Salsalate (salsalate 500 mg) Dailymed
Generic: salsalate is used for the treatment of Arthritis Fever Gastrointestinal Hemorrhage Pain Peptic Ulcer Pregnancy
IMPRINT: AN 513
SHAPE: oval
COLOR: yellow SCORE: 2
All Imprints
salsalate 750 mg - an 513 capsule yellow
salsalate 500 mg - an 512 round yellow
Boxed Warning
Boxed Warning Section
- NSAIDs may cause an increased risk of serious cardiovascular thrombotic events, myocardial infarction, and stroke, which can be fatal. This risk may increase with duration of use. Patients with cardiovascular disease or risk factors for cardiovascular disease may be at greater risk (see WARNINGS and CLINICAL TRIALS).
- Salsalate tablets are contraindicated for the treatment of perioperative pain in the setting of coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery (see WARNINGS ).
- NSAIDs cause an increased risk of serious gastrointestinal adverse events including bleeding, ulceration, and perforation of the stomach or intestines, which can be fatal. These events can occur at any time during use and without warning symptoms. Elderly patients are at greater risk for serious gastrointestinal events (see WARNINGS ).
Go PRO for all pill images
Boxed Warning Section
Cardiovascular Risk
- NSAIDs may cause an increased risk of serious cardiovascular thrombotic events, myocardial infarction, and stroke, which can be fatal. This risk may increase with duration of use. Patients with cardiovascular disease or risk factors for cardiovascular disease may be at greater risk (see WARNINGS and CLINICAL TRIALS).
- Salsalate tablets are contraindicated for the treatment of perioperative pain in the setting of coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery (see WARNINGS ).
Gastrointestinal Risk
- NSAIDs cause an increased risk of serious gastrointestinal adverse events including bleeding, ulceration, and perforation of the stomach or intestines, which can be fatal. These events can occur at any time during use and without warning symptoms. Elderly patients are at greater risk for serious gastrointestinal events (see WARNINGS ).
Description
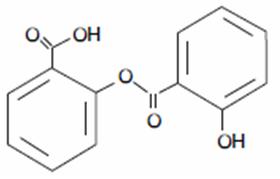
Salsalate USP, is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agent for oral administration. Chemically, salsalate, USP (salicylsalicylic acid or 2-hydroxy-benzoic acid, 2-carboxyphenyl ester) is a dimer of salicylic acid; its structural formula is shown below.
Chemical Structure:
Tablets:
Inactive Ingredients:  Carnauba wax, Colloidal Silicon Dioxide, Croscarmellose
Sodium, D&C Yellow #10, Hypromellose, Microcrystalline Cellulose, Polyethylene Glycol, Stearic Acid, Titanium Dioxide,
Clinical Pharmacology
Salsalate is insoluble in acid gastric fluids (<0.1 mg/ml at pH 1.0), but readily soluble in the small intestine where it is partially hydrolyzed to two molecules of salicylic acid. A significant portion of the parent compound is absorbed unchanged and undergoes rapid esterase hydrolysis in the body: its half-life is about one hour. About 13% is excreted through the kidneys as a glucuronide conjugate of the parent compound, the remainder as salicylic acid and its metabolites. Thus, the amount of salicylic acid available from salsalate is about 15% less than from aspirin, when the two drugs are administered on a salicylic acid molar equivalent basis (3.6 g salsalate/5 g aspirin). Salicylic acid biotransformation is saturated at anti-inflammatory doses of salsalate. Such capacity-limited biotransformation results in an increase in the half-life of salicylic acid from 3.5 to 16 or more hours. Thus, dosing with salsalate twice a day will satisfactorily maintain blood levels within the desired therapeutic range (10 to 30 mg/100 ml) throughout the 12-hour intervals. Therapeutic blood levels continue for up to 16 hours after the last dose. The parent compound does not show capacity-limited biotransformation, nor does it accumulate in the plasma on multiple dosing. Food slows the absorption of all salicylates including salsalate.
The mode of anti-inflammatory action of salsalate and other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs is not fully defined. Although salicylic acid (the primary metabolite of salsalate) is a weak inhibitor of prostaglandin synthesis in vitro , salsalate appears to selectively inhibit prostaglandin synthesis in vivo 1, providing anti-inflammatory activity equivalent to aspirin2 and indomethacin3. Unlike aspirin, salsalate does not inhibit platelet aggregation4. The usefulness of salicylic acid, the active in vivo product of salsalate, in the treatment of arthritic disorders has been established5,6. In contrast to aspirin, salsalate causes no greater fecal gastrointestinal blood loss than placebo7.
Indications And Usage
Carefully consider the potential benefits and risks of Salsalate tablets and other treatment options before deciding to use Salsalate tablets. Use the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration consistent with individual patient treatment goals (see WARNINGS ). Salsalate is indicated for relief of the signs and symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis and related rheumatic disorder.
Contraindications
Salsalate tablets are contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to salsalate. Salsalate tablets should not be given to patients who have experienced asthma, urticaria, or allergic-type reactions after taking aspirin or other NSAIDs. Severe, rarely fatal, anaphylactic-like reactions to NSAIDs have been reported in such patients (see¬† WARNINGS ‚Äď Anaphylactoid Reactions , and¬† PRECAUTIONS - Preexisting Asthma ).
Salsalate tablets are contraindicated for the treatment of peri-operative pain in the setting of coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery (see  WARNINGS ).
Warnings
Reye’s Syndrome may develop in individuals who have chicken pox, influenza, or flu symptoms. Some studies suggest a possible association between the development of Reye’s Syndrome and the use of medicines containing salicylate or aspirin. Salsalate contains a salicylate and therefore is not recommended for  use in patients with chicken pox, influenza, or flu symptoms.
CARDIOVASCULAR EFFECTS
Cardiovascular Thrombotic Events
Clinical trials of several COX-2 selective and nonselective NSAIDs of up to three years duration have shown an increased risk of serious cardiovascular (CV) thrombotic events, myocardial infarction, and stroke, which can be fatal. All NSAIDs, both COX-2 selective and nonselective, may have a similar risk. Patients with known CV disease or risk factors for CV disease may be at greater risk. To minimize the potential risk for an adverse CV event in patients treated with an NSAID, the lowest effective dose should be used for the shortest duration possible. Physicians and patients should remain alert for the development of such events, even in the absence of previous CV symptoms. Patients should be informed about the signs and/or symptoms of serious CV events and the steps to take if they occur. There is no consistent evidence that concurrent use of aspirin mitigates the increased risk of serious CV thrombotic events associated with NSAID use. The concurrent use of aspirin and an NSAID does increase the risk of serious GI events (see  GI WARNINGS ).
Two large, controlled, clinical trials of a COX-2 selective NSAID for the treatment of pain in the first 10 to 14 days following CABG surgery found an increased incidence of myocardial infarction and stroke (see  CONTRAINDICATIONS ).
Hypertension
NSAIDs, including Salsalate tablets, can lead to onset of new hypertension or worsening of pre-existing hypertension, either of which may contribute to the increased incidence of CV events. Patients taking thiazides or loop diuretics may have impaired response to these therapies when taking NSAIDs. NSAIDs, including Salsalate tablets, should be used with caution in patients with hypertension. Blood pressure (BP) should be monitored closely during the initiation of NSAID treatment and throughout the course of therapy.
Congestive Heart Failure and Edema
Fluid retention and edema have been observed in some patients taking NSAIDs. Salsalate tablets should be used with caution in patients with fluid retention or heart failure.
Gastrointestinal Effects-Risk of Ulceration, Bleeding, and Perforation
NSAIDs, including Salsalate tablets, can cause serious gastrointestinal (GI) adverse events including inflammation, bleeding, ulceration, and perforation of the stomach, small intestine, or large intestine, which can be fatal. These serious adverse events can occur at any time, with or without warning symptoms, in patients treated with NSAIDs. Only one in five patients, who develop a serious upper GI adverse event on NSAID therapy, is symptomatic. Upper GI ulcers, gross bleeding, or perforation caused by NSAIDs occur in approximately 1% of patients treated for 3 to 6 months, and in about 2% to 4% of patients treated for one year. These trends continue with longer duration of use, increasing the likelihood of developing a serious GI event at some time during the course of therapy.
However, even short-term therapy is not without risk. NSAIDs should be prescribed with extreme caution in those with a prior history of ulcer disease or gastrointestinal bleeding. Patients with a prior history of peptic ulcer disease and/or gastrointestinal bleeding who use NSAIDs have a greater than 10-fold increased risk for developing a GI bleed compared to patients with neither of these risk factors. Other factors that increase the risk for GI bleeding in patients treated with NSAIDs include concomitant use of oral corticosteroids or anticoagulants, longer duration of NSAID therapy, smoking, use of alcohol, older age, and poor general health status. Most spontaneous reports of fatal GI events are in elderly or debilitated patients and therefore, special care should be taken in treating this population. To minimize the potential risk for an adverse GI event in patients treated with an NSAID, the lowest effective dose should be used for the shortest possible duration. Patients and physicians should remain alert for signs and symptoms of GI ulceration and bleeding during NSAID therapy and promptly initiate additional evaluation and treatment if a serious GI adverse event is suspected. This should include discontinuation of the NSAID until a serious GI adverse event is ruled out. For high risk patients, alternate therapies that do not involve NSAIDs should be considered.
Renal Effects
Long-term administration of NSAIDs has resulted in renal papillary necrosis and other renal injury. Renal toxicity has also been seen in patients in whom renal prostaglandins have a compensatory role in the maintenance of renal perfusion. In these patients, administration of a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug may cause a dose-dependent reduction in prostaglandin formation and, secondarily, in renal blood flow, which may precipitate overt renal decompensation. Patients at greatest risk of this reaction are those with impaired renal function, heart failure, liver dysfunction, those taking diuretics and ACE inhibitors, and the elderly. Discontinuation of NSAID therapy is usually followed by recovery to the pretreatment state.
Advanced Renal Disease
No information is available from controlled clinical studies regarding the use of Salsalate tablets in patients with advanced renal disease. Therefore, treatment with Salsalate tablets are not recommended in these patients with advanced renal disease. If Salsalate tablets therapy must be initiated, close monitoring of the patient's renal function is advisable.
Anaphylactoid Reactions
Fetal Toxicity
Premature Closure of Fetal Ductus Arteriosus:
Avoid use of NSAIDs, including salsalate, in pregnant women at about 30 weeks gestation and later. NSAIDs, including salsalate, increase the risk of premature closure of the fetal ductus arteriosus at approximately this gestational age.
Oligohydramnios/Neonatal Renal Impairment:
Use of NSAIDs, including salsalate, at about 20 weeks gestation or later in pregnancy may cause fetal renal dysfunction leading to oligohydramnios and, in some cases, neonatal renal impairment. These adverse outcomes are seen, on average, after days to weeks of treatment, although oligohydramnios has been infrequently reported as soon as 48 hours after NSAID initiation. Oligohydramnios is often, but not always, reversible with treatment discontinuation. Complications of prolonged oligohydramnios may, for example, include limb contractures and delayed lung maturation. In some postmarketing cases of impaired neonatal renal function, invasive procedures such as exchange transfusion or dialysis were required.
If NSAID treatment is necessary between about 20 weeks and 30 weeks gestation, limit salsalate use to the lowest effective dose and shortest duration possible. Consider ultrasound monitoring of amniotic fluid if salsalate treatment extends beyond 48 hours. Discontinue salsalate if oligohydramnios occurs and follow up according to clinical practice (see PRECAUTIONS: Pregnancy).
Inform pregnant women to avoid use of salsalate and other NSAIDs starting at 30 weeks gestation because of the risk of the premature closing of the fetal ductus arteriosus. If treatment with salsalate is needed for a pregnant woman between about 20 to 30 weeks gestation, advise her that she may need to be monitored for oligohydramnios, if treatment continues for longer than 48 hours (see WARNINGS: Fetal Toxicity, PRECAUTIONS: Pregnancy ).
Precautions
General
Patients on treatment with salsalate should be warned not to take other salicylates so as to avoid potentially toxic concentrations. Great care should be exercised when salsalate is prescribed in the presence of chronic renal insufficiency or peptic ulcer disease. Protein binding of salicylic acid can be influenced by nutritional status, competitive binding of other drugs, and fluctuations in serum proteins caused by disease (rheumatoid arthritis, etc.).
Although cross reactivity, including bronchospasm, has been reported occasionally with non-acetylated salicylates, including salsalate, in aspirin-sensitive patients8,9, salsalate is less likely than aspirin to induce asthma in such patients10.
Salsalate tablets cannot be expected to substitute for corticosteroids or to treat corticosteroid insufficiency. Abrupt discontinuation of corticosteroids may lead to disease exacerbation. Patients on prolonged corticosteroid therapy should have their therapy tapered slowly if a decision is made to discontinue corticosteroids. The pharmacological activity of Salsalate tablets in reducing [fever and] inflammation may diminish the utility of these diagnostic signs in detecting complications of presumed noninfectious, painful conditions.
Hepatic Effects
Borderline elevations of one or more liver tests may occur in up to 15% of patients taking NSAIDs including Salsalate tablets. These laboratory abnormalities may progress, may remain unchanged, or may be transient with continuing therapy. Notable elevations of ALT or AST (approximately three or more times the upper limit of normal) have been reported in approximately 1% of patients in clinical trials with NSAIDs. In addition, rare cases of severe hepatic reactions, including jaundice and fatal fulminant hepatitis, liver necrosis and hepatic failure, some of them with fatal outcomes have been reported.
A patient with symptoms and/or signs suggesting liver dysfunction, or in whom an abnormal liver test has occurred, should be evaluated for evidence of the development of a more severe hepatic reaction while on therapy with Salsalate tablets. If clinical signs and symptoms consistent with liver disease develop, or if systemic manifestations occur (e.g., eosinophilia, rash, etc.), Salsalate tablets should be discontinued.
Hematological Effects
Anemia is sometimes seen in patients receiving NSAIDs, including Salsalate tablets. This may be due to fluid retention, occult or gross GI blood loss, or an incompletely described effect upon erythropoiesis. Patients on long-term treatment with NSAIDs, including Salsalate tablets, should have their hemoglobin or hematocrit checked if they exhibit any signs or symptoms of anemia. NSAIDs inhibit platelet aggregation and have been shown to prolong bleeding time in some patients. Unlike aspirin, their effect on platelet function is quantitatively less, of shorter duration, and reversible. Patients receiving Salsalate tablets, who may be adversely affected by alterations in platelet function, such as those with coagulation disorders or patients receiving anticoagulants, should be carefully monitored.
Preexisting Asthma
Patients with asthma may have aspirin-sensitive asthma. The use of aspirin in patients with aspirin-sensitive asthma has been associated with severe bronchospasm which can be fatal. Since cross reactivity, including bronchospasm, between aspirin and other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs has been reported in such aspirin-sensitive patients, Salsalate tablets should not be administered to patients with this form of aspirin sensitivity and should be used with caution in patients with preexisting asthma.
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS
  Patients should be informed of the following information before initiating therapy with an NSAID and periodically during the course of ongoing therapy. Patients should also be encouraged to read the NSAID Medication Guide that accompanies each prescription dispensed.
1. Salsalate tablets, like other NSAIDs, may cause serious CV side effects, such as MI or stroke, which may result in hospitalization and even death. Although serious CV events can occur without warning symptoms, patients should be alert for the signs and symptoms of chest pain, shortness of breath, weakness, slurring of speech, and should ask for medical advice when observing any indicative sign or symptoms. Patients should be apprised of the importance of this follow-up (see  WARNINGS, Cardiovascular Effects ).
2. Salsalate tablets, like other NSAIDs, can cause GI discomfort and, rarely, serious GI side effects, such as ulcers and bleeding, which may result in hospitalization and even death. Although serious GI tract ulcerations and bleeding can occur without warning symptoms, patients should be alert for the signs and symptoms of ulcerations and bleeding, and should ask for medical advice when observing any indicative sign or symptoms including epigastric pain, dyspepsia, melena, and hematemesis. Patients should be apprised of the importance of this follow-up (see  WARNINGS, Gastrointestinal Effects: Risk of Ulceration, Bleeding, and Perforation ).
3. Salsalate tablets like other NSAIDs, can cause serious skin side effects such as exfoliative dermatitis, SJS, and TEN, which may result in hospitalizations and even death. Although serious skin reactions may occur without warning, patients should be alert for the signs and symptoms of skin rash and bulers, fever, or other signs of hypersensitivity such as itching, and should ask for medical advice when observing any indicative signs or symptoms. Patients should be advised to stop the drug immediately if they develop any type of rash and contact their physicians as soon as possible.
4. Patients should promptly report signs or symptoms of unexplained weight gain or edema to their physicians.
5. Patients should be informed of the warning signs and symptoms of hepatotoxicity (e.g., nausea, fatigue, lethargy, pruritus, jaundice, right upper quadrant tenderness, and "flu-like" symptoms). If these occur, patients should be instructed to stop therapy and seek immediate medical therapy.
6. Patients should be informed of the signs of an anaphylactoid reaction (e.g. difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat). If these occur, patients should be instructed to seek immediate emergency help (see  WARNINGS ).
7. In late pregnancy, as with other NSAIDs, Salsalate tablets should be avoided because it will cause premature closure of the ductus arteriosus.
LABORATORY TESTS
Plasma salicylic acid concentrations should be periodically monitored during long-term treatment with salsalate to aid maintenance of therapeutically effective levels: 10 to 30 mg/100 ml. Toxic manifestations are not usually seen until plasma concentrations exceed 30 mg/100 ml (see  OVERDOSAGE ). Urinary pH should also be regularly monitored: sudden acidification, as from pH 6.5 to 5.5, can double the plasma level, resulting in toxicity.
Because serious GI tract ulcerations and bleeding can occur without warning symptoms, physicians should monitor for signs or symptoms of GI bleeding. Patients on long-term treatment with NSAIDs, should have their CBC and a chemistry profile checked periodically. If clinical signs and symptoms consistent with liver or renal disease develop, systemic manifestations occur (e.g., eosinophilia, rash, etc.) or if abnormal liver tests persist or worsen, Salsalate tablets should be discontinued.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
ACE-inhibitors
Reports suggest that NSAIDs may diminish the antihypertensive effect of ACE-inhibitors. This interaction should be given consideration in patients taking NSAIDs concomitantly with ACE-inhibitors.
Aspirin
Salicylates antagonize the uricosuric action of drugs used to treat gout. ASPIRIN AND OTHER SALICYLATE DRUGS WILL BE ADDITIVE TO SALSALATE AND MAY INCREASE PLASMA CONCENTRATIONS OF SALICYLIC ACID TO TOXIC LEVELS. Drugs and foods that raise urine pH will increase renal clearance and urinary excretion of salicylic acid, thus lowering plasma levels: acidifying drugs or foods will decrease urinary excretion and increase plasma levels. Salicylates given concomitantly with anticoagulant drugs may predispose to systemic bleeding. Salicylates may enhance the hypoglycemic effect of oral antidiabetic drugs of the sulfonylurea class. Salicylate competes with a number of drugs for protein binding sites, notably penicillin, thiopental, thyroxine, triiodothyronine, phenytoin, sulfinpyrazone, naproxen, warfarin, methotrexate, and possibly corticosteroids. [When Salsalate tablets are administered with aspirin, its protein binding is reduced, although the clearance of free Salsalate tablets are not altered. The clinical significance of this interaction is not known; however,] as with other NSAIDs, concomitant administration of salsalate and aspirin is not generally recommended because of the potential of increased adverse effects.
Furosemide
Clinical studies, as well as post marketing observations, have shown that Salsalate tablets can reduce the natriuretic effect-of furosemide and thiazides in some patients. This response has been attributed to inhibition of renal prostaglandin synthesis. During concomitant therapy with NSAIDs, the patient should be observed closely for signs of renal failure (see  PRECAUTIONS, Renal Effects ), as well as to assure diuretic efficacy.
Lithium
NSAIDs have produced an elevation of plasma lithium levels and a reduction in renal lithium clearance. The mean minimum lithium concentration increased 15% and the renal clearance was decreased by approximately 20%. These effects have been attributed to inhibition of renal prostaglandin synthesis by the NSAID. Thus, when NSAIDs and lithium are administered concurrently, subjects should be observed carefully for signs of lithium toxicity.
Methotrexate
NSAIDs have been reported to competitively inhibit methotrexate accumulation in rabbit kidney slices. This may indicate that they could enhance the toxicity of methotrexate. Caution should be used when NSAIDs are administered concomitantly with methotrexate.
Warfarin
The effcts of warfarin and NSAIDs on GI bleeding are synergistic, such that users of both drugs together have a risk of serious GI bleeding higher than users of either drug alone.
Drug/Laboratory Test Interactions: Salicylate competes with thyroid hormone for binding to plasma proteins, which may be reflected in a depressed plasma T4 value in some patients; thyroid function and basal metabolismare unaffected.
Carcinogenesis
No long-term animal studies have been performed with salsalate to evaluate its carcinogenic potential.
Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Use of NSAIDs, including salsalate, can cause premature closure of the fetal ductus arteriosus and fetal renal dysfunction leading to oligohydramnios and, in some cases, neonatal renal impairment. Because of these risks, limit dose and duration of salsalate use between about 20 and 30 weeks of gestation, and avoid salsalate use at about 30 weeks of gestation and later in pregnancy (see Clinical Considerations, Data).
Premature Closure of Fetal Ductus Arteriosus
Use of NSAIDs, including salsalate, at about 30 weeks gestation or later in pregnancy increases the risk of premature closure of the fetal ductus arteriosus.
Oligohydramnios/Neonatal Renal Impairment
Use of NSAIDs at about 20 weeks gestation or later in pregnancy has been associated with cases of fetal renal dysfunction leading to oligohydramnios, and in some cases, neonatal renal impairment.
Data from observational studies regarding other potential embryofetal risks of NSAID use in women in the first or second trimesters of pregnancy are inconclusive. In the general U.S. population, all clinically recognized pregnancies, regardless of drug exposure, have a background rate of 2% to 4% for major malformations, and 15% to 20% for pregnancy loss. Reproductive studies conducted in rats and rabbits have not demonstrated evidence of developmental abnormalities. However, animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response. There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Based on animal data, prostaglandins have been shown to have an important role in endometrial vascular permeability, blastocyst implantation, and decidualization. In animal studies, administration of prostaglandin synthesis inhibitors such as [active moiety], resulted in increased pre- and post-implantation loss. Prostaglandins also have been shown to have an important role in fetal kidney development. In published animal studies, prostaglandin synthesis inhibitors have been reported to impair kidney development when administered at clinically relevant doses.
Clinical Considerations
 
Fetal/Neonatal Adverse Reactions
Premature Closure of Fetal Ductus Arteriosus:
Avoid use of NSAIDs in women at about 30 weeks gestation and later in pregnancy, because NSAIDs, including salsalate, can cause premature closure of the fetal ductus arteriosus (see Data).
Oligohydramnios/Neonatal Renal Impairment
If an NSAID is necessary at about 20 weeks gestation or later in pregnancy, limit the use to the lowest effective dose and shortest duration possible. If salsalate treatment extends beyond 48 hours, consider monitoring with ultrasound for oligohydramnios. If oligohydramnios occurs, discontinue salsalate and follow up according to clinical practice (see Data).
Data
Human Data
Premature Closure of Fetal Ductus Arteriosus:
Published literature reports that the use of NSAIDs at about 30 weeks of gestation and later in pregnancy may cause premature closure of the fetal ductus arteriosus.
Oligohydramnios/Neonatal Renal Impairment:
Published studies and postmarketing reports describe maternal NSAID use at about 20 weeks gestation or later in pregnancy associated with fetal renal dysfunction leading to oligohydramnios, and in some cases, neonatal renal impairment. These adverse outcomes are seen, on average, after days to weeks of treatment, although oligohydramnios has been infrequently reported as soon as 48 hours after NSAID initiation. In many cases, but not all, the decrease in amniotic fluid was transient and reversible with cessation of the drug. There have been a limited number of case reports of maternal NSAID use and neonatal renal dysfunction without oligohydramnios, some of which were irreversible. Some cases of neonatal renal dysfunction required treatment with invasive procedures, such as exchange transfusion or dialysis.
Methodological limitations of these postmarketing studies and reports include lack of a control group; limited information regarding dose, duration, and timing of drug exposure; and concomitant use of other medications. These limitations preclude establishing a reliable estimate of the risk of adverse fetal and neonatal outcomes with maternal NSAID use. Because the published safety data on neonatal outcomes involved mostly preterm infants, the generalizability of certain reported risks to the full-term infant exposed to NSAIDs through maternal use is uncertain.
Labor and Delivery
There exist no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Although adverse effects on mother or infant have not been reported with salsalate use during labor, caution is advised when anti-inflammatory dosage is involved. However, other salicylates have been associated with prolonged gestation and labor, maternal and neonatal bleeding sequelae, potentiation of narcotic and barbiturate effects (respiratory or cardiac arrest in the mother), delivery problems and stillbirth. In rat studies with NSAIDs, as with other drugs known to inhibit prostaglandin synthesis, an increased incidence of dystocia, delayed parturition, and decreased pup survival occurred. The effects of Salsalate tablets on labor and delivery in pregnant women are unknown.
Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether salsalate per se is excreted in human milk; salicylic acid, the primary metabolite of salsalate, has been shown to appear in human milk in concentrations approximating the maternal blood level. Thus, the infant of a mother on salsalate therapy might ingest in mother’s milk 30 to 80% as much salicylate per kg body weight as the mother is taking. Accordingly, caution should be exercised when salsalate is administered to a nursing woman.
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of salsalate use in children have not been established (see  WARNINGS section).
Geriatric Use
As with any NSAIDs, caution should be exercised in treating the elderly (65 years and older).
Adverse Reactions
In two well-controlled clinical trials, the following reversible adverse experiences characteristic of salicylates were most commonly reported with salsalate (n-280 pts; uled in descending order of frequency): tinnitus, nausea, hearing impairment, rash, and vertigo. These common symptoms of salicylates, i.e., tinnitus or reversible hearing impairment, are often used as a guide to therapy.
Although cause-and-effect relationships have not been established, spontaneous reports over a ten-year period have included the following additional medically significant adverse experiences: abdominal pain, abnormal hepatic function, anaphylactic shock, angioedema, bronchospasm, decreased creatinine clearance, diarrhea, G.I. bleeding, hepatitis, hypotension, nephritis and urticaria.
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Amneal Pharmaceuticals at 1-877-835-5472 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Abuse And Dependence
Drug abuse and dependence have not been reported with salsalate.
Overdosage
Death has followed ingestion of 10 to 30 g of salicylates in adults, but much larger amounts have been ingested without fatal outcome.
Symptoms: The usual symptoms of salicylism - tinnitus, vertigo, headache, confusion, drowsiness, sweating, hyperventilation, vomiting and diarrhea - will occur. More severe intoxication will lead to disruption of electrolyte balance and blood pH, and hyperthermia and dehydration.
Treatment: Further absorption of salsalate from the G.I. tract should be prevented by emesis (syrup of ipecac), and, if necessary, by gastric lavage.
Fluid and electrolyte imbalance should be corrected by the administration of appropriate I.V. therapy. Adequate renal function should be maintained. Hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis may be required in extreme cases.
Dosage And Administration
Carefully consider the potential benefits and risks of Salsalate tablets and other treatment options before deciding to use Salsalate tablets. Use the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration consistent with individual patient treatment goals (see  WARNINGS ).
After observing the response to initial therapy with Salsalate tablets, the dose and frequency should be adjusted to suit an individual patient's needs. Salsalate is indicated for relief of the signs and symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis and related rheumatic disorder.
Adults: The usual dosage is 3000 mg daily, given in divided doses as follows:
1) two doses of two 750 mg tablets; 2) two doses of three 500 mg tablets; or 3) three doses of two 500 mg tablets. Some patients, e.g., the elderly, may require a lower dosage to achieve therapeutic blood concentrations and to avoid the more common side effects such as auditory.
Alleviation of symptoms is gradual, and full benefit may not be evident for 3 to 4 days, when plasma salicylate levels have achieved steady-state. There is no evidence for development of tissue tolerance (tachyphylaxis), but salicylate therapy may induce increased activity of metabolizing liver enzymes, causing a greater rate of salicyluric acid production and excretion, with a resultant increase in dosage requirement for maintenance of therapeutic serum salicylate levels.
Children: Dosage recommendations and indications for salsalate use in children have not been established.
How Supplied
Salsalate tablets, USP¬†500 mg¬†are available as yellow colored, round, film-coated tablets debossed ‚ÄúAN‚ÄĚ over ‚Äú512‚ÄĚ on one side and plain on the other.They are supplied as follows:
Bottles of 100             NDC 65162-512-10Bottles of 500             NDC 65162-512-50Bottles of 1,000ct       NDC 65162-512-11
Salsalate tablets, USP¬†750 mg¬†are available as yellow colored, capsule-shaped, scored, film-coated tablets debossed ‚ÄúAN 513‚ÄĚ on one side and plain on the other.They are supplied as follows:
Bottles of100              NDC 65162-513-10Bottles of 500             NDC 65162-513-50Bottles of 1,000          NDC 65162-513-11
Dispense contents with a child-resistant closure (as required) and in a tight container as defined in the USP.
Store at 20¬įC to 25¬įC (68¬įF to 77¬įF); excursions permitted between 15¬į to 30¬įC (59¬į to 86¬įF) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Rx only
References
1. Morris HG, Sherman NA, McQuain C, et al: Effects of Salsalate (Non-
Acetylated Salicylate) and Aspirin (ASA) on Serum Prostaglandins in Humans. Ther. Drug Monit. 7:435-438, 1985.
2. April PA, Curran NJ, Ekohlm BP, et al: Multicenter Comparative Study of Salsalate (SSA) vs Aspirin (ASA) in Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA), Arthritis Rheumatism 30 (4 supplement):S93, 1987.
3. Deodhar SD, McLeod MM, Dick WC, et al: A Short-Term Comparative Trial of Salsalate and Indomethacin in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Curr. Med. Res. Opin., 5:185-188, 1977.
4. Estes D, Kaplan K: Lack of Platelet Effect With the Aspirin Analog, Salsalate, Arthritis and Rheumatism, 23:1303-1307, 1980.
5. Dick C, Dick PH, Nuki G, et al: Effect of Anti-inflammatory Drug Therapy on Clearance of 133Xe from Knee Joints of Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. British Med. J. 3:278-280, 1969.
6. Dick WC, Grayson MF, Woodburn A, et al: Indices of Inflammatory Activity. Ann. of the Rheum. Dis. 29:643-648, 1970.
7. Cohen A:Fecal Blood Loss and Plasma Salicylate Study of Salicylsalicylic Acid and Aspirin. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 19:242-247, 1979.
8. Chudwin DS, Strub M. Golden HE, et al: Sensitivity to Non-Acetylated Salicylates in a Patient with Asthma, Nasal Polyps, and Rheumatoid Arthritis. Annals of Allergy 57:133-134, 1986.
9. Spector SL, Wangaard CH, Farr RS: Aspirin and Concomitant Idiosyncrasies in Adult Asthmatic Patients. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol 64:500-506, 1979.
10. Stevenson DD, Schrank PJ, Hougham AJ, et al: Salsalate Cross Sensitivity in Aspirin-Sensitive Asthmatics. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol 81:181, 1988.
Distributed by: Amneal Pharmaceuticals LLC Bridgewater, NJ 08807
Rev. 08-2022-02
Dispense with Medication Guide available at: documents.amneal.com/mg/salsalate.pdf
Medication Guide For Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (nsaids)
Dispense with Medication Guide available at: documents.amneal.com/mg/salsalate.pdf
What is the most important information I should know about medicines called Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)?
NSAIDs can cause serious side effects, including:
- Increased risk of a heart attack or stroke that can lead to death. This risk may happen early in treatment and may increase:
- with increasing doses of NSAIDs
- with longer use of NSAIDs
Do not take NSAIDs right before or after a heart surgery called a ‚Äúcoronary artery bypass graft (CABG).‚ÄĚ
Avoid taking NSAIDs after a recent heart attack, unless your healthcare provider tells you to. You may have an increased risk of another heart attack if you take NSAIDs after a recent heart attack.
- Increased risk of bleeding, ulcers, and tears (perforation) of the esophagus (tube leading from the mouth to the stomach), stomach and intestines:
- anytime during use
- without warning symptoms
- that may cause death
The risk of getting an ulcer or bleeding increases with:
- past history of stomach ulcers, or stomach or intestinal bleeding with use of NSAIDs
- taking medicines called ‚Äúcorticosteroids‚ÄĚ, ‚Äúanticoagulants‚ÄĚ, ‚ÄúSSRIs‚ÄĚ, or ‚ÄúSNRIs‚ÄĚ
- increasing doses of NSAIDs
- longer use of NSAIDs
- smoking
- drinking alcohol
- oolder age
- poor health
- advanced liver disease
- bleeding problems
NSAIDs should only be used:
- exactly as prescribed
- at the lowest dose possible for your treatment
- for the shortest time needed
What are NSAIDs? NSAIDs are used to treat pain and redness, swelling, and heat (inflammation) from medical conditions such as different types of arthritis, menstrual cramps, and other types of short-term pain.
Who should not take NSAIDs? Do not take NSAIDS:
- if you have had an asthma attack, hives, or other allergic reaction with aspirin or any other NSAIDs.
- right before or after heart bypass surgery.
Before taking NSAIDs, tell your health care provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
- have liver or kidney problems
- have high blood pressure
- have asthma
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. Taking NSAIDs at about 20 weeks of pregnancy or later may harm your unborn baby. If you need to take NSAIDs for more than 2 days when you are between 20 and 30 weeks of pregnancy, your healthcare provider may need to monitor the amount of fluid in your womb around your baby. You should not take NSAIDs after about 30 weeks of pregnancy.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breast feed.
Tell your health care provider about all of the medicines you take, including prescription or over-the-counter medicines, vitamins or herbal supplements. NSAIDs and some other medicines can interact with each other and cause serious side effects. Do not start taking new medicine without talking to your health care provider first.
What are the possible side effects of NSAIDs? NSAIDs can cause serious side effects, including: See ‚ÄúWhat is the most important information I should know about medicines called Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)?‚ÄĚ
- ·new or worse high blood pressure
- heart failure
- liver problems including liver failure
- kidney problems including kidney failure
- low red blood cells (anemia)
- life-threatening skin reactions
- life-threatening allergic reactions
- Other side effects of NSAIDs include: stomach pain, constipation, diarrhea, gas, heartburn, nausea, vomiting and dizziness.
Get emergency help right away if you get any of the following symptoms:
- shortness of breath or trouble breathing
- chest pain
- weakness in one part or side of your body
- slurred speech
- swelling of the face or throat
Stop taking your NSAID and call your health care provider right away if you get any of the following symptoms:
- ·nausea
- more tired or weaker than usual
- diarrhea
- itching
- your skin or eyes look yellow
- indigestion or stomach pain
- flu-like symptoms
- ·vomit blood
- there is blood in your bowel movement or it is black and sticky like tar
- unusual weight gain
- skin rash or bulers with fever
- swelling of the arms, legs, hands, and feet
If you take too much of your NSAID, call your health care provider or get medical help right away. These are not all the possible side effects of NSAIDs. For more information, ask your health care provider or pharmacist about NSAIDs. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
Other information about NSAIDs
- Aspirin is an NSAID but it does not increase the chance of a heart attack. Aspirin can cause bleeding in the brain, stomach, and intestines. Aspirin can also cause ulcers in the stomach and intestines.
- Some NSAIDs are sold in lower doses without a prescription (over-the-counter). Talk to your health care provider before using over-the-counter NSAIDs for more than 10 days.
General information about the safe and effective use of NSAIDs Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those uled in a Medication Guide. Do not use NSAIDs for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give NSAIDs to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. If you would like more information about NSAIDs, talk with your health care provider. You can ask your pharmacist or health care provider for information about NSAIDs that is written for health professionals.
Distributed by: Amneal Pharmaceuticals LLC
Bridgewater, NJ 08807 For more information, go to www.amneal.com or call 1-877-835-5472.
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Revised: 08-2022-00
 
 
Package Label.principal Display Panel
Package Label.principal Display Panel
DISCLAIMER:
"This tool does not provide medical advice, and is for informational and educational purposes only, and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, treatment or diagnosis. Call your doctor to receive medical advice. If you think you may have a medical emergency, please dial 911."
"Do not rely on openFDA to make decisions regarding medical care. While we make every effort to ensure that data is accurate, you should assume all results are unvalidated. We may limit or otherwise restrict your access to the API in line with our Terms of Service."
"This product uses publicly available data from the U.S. National Library of Medicine (NLM), National Institutes of Health, Department of Health and Human Services; NLM is not responsible for the product and does not endorse or recommend this or any other product."
PillSync may earn a commission via links on our site




