational and educational purposes only, and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, treatment or diagnosis. Call your doctor to receive medical advice. If you think you may have a medical emergency, please dial 911."
"Do not rely on openFDA to make decisions regarding medical care. While we make every effort to ensure that data is accurate, you should assume all results are unvalidated. We may limit or otherwise restrict your access to the API in line with our Terms of Service."
"This product uses publicly available data from the U.S. National Library of Medicine (NLM), National Institutes of Health, Department of Health and Human Services; NLM is not responsible for the product and does not endorse or recommend this or any other product."
PillSync may earn a commission via links on our site