SUNITINIB MALATE Dailymed
Generic: sunitinib malate is used for the treatment of Carcinoma, Renal Cell Pancreatic Neoplasms Neuroendocrine Tumors Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors
Boxed Warning
Warning: Hepatotoxicity
Go PRO for all pill images
Warning: Hepatotoxicity
                                                                                     
Hepatotoxicity may be severe, and in some cases, fatal. Monitor hepatic function and interrupt, dose reduce, or discontinue sunitinib malate as recommended [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
WARNING: HEPATOTOXICITY
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
Hepatotoxicity may be severe, and in some cases fatal. Monitor hepatic function and interrupt, dose reduce, or discontinue sunitinib malate as recommended   [seeWarnings and Precautions (5.1) ].
1 Indicationsand Usage
Sunitinib malate is a kinase inhibitor indicated for:
- treatment of adult patients with gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) after disease progression on or intolerance to imatinib mesylate. (
1.1 )- treatment of adult patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC). (
1.2 )- adjuvant treatment of adult patients at high risk of recurrent RCC following nephrectomy.  (
1.3 )- treatment of progressive, well-differentiated pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (pNET) in adult patients with unresectable locally advanced or metastatic disease. (
1.4 )1.1 Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor
Sunitinib malate capsules are indicated for the treatment of adult patients with gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) after disease progression on or intolerance to imatinib mesylate.
1.2 Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma
Sunitinib malate capsules are indicated for the treatment of adult patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC).
1.3 Adjuvant Treatment of Renal Cell Carcinoma
Sunitinib malate capsules are indicated for the adjuvant treatment of adult patients at high risk of recurrent RCC following nephrectomy.
1.4 Advanced Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors
Sunitinib malate capsules are indicated for the treatment of progressive, well-differentiated pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (pNET) in adult patients with unresectable locally advanced or metastatic disease.
2 Dosage And Administration
GIST and Advanced RCC:
- The recommended dosage is 50 mg orally once daily for the first 4 weeks of each 6-week cycle (Schedule 4/2). (
2.1 )
Adjuvant Treatment of RCC:
-  The recommended dosage is 50 mg orally once daily for the first 4 weeks of a 6-week cycle (Schedule 4/2) for a maximum of 9 cycles. (
2.2 )
pNET:
- The recommended dosage is 37.5 mg orally once daily. (
2.3) 2.1 Recommended Dosage for GIST and Advanced RCC
The recommended dosage of sunitinib malate capsules for gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) and advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is 50 mg taken orally once daily, on a schedule of 4 weeks on treatment followed by 2 weeks off (Schedule 4/2) until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. Sunitinib malate capsules may be taken with or without food.
2.2 Recommended Dosage for Adjuvant Treatment of RCC
The recommended dosage of sunitinib malate capsules for the adjuvant treatment of RCC is 50 mg taken orally once daily, on a schedule of 4 weeks on treatment followed by 2 weeks off (Schedule 4/2), for nine 6-week cycles. Sunitinib malate capsules may be taken with or without food.
2.3 Recommended Dosage for pNET
The recommended dosage of sunitinib malate capsules for pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (pNET) is 37.5 mg taken orally once daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. Sunitinib malate capsules may be taken with or without food.
2.4 DosageModifications for Adverse Reactions
To manage adverse reactions, the recommended dosage modifications are provided in Table 1. Table 2 provides the recommended dosage reductions of sunitinib malate capsules for adverse reactions.
Table 1. Recommended Dosage Reductions of Sunitinib Malate Capsules for Adverse Reactions
Indications GIST RCC pNET     Advanced RCC Adjuvant RCC First dose reduction 37.5 mg once daily 37.5 mg once daily 37.5 mg once daily 25 mg once daily Second dose reduction 25 mg once daily 25 mg once daily NA NA
Table 2. Recommended Dosage Modifications for Sunitinib Malate Capsules for Adverse Reactions
Adverse Reaction Severity Dosage Modifications for Sunitinib Malate Capsules Hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] Grade 3
- Withhold until resolution to Grade 0 to 1 or baseline.
- Resume at a reduced dose.
- For recurring Grade 3 permanently discontinue.
Grade 4 ‚ÄĘ Permanently discontinue. Cardiovascular events [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] Asymptomatic cardiomyopathy (left ventricular ejection fraction greater than 20% but less than 50% below baseline or below the lower limit of normal if baseline was not obtained)
- Withhold until resolution to Grade 0 to 1 or baseline.
- Resume at reduced dose.
Clinically manifested congestive heart failure (CHF)
- Permanently discontinue.
Hypertension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)] Grade 3
- Withhold until resolution to Grade 0 to 1 or baseline.
- Resume at a reduced dose.
Grade 4
- Permanently discontinue.
Hemorrhagic events [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)] Grade 3 or 4
- Withhold until resolution to Grade 0 to 1 or baseline.
- Either resume at a reduced dose or discontinue depending on the severity and persistence of adverse reaction.
Thrombotic microangiopathy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)] Any Grade
- Permanently discontinue.
Proteinuria or Nephrotic syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)] 3 or more grams proteinuria in 24 hours in the absence of nephrotic syndrome  
- Withhold until resolution to Grade 0 to 1 or baseline.
- Resume at a reduced dose.
Nephrotic syndrome or recurrent proteinuria of 3 or more grams per 24 hours despite dose reductions
- Permanently discontinue.
Dermatological toxicities Erythema multiforme (EM), Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS), toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), Necrotizing fasciitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)] Any Grade  
- Permanently discontinue.
Reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)] Any Grade
- Permanently discontinue.
Osteonecrosis of the jaw [see Warnings and Precautions (5.13)] Any Grade
- The safety of resumption of sunitinib malate capsules after osteonecrosis has not been established.
- Either resume at a reduced dose or discontinue depending on the severity and persistence of the adverse reaction.
Impaired wound healing [see Warnings and Precautions (5.14)] Any Grade
- The safety of resumption of sunitinib malate capsules after resolution of wound healing has not been established.
- Either resume at a reduced dose or discontinue depending on the severity and persistence of the adverse reaction.
2.5 Dosage Modification for Drug Interactions
Strong CYP3A4 Inhibitors
Select an alternate concomitant medication with no or minimal enzyme inhibition potential. If coadministration of sunitinib malate capsules with a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor cannot be avoided, consider a dose reduction for sunitinib malate capsules to a minimum dosage as follows [see Drug Interactions (7.1)] :
- GIST and RCC: 37.5 mg orally once daily, on a schedule of 4 weeks on treatment followed by 2 weeks off (Schedule 4/2)
- pNET: 25 mg orally once daily
Strong CYP3A4 Inducers
Select an alternate concomitant medication with no or minimal enzyme induction potential. If coadministration of sunitinib malate capsules with a strong CYP3A4 inducer cannot be avoided, consider a dose increase for sunitinib malate capsules to a maximum dosage as follows:
- GIST and RCC: 87.5 mg orally once daily, on a schedule of 4 weeks on treatment followed by 2 weeks off (Schedule 4/2)
- pNET: 62.5 mg orally once daily
If the dose of sunitinib malate capsules is increased, monitor patients carefully for adverse reactions [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
2.6 Dosage Modification for End-Stage Renal Disease Patients on Hemodialysis
No starting dose adjustment is required in patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) on hemodialysis. However, given the decreased exposure compared to patients with normal renal function, subsequent doses may be increased gradually up to 2-fold based on safety and tolerability [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
3 Dosage Formsand Strengths
Capsules, hard gelatin:
¬†¬†¬†¬† ‚Äʬ†12.5 mg sunitinib: red opaque cap and red opaque body imprinted ‚ÄėS12.5‚Äô on body with white ink and plain cap, containing yellow to orange granules.
¬†¬†¬†¬† ‚Äʬ†25 mg sunitinib: olive green opaque cap and red opaque body imprinted ‚ÄėS25‚Äô on body with white ink and plain cap, containing yellow to orange granules.
¬†¬†¬†¬† ‚Äʬ†37.5 mg sunitinib: light green opaque cap and light green opaque body imprinted ‚ÄėS37.5‚Äô on body with black ink and plain cap, containing yellow to orange granules.
¬†¬†¬†¬† ‚Äʬ†50 mg sunitinib: olive green opaque cap and olive green opaque body imprinted ‚ÄėS50‚Äô on body with black ink and plain cap, containing yellow to orange granules.
Capsules: 12.5 mg, 25 mg, 37.5 mg, 50 mg sunitinib (3 )
4 Contraindications
None.
None (4 )
5 Warnings And Precautions
- Hepatotoxicity: Fatal liver failure has been observed. Monitor liver function tests at baseline, during each cycle, and as clinically indicated. Interrupt sunitinib malate for Grade 3 hepatotoxicity until resolution to Grade ‚ȧ1 or baseline and resume sunitinib malate at a reduced dose; discontinue if no resolution. Discontinue sunitinib malate in patients with Grade 4 hepatoxicity, in patients who have subsequent severe changes in liver function tests or other signs and symptoms of liver failure. (
2.4 ,5.1 )- Cardiovascular Events: Myocardial ischemia, myocardial infarction, heart failure, cardiomyopathy, and decreased left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) to below the lower limit of normal including death have occurred. Monitor for signs and symptoms of congestive heart failure and consider monitoring LVEF at baseline and periodically during treatment. Discontinue sunitinib malate for clinical manifestations of congestive heart failure. Interrupt and/or dose reduce for decreased LVEF. (
5.2 )- QT Interval Prolongation and Torsade de Pointes: Monitor patients at higher risk for developing QT interval prolongation. Consider monitoring of electrocardiograms and electrolytes. (
5.3 )- Hypertension: Monitor blood pressure at baseline and as clinically indicated. Initiate and/or adjust antihypertensive therapy as appropriate. Interrupt sunitinib malate for Grade 3 hypertension until resolution to Grade ‚ȧ1 or baseline, then resume sunitinib malate at a reduced dose. Discontinue sunitinib malate in patients who develop Grade 4 hypertension. (
5.4 )- Hemorrhagic Events: Tumor-related hemorrhage and viscus perforation (both with fatal events) have occurred. Perform serial complete blood counts and physical examinations. Interrupt sunitinib malate for Grade 3 or 4 hemorrhagic events until resolution to Grade ‚ȧ1 or baseline, then resume at a reduced dose; discontinue if no resolution. (
5.5 )- Tumor Lysis Syndrome (TLS): TLS (some fatal) has been reported primarily in patients with RCC and GIST. Monitor these patients and treat as clinically indicated. (
5.6 )- Thrombotic microangiopathy (TMA): TMA, including thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura and hemolytic uremic syndrome, sometimes leading to renal failure or a fatal outcome, has been reported. Discontinue sunitinib malate for TMA. (
5.7 )- Proteinuria: Renal failure or a fatal outcome has occurred. Monitor urine protein. Interrupt treatment for 24-hour urine protein of 3 or more grams. Discontinue for repeat episodes of 24-hour urine protein of 3 or more grams despite dose reductions or nephrotic syndrome. (
5.8 ) - Dermatologic Toxicities: Necrotizing fasciitis, erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS), and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) (some fatal) have occurred. Discontinue sunitinib malate for these events. (
5.9 )- Reversible Posterior Leukoencephalopathy Syndrome (RPLS): RPLS (some fatal) has been reported. Monitor for signs and symptoms of RPLS. Withhold sunitinib malate until resolution. (
5.10 )- Thyroid Dysfunction: Monitor thyroid function at baseline, periodically during treatment, and as clinically indicated. Initiate and/or adjust therapy for thyroid dysfunction as appropriate. (
5.11 )- Hypoglycemia: Check blood glucose levels regularly and assess if antidiabetic drug dose modifications are required. (
5.12 )- Osteonecrosis of the Jaw (ONJ): Withhold sunitinib malate for at least 3 weeks prior to invasive dental procedure and for development of ONJ until complete resolution. (
5.13 )- Impaired Wound Healing: Withhold sunitinib malate for at least 3 weeks prior to elective surgery. Do not administer for at least 2 weeks following major surgery and until adequate wound healing. The safety of resumption of sunitinib malate after resolution of wound healing complications has not been established. (
5.14 )- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: Can cause fetal harm. Advise patients of potential risk to a fetus and to use effective contraception. (
5.15 ,8.1 ,8.3 )5.1 Hepatotoxicity
Sunitinib malate can cause severe hepatotoxicity, resulting in liver failure or death.¬†In the pooled safety population, liver failure occurred in <1% of patients in clinical trials. Liver failure include jaundiced, elevated transaminases and/or hyperbilirubinemia in conjunction with encephalopathy, coagulopathy, and/or renal failure. Monitor liver function tests (alanine aminotransferase [ALT], aspartate aminotransferase [AST], and bilirubin) at baseline, during each cycle, and as clinically indicated. Interrupt sunitinib malate for Grade 3 hepatotoxicity until resolution to Grade ‚ȧ1 or baseline, then resume sunitinib malate at a reduced dose. Discontinue sunitinib malate in patients with Grade 4 hepatotoxicity, in patients without resolution of Grade 3 hepatotoxicity, in patients who subsequently experience severe changes in liver function tests and in patients who have other signs and symptoms of liver failure. Safety in patients with ALT or AST >2.5 x upper limit of normal (ULN) or with >5 x ULN and liver metastases has not been established.
5.2 Cardiovascular Events
Cardiovascular events, including heart failure, cardiomyopathy, myocardial ischemia,¬†and myocardial infarction, some of which were fatal, have been reported. In pooled safety population, 3% of patients experienced heart failure; 71% of the patients with heart failure were reported as recovered. Fatal cardiac failure was reported in <1% of patients. In the adjuvant treatment of RCC study, 11 patients experienced Grade 2 decreased ejection fraction (left ventricular ejection fraction [LVEF] 40% to 50% and a 10% to 19% decrease from baseline). In 3 of these 11 patients, the ejection fractions arm did not return to ‚Č•50% or baseline by the time of last measurement. No patients who received sunitinib malate were diagnosed with CHF. Patients who presented with cardiac events within 12 months prior to sunitinib malate administration, such as myocardial infarction (including severe/unstable angina), coronary/peripheral artery bypass graft, symptomatic CHF, cerebrovascular accident or transient ischemic attack, or pulmonary embolism were excluded from sunitinib malate clinical studies. Patients with prior anthracycline use or cardiac radiation were also excluded from some studies. It is unknown whether patients with these concomitant conditions may be at a higher risk of developing left ventricular dysfunction. Consider monitoring LVEF at baseline and periodically as clinically indicated. Carefully monitor patients for clinical signs and symptoms of congestive heart failure (CHF). Discontinue sunitinib malate in patients who experience clinical manifestations of CHF. Interrupt sunitinib malate and/or reduce the dose in patients without clinical evidence of CHF who have an ejection fraction of greater than 20% but less than 50% below baseline or below the lower limit of normal if baseline ejection fraction was not obtained.
5.3 QT Interval Prolongation and Torsade de Pointes
Sunitinib malate can cause QT interval prolongation in a dose-dependent manner, which may lead to an increased risk for ventricular arrhythmias including Torsade de Pointes. Torsade de Pointes was observed in <0.1% of patients. Monitor patients who are at higher risk of developing QT interval prolongation, including patients with a history of QT interval prolongation, patients who are taking antiarrhythmics, or patients with relevant pre-existing cardiac disease, bradycardia, or electrolyte disturbances. Consider periodic monitoring of electrocardiograms and electrolytes (i.e., magnesium, potassium) during treatment with sunitinib malate. Monitor QT interval more frequently when sunitinib malate is concomitantly administered with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors or drugs known to prolong QT interval. Consider dose reducing sunitinib malate [see Dosage and Administration (2.5), Drug Interactions (7.2)].
5.4 Hypertension
In¬†the pooled safety population, 29% of patients experienced hypertension. Grade 3 hypertension was reported in 7% of patients, and Grade 4 hypertension was reported in 0.2%. Monitor blood pressure at baseline and as clinically indicated. Initiate and/or adjust antihypertensive therapy as appropriate. In cases of Grade 3 hypertension, withhold sunitinib malate until resolution to Grade ‚ȧ1 or baseline, then resume sunitinib malate at a reduced dose. Discontinue sunitinib malate in patients with who develop Grade 4 hypertension.
5.5 Hemorrhagic Events and Viscus Perforation
Hemorrhagic events, some of which were fatal, have involved the gastrointestinal tract, respiratory tract, tumor, urinary tract, and brain. In the pooled safety population, 30% of patients experienced hemorrhagic events, including Grade 3¬†or 4 in 4.2% of patients. Epistaxis was the most common hemorrhagic event and gastrointestinal hemorrhage was the most common Grade¬†3 to 5 event. Tumor-related hemorrhage was observed in patients treated with sunitinib malate. These events may occur suddenly, and in the case of pulmonary tumors, may present as severe and life-threatening hemoptysis or pulmonary hemorrhage. Pulmonary hemorrhage, some with a fatal outcome, was observed in patients treated with sunitinib malate for metastatic RCC, GIST, and metastatic lung cancer. Sunitinib malate is not approved for use in patients with lung cancer. Serious, sometimes fatal, gastrointestinal complications including gastrointestinal perforation, have been reported in patients with intra-abdominal malignancies treated with sunitinib malate. Include serial complete blood counts (CBCs) and physical examinations with the clinical assessment of hemorrhagic events. Interrupt sunitinib malate for Grade 3 or 4 hemorrhagic events until resolution to Grade ‚ȧ1 or baseline, then resume sunitinib malate at a reduced dose.
Discontinue sunitinib malate in patients without resolution of Grade 3 or 4 hemorrhagic events.
5.6 Tumor Lysis Syndrome
Tumor Lysis Syndrome (TLS), some fatal, occurred in clinical trials and has been reported in postmarketing experience, primarily in patients with RCC or GIST. Patients generally at risk of TLS are those with high tumor burden prior to treatment. Monitor these patients for TLS and manage as appropriate.
5.7 Thrombotic Microangiopathy
Thrombotic Microangiopathy (TMA), including thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura and hemolytic uremic syndrome, sometimes leading to renal failure or a fatal outcome, occurred in clinical trials and in postmarketing experience of sunitinib malate as monotherapy and administered in combination with bevacizumab. Sunitinib malate is not approved for use in combination with bevacizumab. Discontinue sunitinib malate in patients developing TMA. Reversal of the effects of TMA has been observed after sunitinib malate was discontinued.
5.8 Proteinuria
Proteinuria and nephrotic syndrome have been reported. Some of these cases have resulted in renal failure and fatal outcomes. Monitor patients for the development or worsening of proteinuria. Perform baseline and periodic urinalyses during treatment, with follow up measurement of 24-hour urine protein as clinically indicated. Interrupt sunitinib malate and dose reduce for 24-hour urine protein of 3 or more grams. Discontinue sunitinib malate for patients with nephrotic syndrome or repeat episodes of 24-hour urine protein of 3 or more grams despite dose reductions. The safety of continued sunitinib malate treatment in patients with moderate to severe proteinuria has not been evaluated.
5.9 Dermatologic Toxicities
Severe cutaneous adverse reactions have been reported, including erythema multiforme (EM), Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS), and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), some of which were fatal. Permanently discontinue sunitinib malate for these severe cutaneous adverse reactions. Necrotizing fasciitis, including fatal cases, has been reported in patients treated with sunitinib malate, including of the perineum and secondary to fistula formation. Discontinue sunitinib malate in patients who develop necrotizing fasciitis.
5.10 Reversible Posterior Leukoencephalopathy Syndrome
Reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome (RPLS) has been reported in <1% of patients, some of which were fatal. Patients can present with hypertension, headache, decreased alertness, altered mental functioning, and visual loss, including cortical blindness. Magnetic resonance imaging is necessary to confirm the diagnosis. Discontinue sunitinib malate in patients developing RPLS.
5.11 Thyroid Dysfunction
Hyperthyroidism, some followed by hypothyroidism, have been reported in clinical trials and through postmarketing experience of sunitinib malate. Monitor thyroid function at baseline, periodically during treatment and as clinically indicated. Monitor patients closely for signs and symptoms of thyroid dysfunction, including hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, and thyroiditis, during treatment with sunitinib malate. Initiate and/or adjust therapies for thyroid dysfunction as appropriate.
5.12 Hypoglycemia
Sunitinib malate can result in symptomatic hypoglycemia, which may lead to loss of consciousness, or require hospitalization. In the pooled safety population, hypoglycemia occurred in 2% of the patients treated with sunitinib malate. Hypoglycemia has occurred in clinical trials in 2% of the patients treated with sunitinib malate for advanced RCC (Study 3) and GIST (Study 1) (n=577) and in approximately 10% of the patients treated with sunitinib malate for pNET (Study 6) (n=83). For patients being treated with sunitinib malate for pNET, pre-existing abnormalities in glucose homeostasis were not present in all patients who experienced hypoglycemia. Reductions in blood glucose levels may be worse in patients with diabetes. Check blood glucose levels at baseline, regularly during treatment, as clinically indicated and after discontinuation of sunitinib malate. In patients with diabetes, assess if antidiabetic therapies need to be adjusted to minimize the risk of hypoglycemia.
5.13 Osteonecrosis of the Jaw
Osteonecrosis of the Jaw (ONJ) occurred in patients treated with sunitinib malate. Concomitant exposure to other risk factors, such as bisphosphonates or dental disease/invasive dental procedures, may increase the risk of ONJ. Perform an oral examination prior to initiation of sunitinib malate and periodically during sunitinib malate therapy. Advise patients regarding good oral hygiene practices. Withhold sunitinib malate treatment for at least 3 weeks prior to scheduled dental surgery or invasive dental procedures, if possible. Withhold sunitinib malate for development of ONJ until complete resolution. The safety of resumption of sunitinib malate after resolution of osteonecrosis of the jaw has not been established.
5.14 Impaired Wound Healing
Impaired wound healing has been reported in patients who received sunitinib malate [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)]. Withhold sunitinib malate for at least 3 weeks prior to elective surgery. Do not administer for at least 2 weeks following major surgery and until adequate wound healing. The safety of resumption of sunitinib malate after resolution of wound healing complications has not been established.
5.15 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on findings from animal studies and its mechanism of action, sunitinib malate can cause fetal harm when administered to pregnant woman. Administration of sunitinib to pregnant rats and rabbits during the period of organogenesis resulted in teratogenicity at approximately 5.5 and 0.3 times the combined systemic exposure [combined area under the curve (AUC) of sunitinib plus its active metabolite] in patients administered the recommended daily dose (RDD) of 50 mg, respectively.
Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with sunitinib malate and for 4 weeks following the final dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)].
6 Adverse Reactions
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling.
- Hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Cardiovascular Events [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- QT Interval Prolongation and Torsade de Pointes [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Hypertension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Hemorrhagic Events [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Tumor Lysis Syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Thrombotic Microangiopathy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- Proteinuria [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
- Dermatologic Toxicities [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]
- Reversible Posterior Leukoencephalopathy Syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)]
- Thyroid Dysfunction [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)]
- Hypoglycemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12)]
- Osteonecrosis of the Jaw [see Warnings and Precautions (5.13)]
- Impaired Wound Healing [see Warnings and Precautions (5.14)]
- The most common adverse reactions (‚Č•25%) are fatigue/asthenia, diarrhea, mucositis/stomatitis, nausea, decreased appetite/anorexia, vomiting, abdominal pain, hand-foot syndrome, hypertension, bleeding events, dysgeusia/altered taste, dyspepsia, and thrombocytopenia. (
6 )
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Aurobindo Pharma USA, Inc. at 1-866-850-2876 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The pooled safety population described in the Warnings and Precautions reflect exposure to sunitinib malate in 7527 patients with GIST, RCC (advanced and adjuvant), or pNET. In this pooled safety population, the most common adverse reactions (‚Č•25%) were fatigue/asthenia, diarrhea, mucositis/stomatitis, nausea, decreased appetite/anorexia, vomiting, abdominal pain, hand-foot syndrome, hypertension, bleeding events, dysgeusia/altered taste, dyspepsia, and thrombocytopenia.
Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor
The safety of sunitinib malate was evaluated in Study 1, a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in which previously treated patients with GIST received sunitinib malate 50 mg daily on Schedule 4/2 (n=202) or placebo (n=102). Median duration of blinded study treatment was 2 cycles for patients on sunitinib malate (mean: 3.0; range: 1 to 9) and 1 cycle (mean; 1.8; range: 1 to 6) for patients on placebo at the time of the interim analysis.
Permanent discontinuation due to an adverse reaction occurred in 7% of patients in the sunitinib malate arm. Dose reductions occurred in 11% and dose interruptions occurred in 29% of patients who received sunitinib malate.
Table 3 summarizes the adverse reactions for Study 1.
Table 3. Adverse Reactions Reported in ‚Č• 10% of GIST Patients Who Received Sunitinib Malate in the Double-Blind Treatment Phase and More Commonly Than in Patients Given Placebo* in Study 1
 
   Adverse Reaction GIST Sunitinib Malate (N=202) Placebo (N=102) All Grade s % Grade 3 to 4 % All Grade s % Grade 3 to 4 % Any Adverse Reaction 94 56 97 51 Gastrointestinal    Diarrhea    Mucositis/stomatitis    Constipation   40 29 20  410   27 18 14  022 Metabolism/Nutrition    Anorexiaa    Asthenia   33 22  15   29 11  53 Dermatology    Skin discoloration    Rash    Hand-foot syndrome   30 14 14  014   239 10  003 Neurology    Altered taste   21  0   12  0 Cardiac    Hypertension   15  4   11  0 Musculoskeletal    Myalgia/limb pain   14  1  9  1
* Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE), version 3.0.
Abbreviations: GIST=gastrointestinal stromal tumor; N=number of patients.
a Includes decreased appetite.
 
Other clinically relevant adverse reactions included oral pain other than mucositis/stomatitis in 6%; hair color changes in 7%; alopecia in 5% of patients who received sunitinib malate.
Table 4 summarizes the laboratory abnormalities in Study 1.
Table 4. Laboratory Abnormalities Reported in ‚Č• 10% of GIST Patients Who Received Sunitinib Malate or Placebo in the Double-Blind Treatment Phase* in Study 1
      Laboratory Abnormality GIST Sunitinib Malate (N=202) Placebo (N=102) All Grades * % Grade 3 to 4*,a % All Grades * % Grade 3 to 4*, b % Any Laboratory Abnormality   34   22 Hematology    Neutrophils decreased    Lymphocytes decreased    Platelets decreased    Hemoglobin decreased  53383826   10 0 5 3  416422   0 0 0 2 Gastrointestinal     AST/ALT increased     Lipase increased     Alkaline phosphatase increased    Amylase increased    Total bilirubin increased    Indirect bilirubin increased   39 25 24 17 16 10   2 104510   23 17 21 1284   174300 Renal/Metabolic    Creatinine increased    Potassium decreased    Sodium increased   12 12 10   110   744   001 Cardiac    Decreased LVEF   11   1   3   0
* Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE), version 3.0.
Abbreviations: ALT=alanine aminotransferase; AST=aspartate aminotransferase; GIST=gastrointestinal stromal tumor; LVEF=left ventricular ejection fraction; N=number of patients.
a Grade 4 laboratory abnormalities in patients on sunitinib malate included alkaline phosphatase (1%), lipase (2%), creatinine (1%), potassium decreased (1%), neutrophils (2%), hemoglobin (2%), and platelets (1%).
b Grade 4 laboratory abnormalities in patients on placebo included amylase (1%), lipase (1%), and hemoglobin (2%).
After an interim analysis, the study was unblinded and patients on the placebo arm were given the opportunity to receive open-label sunitinib malate [see Clinical Studies (14.1)]. For 241 patients randomized to the sunitinib malate arm, including 139 who received sunitinib malate in both the double-blind and open-label phases, the median duration of sunitinib malate treatment was 6 cycles (mean: 8.5; range: 1 to 44). For the 255 patients who ultimately received open-label sunitinib malate treatment, median duration of treatment was 6 cycles (mean: 7.8; range: 1 to 37) from the time of the unblinding.
Permanent discontinuation due to an adverse reaction occurred in 20% of patients who received sunitinib malate. Dosage interruption occurred in 46% and dose reduction occurred in 28% of patients who received sunitinib malate.
The most common Grade 3 or 4 adverse reactions in patients who received sunitinib malate in the open-label phase were fatigue (10%), hypertension (8%), asthenia (5%), diarrhea (5%), hand-foot syndrome (5%), nausea (4%), abdominal pain (3%), anorexia (3%), mucositis (2%), vomiting (2%), and hypothyroidism (2%).
Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma
The safety of sunitinib malate was evaluated in Study 3, a double-blind, active-controlled trial in which previously untreated patients with locally advanced or metastatic RCC received sunitinib malate 50 mg daily on Schedule 4/2 (n=375) or interferon alfa 9 million International Units (MIU) (n=360). The median duration of treatment was 11.1 months (range: 0.4 to 46.1) for sunitinib malate treatment and 4.1 months (range: 0.1 to 45.6) for interferon alfa treatment.
Permanent discontinuation due to an adverse reaction occurred in 20% of patients in the sunitinib malate arm. Dose interruptions occurred in 54% and dose reductions occurred in 52% of patients who received sunitinib malate.
Table 5 summarizes the adverse reactions for Study 3.
 
Table 5. Adverse Reactions Reported in ‚Č• 10% of Patients With RCC Who Received Sunitinib Malate or Interferon Alfa* in Study 3
 
Adverse Reaction Treatment -Na√Įve RCC Sunitinib Malate (N=375) Interferon Alfa (N=360) All Grades % Grade 3 to 4a % All Grades % Grade 3 to 4b % Any Adverse Reaction 99 77 99 55 Gastrointestinal ¬†¬† Diarrhea¬†¬† Nausea¬†¬† Mucositis/stomatitis¬†¬† Vomiting¬†¬† Dyspepsia¬†¬† Abdominal painc ¬†¬† Constipation¬†¬† Dry mouth¬†¬† Oral pain¬†¬† Flatulence¬†¬† GERD/reflux esophagitis¬†¬† Glossodynia ¬†¬† Hemorrhoids ¬† 66 58 47 39 34 30 23 13 14 14 12 11 10 ¬† 106352510 <10 <100 ¬† 21 415 174 12 14712112 ¬† <12 <1101 <1 <100000 Constitutional ¬†¬† Fatigue ¬†¬† Asthenia¬†¬† Fever ¬†¬† Weight decreased ¬†¬†¬†Chills ¬†¬† Chest Pain ¬†¬† Influenza like illness ¬† 62 26 22 16 14 135 ¬† 15 111 <1120 ¬† 56 22 37 17 317 15 ¬† 156 <1101 <1 Metabolism/Nutrition ¬†¬† Anorexiad ¬†48 ¬†3 ¬†42 ¬†2 Neurology ¬†¬† Altered tastee ¬†¬† Headache ¬†¬† Dizziness ¬†472311 ¬†<11<1 ¬†151914 ¬†001 Hemorrhage/Bleeding ¬†¬† Bleeding, all sites 37 4f 10 1 Cardiac ¬†¬† Hypertension ¬†¬† Edema peripheral ¬†¬† Ejection fraction decreased ¬† 34 24 16 ¬† 1323 ¬† 455 ¬† <112 Dermatology ¬†¬† Rash ¬†¬† Hand-foot syndrome ¬†¬†¬† Skin discoloration/yellow skin¬†¬† Dry skin ¬†¬† Hair color changes ¬†¬† Alopecia ¬†¬† Erythema ¬†¬† Pruritus ¬† 29 29 25 23 20 14 12 12 ¬† 28 <1 <100 <1 <1 ¬† 11107 <1917 ¬† <1000000 <1 Musculoskeletal ¬†¬† Pain in extremity/limb discomfort ¬†¬† Arthralgia ¬†¬† Back pain ¬† 40 30 28 ¬† 535 ¬† 30 19 14 ¬† 212 Respiratory ¬†¬† Cough ¬†¬† Dyspnea ¬†¬† Nasopharyngitis ¬†¬† Oropharyngeal pain ¬†¬† Upper respiratory tract infection ¬† 27 26 14 14 11 ¬† 160 <1 <1 ¬† 14 20222 ¬† <14000 Endocrine ¬†¬† Hypothyroidism ¬† 16 ¬† 2 ¬† 1 ¬† 0 Psychiatric ¬†¬† Insomnia ¬†¬† Depressiong ¬† 15 11 ¬† <10 ¬† 10 14 ¬† 01
* Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE), version 3.0.
Abbreviations: ARs=adverse reactions; N=number of patients; RCC=renal cell carcinoma.
a Grade 4 ARs in patients on sunitinib malate included back pain (1%), arthralgia (<1%), dyspnea (<1%), asthenia (<1%), fatigue (<1%), limb pain (<1%), and rash (<1%).
b Grade 4 ARs in patients on interferon alfa included dyspnea (1%), fatigue (1%), abdominal pain (<1%), and depression (<1%).
c Includes flank pain.
d Includes decreased appetite.
e Includes ageusia, hypogeusia, and dysgeusia.
f  Includes 1 patient with Grade 5 gastric hemorrhage.
g Includes depressed mood.
Table 6 summarizes the laboratory abnormalities in Study 3.
 
Table 6. Laboratory Abnormalities Reported in ‚Č• 10% of RCC Patients Who Received Sunitinib Malate or Interferon Alfa in Study 3
 
¬† ¬† ¬† Laboratory Abnormality Treatment -Na√Įve RCC Sunitinib Malate (N=375) Interferon Alfa (N=360) All Grades * % Grade 3 to 4*,a % All Grades * % Grade 3 to 4*,b % Hematology ¬†¬† Hemoglobin decreased ¬†¬† Neutrophils decreased ¬†¬† Platelets decreased ¬†¬† Lymphocytes decreased ¬† 79 77 68 68 ¬† 8179 18 ¬† 69 49 24 68 ¬† 591 26 Renal/Metabolic ¬†¬† Creatinine increased ¬†¬† Creatine kinase increased ¬†¬† Uric acid increased ¬†¬† Calcium decreased ¬†¬†¬†Phosphorus decreased ¬†¬† Albumin decreased ¬†¬† Glucose increased ¬†¬† Sodium decreased ¬†¬† Glucose decreased ¬†¬† Potassium increased ¬†¬†¬†Calcium increased ¬†¬† Potassium decreased ¬†¬† Sodium increased ¬† 70 49 46 42 31 28 23 20 17 16 13 13 13 ¬† <12 141616803 <110 ¬† 51 11 33 40 24 20 15 15 12 17 102 10 ¬† <11816064 <141 <10 Gastrointestinal ¬†¬† AST increased ¬†¬† Lipase increased ¬†¬† ALT increased ¬†¬† Alkaline phosphatase increased ¬†¬† Amylase increased ¬†¬† Total bilirubin increased ¬†¬†¬† Indirect bilirubin increased ¬† 56 56 51 46 35 20 13 ¬† 218 32611 ¬† 38 46 40 37 3221 ¬† 2822300
* Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE), version 3.0.
Abbreviations: ALT=alanine aminotransferase; AST=aspartate aminotransferase; N=number of patients; RCC=renal cell carcinoma.
a Grade 4 laboratory abnormalities in patients on sunitinib malate included uric acid (14%), lipase (3%), neutrophils (2%), lymphocytes (2%), hemoglobin (2%), platelets (1%), amylase (1%), ALT (<1%), creatine kinase (<1%), creatinine (<1%), glucose increased (<1%), calcium decreased (<1%), phosphorous (<1%), potassium increased (<1%), and sodium decreased (<1%).
b Grade 4 laboratory abnormalities in patients on interferon alfa included uric acid (8%), lymphocytes (2%), lipase (1%), neutrophils (1%), amylase (<1%), calcium increased (<1%), glucose decreased (<1%), potassium increased (<1%), and hemoglobin (<1%).
Long-Term Safety in RCC
The long-term safety of sunitinib malate in patients with metastatic RCC was analyzed across 9 completed clinical studies conducted in the first-line, bevacizumab-refractory, and cytokine-refractory treatment settings. The analysis included 5739 patients, of whom 807 (14%) were treated for at least 2 years and 365 (6%) for at least 3 years. Prolonged treatment with sunitinib malate did not appear to be associated with new types of adverse reactions. There appeared to be no increase in the yearly incidence of adverse reactions at later time points. Hypothyroidism increased during the second year of treatment with new cases reported up to year 4.
Adjuvant Treatment of RCC
The safety of sunitinib malate was evaluated in S-TRAC, a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in which patients who had undergone nephrectomy for RCC received sunitinib malate 50 mg daily on Schedule 4/2 (n=306) or placebo (n=304). The median duration of treatment was 12.4 months (range: 0.13 to 14.9) for sunitinib malate and 12.4 months (range: 0.03 to 13.7) for placebo.
Permanent discontinuation due to an adverse reaction occurred in 28% of patients in the sunitinib malate arm. Adverse reactions leading to permanent discontinuation in >2% of patients include hand-foot syndrome and fatigue/asthenia. Dosing interruptions occurred in 54% and dose reductions occurred in 46% of patients who received sunitinib malate.
Table 7 summarizes the adverse reactions in S-TRAC.
Table 7. Adverse Reactions Reported in ‚Č•10% of Patients With RCC Who Received Sunitinib Malate and More Commonly Than in Patients Given Placebo* in S-TRAC
 
      Adverse Reaction                 Adjuvant Treatment of RCC   Sunitinib Malate (N=306) Pl a c e b o (N=304)   All Grade s % Grade 3 to 4 % All Grade s % Grade 3 to 4 %   Any Adverse Reaction 99 60 88 15   Gastrointestinal    Mucositis/Stomatitisa    Diarrhea   Nausea    Dyspepsia    Abdominal painb    Vomiting    Constipation   61 57 34 27 25 19 12   6421220   15 22 15797 11   0 <100 <100   Constitutional    Fatigue/Asthenia    Localized edemac    Pyrexia   57 18 12   8 <1 <1   34 <16   200   Dermatology    Hand-foot syndrome   Rashd     Hair color changes    Skin discoloration/Yellow skin   Dry skin   50 24 22 18 14   162000   1012 216   <10000   Cardiac    Hypertensione    Edema/Peripheral edema   39 10  8<1  147  10   Neurology    Alteredtastef    Headache   38 19   <1 <1   6 12   00   Endocrine    Hypothyroidism/TSH increased   24   <1   4                0   Hemorrhage /Bleeding    Bleeding events, all sitesg   24   <1   5  <1   Metabolism /Nutrition    Anorexia/Decreased appetite   19   <1   5  0   Musculoskeletal    Pain in extremity    Arthralgia   15 11   <1 <1   7 10   00  
* Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE), version 3.0.
Abbreviations: ARs=adverse reactions; N=number of patients; RCC=renal cell carcinoma.
a Includes mucosal inflammation, stomatitis aphthous ulcer, mouth ulceration, tongue ulceration, oropharyngeal pain, and oral pain.
b Includes abdominal pain, abdominal pain lower, and abdominal pain upper.
c Includes edema localized, face edema, eyelid edema, periorbital edema, swelling face, and eye edema.
d Includes dermatitis, dermatitis psoriasiform, exfoliative rash, genital rash, rash, rash erythematous, rash follicular, rash generalized, rash macular, rash maculopapular, rash papular, and rash pruritic.
e Includes hypertension, blood pressure increased, blood pressure systolic increased, blood pressure diastolic increased, and hypertensive crisis.
f  Includes ageusia, hypogeusia, and dysgeusia.
g Includes epistaxis, gingival bleeding, rectal hemorrhage, hemoptysis, anal hemorrhage, upper gastrointestinal hemorrhage, and hematuria.
Grade 4 adverse reactions in patients on sunitinib malate included hand-foot syndrome (1%), fatigue (<1%), abdominal pain (< 1%), stomatitis (<1%), and pyrexia (< 1%).
Grade 3 to 4 laboratory abnormalities that occurred in ‚Č•2% of patients receiving sunitinib malate include neutropenia (13%), thrombocytopenia (5%), leukopenia (3%), lymphopenia (3%), elevated alanine aminotransferase (2%), elevated aspartate aminotransferase (2%), hyperglycemia (2%), and hyperkalemia (2%).
Advanced Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors
The safety of sunitinib malate was evaluated in Study 6, a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in which patients with progressive pNET received sunitinib malate 37.5 mg once daily (n=83) or placebo (n=82). The median number of days on treatment was 139 days (range: 13 to 532 days) for patients on sunitinib malate and 113 days (range: 1 to 614 days) for patients on placebo. Nineteen patients (23%) on sunitinib malate and 4 patients (5%) on placebo were on study for >1 year.
Permanent discontinuation due to an adverse reaction occurred in 22% in the sunitinib malate arm. Dose interruptions occurred in 30% and dose reductions occurred in 31% of patients who received sunitinib malate.
Table 8 summarizes the adverse reactions in Study 6.
 
Table 8. Adverse Reactions Reported in ‚Č• 10% of Patients With pNET Who Received Sunitinib Malate and More Commonly Than in Patients Given Placebo* in Study 6
      Adverse Reaction pNET Sunitinib Malate (N=83) Placebo (N=82) All Grade s % Grade 3 to 4a % All Grade s % Grade 3 to 4 % Any Adverse Reaction 99 54 95 50 Gastrointestinal    Diarrhea    Stomatitis/oral syndromesb    Nausea    Abdominal painc    Vomiting    Dyspepsia   59 48 45 39 34 15   561500   39 18 29 34 316   201 1020 Constitutional     Asthenia     Fatigue     Weight decreased   34 33 16   551   27 27 11   490 Dermatology    Hair color changes    Hand-foot syndrome    Rash   Dry skin   29 23 18 15   1600   125 11   0000 Cardiac    Hypertension   27  10   5  1 Hemorrhage/Bleeding    Bleeding eventsd    Epistaxis   22 21  01   10 5  40 Neurology    Dysgeusia   Headache   21 18   00   5 13   01 Psychiatric    Insomnia   18   0   12   0 Musculoskeletal    Arthralgia   15   0   6   0
* Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE), version 3.0.
Abbreviations: N=number of patients; pNET=pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors.
a Grade 4 adverse reactions in patients on sunitinib malate included fatigue (1%).
b Includes aphthous stomatitis, gingival pain, gingivitis, glossitis, glossodynia, mouth ulceration, oral discomfort, oral pain, tongue ulceration, mucosal dryness, mucosal inflammation, and dry mouth.
c Includes abdominal discomfort, abdominal pain, and abdominal pain upper.
d Includes hematemesis, hematochezia, hematoma, hemoptysis, hemorrhage, melena, and metrorrhagia.
Table 9 summarizes the laboratory abnormalities in Study 6.
 
Table 9. Laboratory Abnormalities Reported in ‚Č• 10% of Patients With pNET Who Received Sunitinib Malate in Study 6
 
      Laboratory Abnormality pNET Sunitinib Malate Placebo All Grades * % Grade 3 to 4*,a % All   Grades* % Grade 3 to 4*,b %   Gastrointestinal    AST increased    Alkaline phosphatase increased   ALT increased    Total bilirubin  increased    Amylase increased    Lipase increased   72 6361 37 20 17  5104145   70 7055 28 10 11  3113414 Hematology    Neutrophils decreased    Hemoglobin decreased    Platelets decreased    Lymphocytes decreased   71 65 60 56   16057   16 55 15 35   0104 Renal/Me tabolic    Glucose increased    Albumin decreased    Phosphorus decreased    Calcium decreased    Sodium decreased    Creatinine increased    Glucose decreased    Potassium decreased    Magnesium decreased    Potassium increased   71 41 36 34 29 27 22 21 19 18   12170252401   78 37 22 19 34 28 15 14 10 11   18150354001
* The denominator used to calculate the rate varied from 52 to 82 for sunitinib malate and 39 to 80 for Placebo based on the number of patients with a baseline value and at least one post-treatment value. Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE), version 3.0.
Abbreviations: ALT=alanine aminotransferase; AST=aspartate aminotransferase; N=number of patients; pNET=pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors.
a Grade 4 laboratory abnormalities in patients on sunitinib malate included creatinine (4%), lipase (4%), glucose decreased (2%), glucose increased (2%), neutrophils (2%), ALT (1%), AST (1%), platelets (1%), potassium increased (1%), and total bilirubin (1%).
b Grade 4 laboratory abnormalities in patients on placebo included creatinine (3%), alkaline phosphatase (1%), glucose increased (1%), and lipase (1%).
Venous Thromboembolic Events
In pooled safety population, 3.5% of patients experienced a venous thromboembolic event, including Grade 3 to 4 in 2.2% of patients.
Pancreatic Function
Pancreatitis was observed in 1 patient (1%) in the pNET study, 5 patients (1%) in the treatment-na√Įve RCC study, and 1 patient (<1%) in the adjuvant treatment for RCC study on sunitinib malate.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval use of sunitinib malate. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
- Blood and lymphatic system disorders: hemorrhage associated with thrombocytopenia*.
- Gastrointestinal disorders: esophagitis.
- Hepatobiliary disorders: cholecystitis, particularly acalculous cholecystitis.
- Immune system disorders: hypersensitivity reactions, including angioedema.
- Infections and infestations: serious infection (with or without neutropenia)*. The infections most commonly observed with sunitinib malate include respiratory, urinary tract, skin infections, and sepsis/septic shock.
- Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders: fistula formation, sometimes associated with tumor necrosis and/or regression*; myopathy and/or rhabdomyolysis with or without acute renal failure*.
- Renal and urinary disorders: renal impairment and/or failure*.
- Respiratory disorders: pulmonary embolism*, pleural effusion*.
- Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: pyoderma gangrenosum, including positive de-challenges.
- Vascular disorders: arterial (including aortic) aneurysms, dissections*, and rupture*; arterial thromboembolic events*. The most frequent events included cerebrovascular accident, transient ischemic attack, and cerebral infarction.
- General disorders and administration site conditions: impaired wound healing.
*including some fatalities
7 Drug Interactions
- CYP3A4 Inhibitors: Consider dose reduction of sunitinib malate when administered with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors. (
7.1 )- CYP3A4 Inducers:  Consider dose increase of
sunitinib malate when administered with strong CYP3A4 inducers. ( 7.1 )7.1 Effect of Other Drugs on Sunitinib Malate
Strong CYP3A4 Inhibitors
Co-administration with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors may increase sunitinib plasma concentrations [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Select an alternate concomitant medication with no or minimal enzyme inhibition potential. Consider a dose reduction for sunitinib malate when it is co-administered with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)].
Strong CYP3A4 Inducers
Co-administration with strong CYP3A4 inducers may decrease sunitinib plasma concentrations [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Select an alternate concomitant medication with no or minimal enzyme induction potential. Consider a dose increase for sunitinib malate when it must be co-administered with CYP3A4 inducers [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)].
7.2 Drugs that Prolong QT Interval
Sunitinib malate is associated with QTc interval prolongation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3), Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)]. Monitor the QT interval with ECGs more frequently in patients who require treatment with concomitant medications known to prolong the QT interval.
8 Use In Specific Populations
- Lactation: Advise not to breastfeed. (
8.2 )8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on animal reproduction studies and its mechanism of action, sunitinib malate can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)]. There are no available data in pregnant women to inform a drug-associated risk. In animal developmental and reproductive toxicology studies, oral administration of sunitinib to pregnant rats and rabbits throughout organogenesis resulted in teratogenicity (embryolethality, craniofacial and skeletal malformations) at 5.5 and 0.3 times the combined AUC (the combined systemic exposure of sunitinib plus its active metabolite) in patients administered the recommended daily doses (RDD) of 50 mg, respectively (see Data). Advise females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus.
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated populations are unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriages in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4% and 15 to 20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
In a female fertility and early embryonic development study, female rats were administered oral sunitinib (0.5, 1.5, 5 mg/kg/day) for 21 days prior to mating and for 7 days after mating. Embryolethality was observed at 5 mg/kg/day (approximately 5 times the combined AUC in patients administered the RDD of 50 mg).
In embryo-fetal developmental toxicity studies, oral sunitinib was administered to pregnant rats (0.3, 1.5, 3, 5 mg/kg/day) and rabbits (0.5, 1, 5, 20 mg/kg/day) during the period of organogenesis. In rats, embryolethality and skeletal malformations of the ribs and vertebrae were observed at the dose of 5 mg/kg/day (approximately 5.5 times the combined AUC in patients administered the RDD of 50 mg). No adverse fetal effects were observed in rats at doses ‚ȧ3 mg/kg/day (approximately 2 times the combined AUC in patients administered the RDD of 50 mg). In rabbits, embryolethality was observed at 5 mg/kg/day (approximately 3 times the combined AUC in patients administered the RDD of 50 mg), and craniofacial malformations (cleft lip and cleft palate) were observed at ‚Č•1 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.3 times the combined AUC in patients administered the RDD of 50 mg).
Sunitinib (0.3, 1, 3 mg/kg/day) was evaluated in a pre- and postnatal development study in pregnant rats. Maternal body weight gains were reduced during gestation and lactation at doses ‚Č•1 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.5 times the combined AUC in patients administered the RDD of 50 mg). At 3 mg/kg/day (approximately 2 times the combined AUC in patients administered the RDD of 50 mg), reduced neonate body weights were observed at birth and persisted in the¬†offspring of both sexes during the preweaning period and in males during postweaning period. No adverse developmental effects were observed at doses ‚ȧ1 mg/kg/day.
8.2 Lactation
There is no information regarding the presence of sunitinib and its metabolites in human milk. Sunitinib and its metabolites were excreted in rat milk at concentrations up to 12-fold higher than in plasma (see Data). Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in breastfed infants, advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with sunitinib malate and for at least 4 weeks after the last dose.
Data
Animal Data
In lactating female rats administered 15 mg/kg, sunitinib and its metabolites were excreted in milk at concentrations up to 12-fold higher than in plasma.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Sunitinib malate can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Pregnancy Testing
Verify pregnancy status of females of reproductive potential prior to initiating treatment with sunitinib malate.
Contraception
Females
Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with sunitinib malate and for at least 4 weeks after the last dose.
Males
Based on findings in animal reproduction studies, advise males with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with sunitinib malate and for 7 weeks after the last dose.
Infertility
Based on findings in animals, sunitinib malate may impair male and female fertility [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of sunitinib malate in pediatric patients have not been established. Safety and pharmacokinetics of sunitinib were assessed in an open-label study (NCT00387920) in pediatric patients 2 years to <17 years of age (n=29) with refractory solid tumors. In addition, efficacy, safety and pharmacokinetics of sunitinib was assessed in another open-label study (NCT01462695) in pediatric patients 2 years to <17 years of age (n=27) with high-grade glioma or ependymoma. The maximum tolerated dose (MTD) normalized for body surface area (BSA) was lower in pediatric patients compared to adults. Sunitinib was poorly tolerated in pediatric patients. The occurrence of dose-limiting cardiotoxicity prompted an amendment of the NCT00387920 study to exclude patients with previous exposure to anthracyclines or cardiac radiation. No responses were reported in patients in either of the trials.
Apparent clearance and volume of distribution normalized for BSA for sunitinib and its active major metabolite were lower in pediatrics as compared to adults.
The effect on open tibial growth plates in pediatric patients who received sunitinib malate has not been adequately studied. See Juvenile Animal Toxicity Data below.
Juvenile Animal Toxicity Data
Physeal dysplasia was present in cynomolgus monkeys with open growth plates treated with sunitinib for ‚Č•3 months (3 month dosing 2, 6, 12 mg/kg/day; 8 cycles of dosing 0.3, 1.5, 6 mg/kg/day) at doses that were >0.4 times the combined AUC (the combined systemic exposure of sunitinib plus its active metabolite) in patients administered the RDD of 50 mg. The no-effect level (NOEL) was 1.5 mg/kg/day in monkeys treated intermittently for 8 cycles, but was not identified in monkeys treated continuously for 3 months. In developing rats treated continuously for 3 months (1.5, 5, and 15 mg/kg) or 5 cycles (0.3, 1.5, and 6 mg/kg/day), bone abnormalities consisted of thickening of the epiphyseal cartilage of the femur and an increase of fracture of the tibia at doses ‚Č•5 mg/kg (approximately 10 times the combined AUC in patients administered the RDD of 50 mg). Additionally, tooth caries were present in rats at >5 mg/kg. The incidence and severity of physeal dysplasia were dose related and reversible upon cessation of treatment; however, findings in the teeth were not. In rats, the NOEL in bones was ‚ȧ2 mg/kg/day.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the 7527 patients with GIST, RCC (advanced and adjuvant), or pNET who received sunitinib malate, 32% were 65 years and older, and 7% were 75 years and older. Patients aged 65 years of age and older had a higher incidence of Grade 3 or 4 adverse reactions (67%) than younger patients (60%).
„ÄÄ
In the GIST study, 73 (30%) of the patients who received sunitinib malate were 65 years and older. In the mRCC study, 152 (41%) of patients who received sunitinib malate were 65 years and older. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these patients and younger patients.
„ÄÄ
In the pNET study, 22 (27%) of the patients who received sunitinib malate were 65 years and older. Clinical studies of sunitinib malate did not include sufficient numbers of patients with pNET to determine if patients 65 years of age and older respond differently than younger patients.
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment is required in patients with mild or moderate (Child-Pugh Class A or B) hepatic impairment [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Sunitinib malate was not studied in patients with severe (Child-Pugh Class C) hepatic impairment.
8.7 Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment is recommended in patients with mild (CLcr 50 to 80 mL/min), moderate (CLcr 30 to <50 mL/min), or severe (CLcr <30 mL/min) renal impairment who are not on dialysis [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
No dose adjustment is recommended for patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) on hemodialysis [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
10 Overdosage
Treatment of overdose with sunitinib malate should consist of general supportive measures. There is no specific antidote for overdosage with sunitinib malate. If indicated, elimination of unabsorbed drug should be achieved by emesis or gastric lavage. Cases of accidental overdose have been reported; these cases were associated with adverse reactions consistent with the known safety profile of sunitinib malate, or without adverse reactions. In nonclinical studies, mortality was observed following as few as 5 daily doses of 500 mg/kg (3000 mg/m2) in rats. At this dose, signs of toxicity included impaired muscle coordination, head shakes, hypoactivity, ocular discharge, piloerection, and gastrointestinal distress. Mortality and similar signs of toxicity were observed at lower doses when administered for longer durations.
11 Description
Sunitinib is a kinase inhibitor present in sunitinib malate capules as the malate salt. Sunitinib malate is described chemically as (2S)-2-hydroxybutanedoic acid with N-[2-(diethylamino)ethyl]-5-[(Z)-(5-fluoro-1,2-dihydro-2-oxo-3H-indol-3-ylidine)methyl]-2,4-dimethyl-1H-pyrrole-3-carboxamide (1:1). The molecular formula is C22H27FN4O2‚ÄĘ C4H6O5 and the molecular weight is 532.6 Daltons. The chemical structure of sunitinib malate is:
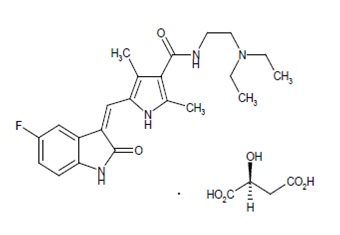
Sunitinib malate is a yellow to orange powder with a pKa of 8.95. The solubility of sunitinib malate in aqueous media over the range pH 1.2 to pH 6.8 is in excess of 25 mg/mL. The log of the distribution coefficient (octanol/water) at pH 7 is 5.2.
Sunitinib malate capsules are supplied as printed hard shell capsules containing 12.5 mg, 25 mg, 37.5 mg or 50 mg of sunitinib (equivalent to 16.71 mg, 33.41 mg, 50.12 mg, or 66.83 mg of sunitinib malate, respectively). The capsules contain the following inactive ingredients:  croscarmellose sodium, magnesium stearate, mannitol, and povidone. The red opaque gelatin capsule shells contain gelatin, iron oxide red, and titanium dioxide; the olive green opaque gelatin capsule shells contain FD&C Blue 2, gelatin, iron oxide red, iron oxide yellow, and titanium dioxide; and the light green opaque gelatin capsule shells contain FD&C Blue 2, gelatin, iron oxide yellow, and titanium dioxide. The white printing ink contains potassium hydroxide, propylene glycol, shellac, and titanium dioxide and the black printing ink contains black iron oxide, potassium hydroxide, propylene glycol, and shellac.
12 Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Sunitinib is a small molecule that inhibits multiple receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs), some of which are implicated in tumor growth, pathologic angiogenesis, and metastatic progression of cancer. Sunitinib was evaluated for its inhibitory activity against a variety of kinases (>80 kinases) and was identified as an inhibitor of platelet-derived growth factor receptors (PDGFRőĪ and PDGFRő≤), vascular endothelial growth factor receptors (VEGFR1, VEGFR2, and VEGFR3), stem cell factor receptor (KIT), Fms-like tyrosine kinase-3 (FLT3), colony stimulating factor receptor Type 1 (CSF-1R), and the glial cell-line derived neurotrophic factor receptor (RET). Sunitinib inhibition of the activity of these RTKs has been demonstrated in biochemical and cellular assays, and inhibition of function has been demonstrated in cell proliferation assays. The primary metabolite exhibits similar potency compared to sunitinib in biochemical and cellular assays.
Sunitinib inhibited the phosphorylation of multiple RTKs (PDGFRő≤, VEGFR2, KIT) in tumor xenografts expressing RTK targets in vivo and demonstrated inhibition of tumor growth or tumor regression and/or inhibited metastases in some experimental models of cancer. Sunitinib demonstrated the ability to inhibit growth of tumor cells expressing dysregulated target RTKs (PDGFR, RET, or KIT) in vitro and to inhibit PDGFRő≤- and VEGFR2-dependent tumor angiogenesis in vivo.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Exposure-Response Relationship Based on population pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic analyses, there were relationships between changes in different pharmacodynamic endpoints (i.e., safety and efficacy endpoints) over time and sunitinib plasma exposures.
Cardiac Electrophysiology
Sunitinib malate can cause QT interval prolongation in a dose-dependent manner, which may lead to an increased risk for ventricular arrhythmias including Torsade de Pointes [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics of sunitinib and sunitinib malate have been evaluated in healthy subjects and in patients with solid tumors.
Sunitinib AUC and Cmax increase proportionately over a dose range of 25 mg to 100 mg (0.5 to 2 times the approved RDD of 50 mg). The pharmacokinetics were similar in healthy subjects and in patients with a solid tumor, including patients with GIST and RCC. No significant changes in the pharmacokinetics of sunitinib or the primary active metabolite were observed with repeated daily administration or with repeated cycles. With repeated daily administration, sunitinib accumulates 3- to 4-fold while the primary metabolite accumulates 7- to 10-fold. Steady-state concentrations of sunitinib and its primary active metabolite are achieved within 10 to 14 days. By Day 14, combined plasma concentrations of sunitinib and its active metabolite ranged from 63 to 101 ng/mL.
Absorption
Following oral administration of sunitinib, the time to maximum plasma concentration (Tmax) ranged from 6 to 12 hours.
Effect of Food
The administration of a single dose of sunitinib malate 50 mg with a high-fat, high-calorie meal (consisting of approximately 150 protein calories and 500 to 600 fat calories) in healthy subjects had no clinically significant effect on sunitinib malate or active metabolites exposure.
Distribution
The apparent volume of distribution (Vd/F) for sunitinib is 2230 L. Binding of sunitinib and its primary active metabolite to human plasma protein in vitro is 95% and 90%, respectively, with no concentration dependence in the range of 100 to 4000 ng/mL.
Elimination
Following administration of a single oral dose in healthy subjects, the terminal half-lives of sunitinib and its primary active metabolite are approximately 40 to 60 hours and 80 to 110 hours, respectively. Sunitinib total oral clearance (CL/F) ranged from 34 to 62 L/h with an interpatient variability of 40%.
Metabolism
Sunitinib is metabolized primarily by CYP3A4 to its primary active metabolite, which is further metabolized by CYP3A4. The primary active metabolite comprises 23% to 37% of the total exposure. After a radiolabeled dose, sunitinib and its active metabolite were the major compounds identified in plasma, accounting for 92% of radioactivity.
Excretion
After a radiolabeled dose of sunitinib, approximately 61% of the dose was recovered in feces and 16% in urine.
Sunitinib and its primary active metabolite were the major compounds identified in urine and feces, representing 86% and 74% of radioactivity, respectively.
Specific Populations
No clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of sunitinib or the primary active metabolite were observed based on age (18 to 84 years), body weight (34 to 168 kg), race (White, Black, or Asian), sex, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) score, mild (Child-Pugh Class A) or moderate (Child-Pugh Class B) hepatic impairment.
Patients with Renal Impairment
No clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of sunitinib or its active metabolite were predicted or observed in patients with mild (CLcr 50 to 80 mL/min), moderate (CLcr 30 to <50 mL/min), or severe (CLcr <30 mL/min) renal impairment who are not on dialysis, compared to patients with normal renal function (CLcr >80 mL/min). Although sunitinib was not eliminated through hemodialysis, the sunitinib systemic exposure was 47% lower in patients with end stage renal disease (ESRD) on hemodialysis compared to patients with normal renal function.
Drug Interaction Studies
Clinical Studies
Effect of strong CYP3A4 inhibitors on sunitinib: Co-administration of a single sunitinib malate dose with ketoconazole (strong CYP3A4 inhibitor) increased the combined sunitinib and its active metabolite Cmax and AUC0-inf by 49% and 51%, respectively, in healthy subjects.
Effect of strong CYP3A4 inducers on sunitinib: Co-administration of a single sunitinib malate dose with rifampin (strong CYP3A4 inducer) reduced the combined sunitinib and its active metabolite Cmax and AUC0-inf by 23% and 46%, respectively in healthy subjects.
In Vitro Studies
In vitro studies in human hepatocytes and microsomes indicated that sunitinib and the primary active metabolite do not induce CYP1A2, CYP2E1, and CYP3A4/5, or inhibit CYP1A2, CYP2A6, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, CYP2E1, CYP3A4/5, and CYP4A9/11 at clinically relevant concentrations.
13 Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
The carcinogenic potential of sunitinib has been evaluated in 2 species: rasH2 transgenic mice and Sprague-Dawley rats. There were similar positive findings in both species. In rasH2 transgenic mice, gastroduodenal carcinomas and/or gastric mucosal hyperplasia, as well as an increased incidence of background hemangiosarcomas were observed at sunitinib daily doses of ‚Č•25 mg/kg/day in studies of 1 or 6 months duration. No proliferative changes were observed in rasH2 transgenic mice at 8 mg/kg/day. Similarly, in a 2-year rat carcinogenicity study, administration of sunitinib in 28-day cycles followed by 7-day dose-free periods resulted in findings of duodenal carcinoma at doses as low as 1 mg/kg/day [approximately 0.9 times the combined AUC (combined systemic exposure of sunitinib plus its active metabolite) in patients administered the RDD of 50 mg]. At the high dose of 3 mg/kg/day (approximately 8 times the combined AUC in patients administered the RDD of 50 mg), the incidence of duodenal tumors was increased and was accompanied by findings of gastric mucous cell hyperplasia and by an increased incidence of pheochromocytoma and hyperplasia of the adrenal gland.
Sunitinib did not cause genetic damage when tested in in vitro assays [bacterial mutation (Ames test), human lymphocyte chromosome aberration] and an in vivo rat bone marrow micronucleus test.
In a female fertility and early embryonic development study, female rats were administered oral sunitinib (0.5, 1.5, 5 mg/kg/day) for 21 days prior to mating and for 7 days after mating. Preimplantation loss was observed in females administered 5 mg/kg/day (approximately 5 times the combined AUC in patients administered the RDD of 50 mg). No adverse effects on fertility were observed at doses ‚ȧ1.5 mg/kg/day (approximately equal to the combined AUC in patients administered the RDD of 50 mg). In addition, effects on the female reproductive system were identified in a 3-month oral repeat-dose monkey study (2, 6, 12 mg/kg/day). Ovarian changes (decreased follicular development) were noted at 12 mg/kg/day (approximately 5 times the combined AUC in patients administered the RDD of 50 mg), while uterine changes (endometrial atrophy) were noted at ‚Č•2 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.4 times the combined AUC in patients administered the RDD of 50 mg). With the addition of vaginal atrophy, the uterine and ovarian effects were reproduced at 6 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.8 times the combined AUC in patients administered the RDD of 50 mg) in a 9-month monkey study (0.3, 1.5, and 6 mg/kg/day administered daily for 28 days followed by a 14-day respite).
In a male fertility study, no reproductive effects were observed in male rats dosed with 1, 3, or 10 mg/kg/day oral sunitinib for 58 days prior to mating with untreated females. Fertility, copulation, conception indices, and sperm evaluation (morphology, concentration, and motility) were unaffected by sunitinib at doses ‚ȧ10 mg/kg/day (approximately ‚Č•26 times the combined AUC in patients administered the RDD of 50 mg).
14 Clinical Studies
14.1 Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor
Study 1
Study 1 (NCT#00075218) was a 2-arm, international, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of sunitinib malate in patients with GIST who had disease progression during prior imatinib mesylate (imatinib) treatment or who were intolerant of imatinib. The objective was to compare time-to-tumor progression (TTP) in patients receiving sunitinib malate plus best supportive care versus patients receiving placebo plus best supportive care. Other objectives included progression-free survival (PFS), objective response rate (ORR), and overall survival (OS). Patients were randomized (2:1) to receive either 50 mg sunitinib malate or placebo orally, once daily, on Schedule 4/2 until disease progression or withdrawal from the study for another reason. Treatment was unblinded at the time of disease progression. Patients randomized to placebo were then offered crossover to open-label sunitinib malate and patients randomized to sunitinib malate were permitted to continue treatment per investigator judgment.
At the time of a prespecified interim analysis, the intent-to-treat (ITT) population included 312 patients. Two hundred seven (207) patients were randomized to the sunitinib malate arm and 105 patients were randomized to the placebo arm. Demographics were comparable between the sunitinib malate and placebo groups with regard to age (69% versus 72% <65 years for sunitinib malate versus placebo, respectively), sex (male: 64% versus 61%), race (White: 88% both arms, Asian: 5% both arms, Black: 4% both arms, remainder not reported), and performance status (ECOG 0: 44% versus 46%, ECOG 1: 55% versus 52%, and ECOG 2: 1% versus 2%). Prior treatment included surgery (94% versus 93%) and radiotherapy (8% versus 15%). Outcome of prior imatinib treatment was also comparable between arms with intolerance (4% versus 4%), progression within 6 months of starting treatment (17% versus 16%), or progression beyond 6 months (78% versus 80%) balanced.
The planned interim efficacy and safety analysis was performed after 149 TTP events had occurred. There was a statistically significant advantage for sunitinib malate over placebo in TTP, meeting the primary endpoint. Efficacy results are summarized in Table 10 and the Kaplan-Meier curve for TTP is shown in Figure 1.
Table 10. GIST Efficacy Results From Study 1 (Double-Blind Treatment Phase)
Efficacy Parameter Sunitinib Malate (N=207) Placebo (N=105) p-value (log-rank test ) HR (95% CI) Time-to-tumor progressiona [median,  weeks (95% CI)] 27.3 (16.0, 32.1) 6.4 (4.4, 10.0) <0.0001* 0.33 (0.23, 0.47) Progression-free survivalb [median,  weeks (95% CI)] 24.1 (11.1, 28.3) 6.0 (4.4, 9.9) <0.0001 0.33 (0.24, 0.47) Objective response rate (PR) [%, (95% CI)] 6.8 (3.7, 11.1) 0 0.006c  
* A comparison is considered statistically significant if the p-value is <0.00417 (O’Brien Fleming stopping boundary).
Abbreviations: CI=confidence interval; GIST=gastrointestinal stromal tumor; HR=hazard ratio; N=number of patients; PR=partial response.
a Time from randomization to progression; deaths prior to documented progression were censored at time of last radiographic evaluation.
b Time from randomization to progression or death due to any cause.
c Pearson chi-square test.
Figure 1. Kaplan-Meier Curve of TTP in GIST Study 1 (Intent-to-Treat Population)
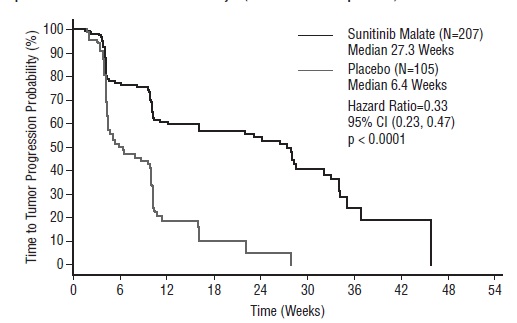
Abbreviations: CI=confidence interval; GIST=gastrointestinal stromal tumor; N=number of patients; TTP=time-to-tumor progression.
The final ITT population enrolled in the double-blind treatment phase of the study included 243 patients randomized to the sunitinib malate arm and 118 patients randomized to the placebo arm. After the primary endpoint was met at the interim analysis, the study was unblinded, and patients on the placebo arm were offered open-label sunitinib malate treatment. Ninety-nine (99) of the patients initially randomized to placebo crossed over to receive sunitinib malate in the open-label treatment phase. At the protocol specified final analysis of OS, the median OS was 72.7 weeks for the sunitinib malate arm and 64.9 weeks for the placebo arm [hazard ratio (HR)=0.876, 95% confidence interval (CI) (0.679, 1.129)].
Study 2
Study 2 was an open-label, multi-center, single-arm, dose-escalation study conducted in patients with GIST following progression on, or intolerance to imatinib. Following identification of the recommended regimen (50 mg once daily on Schedule 4/2), 55 patients in this study received the 50 mg dose of sunitinib malate on treatment Schedule 4/2. Partial responses (PR) were observed in 5 of 55 patients (9.1% PR rate; 95% CI: 3.0%, 20.0%).
14.2 Renal Cell Carcinoma
Treatment-Na√Įve
Study 3 (NCT#00083889) was a multi-center, international, randomized study comparing single-agent sunitinib malate with interferon alfa was conducted in patients with treatment-na√Įve RCC. The objective was to compare PFS in patients receiving sunitinib malate versus patients receiving interferon alfa. Other endpoints included ORR, OS, and safety. Seven hundred fifty (750) patients were randomized (1:1) to receive either 50 mg sunitinib malate once daily on Schedule 4/2 or to receive interferon alfa administered subcutaneously at 9 million international units (MIU) 3 times a week. Patients were treated until disease progression or withdrawal from the study.
The ITT population included 750 patients, 375 randomized to sunitinib malate and 375 randomized to interferon alfa. Demographics were comparable between the sunitinib malate and interferon alfa groups with regard to age (59% versus 67% <65 years for sunitinib malate versus interferon alfa, respectively), sex (male: 71% versus 72%), race (White: 94% versus 91%, Asian: 2% versus 3%, Black: 1% versus 2%, remainder not reported), and performance status (ECOG 0: 62% versus 61%, ECOG 1: 38% each arm, ECOG 2: 0 versus 1%). Prior treatment included nephrectomy (91% versus 89%) and radiotherapy (14% each arm). The most common site of metastases present at screening was the lung (78% versus 80%, respectively), followed by the lymph nodes (58% versus 53%, respectively) and bone (30% each arm); the majority of the patients had multiple (2 or more) metastatic sites at baseline (80% versus 77%, respectively).
There was a statistically significant advantage for sunitinib malate over interferon alfa in the endpoint of PFS (see Table 11 and Figure 2). In the prespecified stratification factors of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) (>1.5 ULN versus ‚ȧ1.5 ULN), ECOG performance status (0 versus 1), and prior nephrectomy (yes versus no), the hazard ratio favored sunitinib malate over interferon alfa. The ORR was higher in the sunitinib malate arm (see Table 11).
¬† Table 11. Treatment -Na√Įve RCC Efficacy Results (Interim Analysis) from Study 3
 Efficacy Parameter Sunitinib Malate (N=375) Interferon Alfa (N=375) p-value (log-rank test)    HR   (95% CI) Progression-free survivala 47.3 22.0 <0.000001b 0.415 [median, weeks (95% CI)] (42.6, 50.7) (16.4, 24.0) (0.320, 0.539) Objective response ratea 27.5 5.3 <0.001c NA [%, (95% CI)] (23.0, 32.3) (3.3, 8.1)
Abbreviations: CI=confidence interval; HR=hazard ratio; N=number of patients; NA=not applicable; RCC=renal cell carcinoma. a Assessed by blinded core radiology laboratory; 90 patients‚Äô scans had not been read at time of analysis. b A comparison is considered statistically significant if the p-value is <0.0042 (O‚ÄôBrien Fleming stopping boundary). c Pearson chi-square test. Figure 2. Kaplan-Meier Curve of PFS in Treatment-Na√Įve RCC Study 3 (Intent-to-Treat Population)¬†
Abbreviations: CI=confidence interval; IFN-őĪ=interferon-alfa; N=number of patients; PFS=progression-free survival; RCC=renal cell carcinoma.
At the protocol-specified final analysis of OS, the median OS was 114.6 weeks for the sunitinib malate arm and 94.9 weeks for the interferon alfa arm (HR=0.821; 95% CI: 0.673, 1.001). The median OS for the interferon alfa arm includes 25 patients who discontinued interferon alfa treatment because of disease progression and crossed over to treatment with sunitinib malate as well as 121 patients (32%) on the interferon alfa arm who received post-study cancer treatment with sunitinib malate.
Cytokine-Refractory
The use of single-agent sunitinib malate in the treatment of cytokine-refractory RCC was investigated in 2 single-arm, multi-center studies. All patients enrolled into these studies experienced failure of prior cytokine-based therapy. In Study 4 (NCT#00077974), failure of prior cytokine therapy was based on radiographic evidence of disease progression defined by response evaluation criteria in solid tumors (RECIST) or World Health Organization (WHO) criteria during or within 9 months of completion of 1 cytokine therapy treatment (interferon alfa, interleukin-2, or interferon alfa plus interleukin-2; patients who were treated with interferon alfa alone must have received treatment for at least 28 days). In Study 5 (NCT#00054886), failure of prior cytokine therapy was defined as disease progression or unacceptable treatment-related toxicity. The endpoint for both studies was ORR. Duration of response (DR) was also evaluated.
One hundred and six patients (106) were enrolled into Study 4 and 63 patients were enrolled into Study 5. Patients received 50 mg sunitinib malate on Schedule 4/2. Therapy was continued until the patients met withdrawal criteria or had progressive disease. The baseline age, sex, race, and ECOG performance statuses of the patients were comparable between Studies 4 and 5. Approximately 86% to 94% of patients in the 2 studies were White. Men comprised 65% of the pooled population. The median age was 57 years and ranged from 24 to 87 years in the studies. All patients had an ECOG performance status <2 at the screening visit.
The baseline malignancy and prior treatment history of the patients were comparable between Studies 4 and 5. Across the 2 studies, 95% of the pooled population of patients had at least some component of clear-cell histology. All patients in Study 4 were required to have a histological clear-cell component. Most patients enrolled in the studies (97% of the pooled population) had undergone nephrectomy; prior nephrectomy was required for patients enrolled in Study 4. All patients had received 1 previous cytokine regimen. Metastatic disease present at the time of study entry included lung metastases in 81% of patients. Liver metastases were more common in Study 4 (27% versus 16% in Study 5) and bone metastases were more common in Study 5 (51% versus 25% in Study 4); 52% of patients in the pooled population had at least 3 metastatic sites. Patients with known brain metastases or leptomeningeal disease were excluded from both studies.
The ORR and DR data from Studies 4 and 5 are provided in Table 12. There were 36 PRs in Study 4 as assessed by a core radiology laboratory for an ORR of 34.0% (95% CI: 25.0%, 43.8%). There were 23 PRs in Study 5 as assessed by the investigators for an ORR of 36.5% (95% CI: 24.7%, 49.6%). The majority (>90%) of objective disease responses were observed during the first 4 cycles; the latest reported response was observed in Cycle 10. DR data from Study 4 is premature as only 9 of 36 patients (25%) responding to treatment had experienced disease progression or died at the time of the data cutoff.
Table 12.  Cytokine-Refractory RCC Efficacy Results from Study 4 and Study 5
Efficacy Parameter Study 4   (N=106) Study 5   (N=63) Objective response rate [%, (95%  CI)] 34.0a   (25.0, 43.8) 36.5b (24.7, 49.6) Duration of response   [median,  weeks (95% CI)] NR* (42.0, *) 54b (34.3, 70.1)
*Data not mature enough to determine upper confidence limit.
Abbreviations: CI=confidence interval; N=number of patients; NR=not reached; RCC=renal cell carcinoma.
a Assessed by blinded core radiology laboratory.
b Assessed by investigators.
Adjuvant Treatment
In the adjuvant treatment setting, sunitinib malate was investigated in S-TRAC (NCT#00375674), a multi-center, international, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, trial in patients with high risk of recurrent RCC following nephrectomy. Patients were required to have clear cell histology and high risk of recurrence defined as ‚Č•T3 and/or N+ tumors. Six hundred fifteen (615) patients were randomized 1:1 to receive either 50 mg sunitinib malate once daily on Schedule 4/2 or placebo. Patients were treated for 9 cycles (approximately 1 year), or until disease recurrence, unacceptable toxicity, or withdrawal of consent.
Demographics were generally comparable between the sunitinib malate and placebo arms with regard to age (median age 58 years), sex (73% male), and race (84% White, 12% Asian and 4% Other). At randomization, most patients had an ECOG performance status of 0 (74% sunitinib malate and 72% placebo). The remainder of the patients had an ECOG performance status of 1; 1 patient on sunitinib malate had a performance status of 2.
The major efficacy outcome measure was disease-free survival (DFS) in patients receiving sunitinib malate versus placebo as assessed by blinded independent central review (BICR). Overall survival was an additional endpoint. There was a statistically significant improvement in DFS in patients who were treated with sunitinib malate compared to placebo (Table 13 and Figure 3). Prespecified subgroup analyses are presented in Table 14. At the time of the DFS analysis, overall survival data were not mature, with 141/615 (23%) patient deaths.
Table 13. Disease-free Survival Results as Assessed by BICR in Adjuvant RCC (Intent to Treat Population) from S-TRAC
  Sunitinib Malate N= 309 Placebo  N= 306            p-value a              HRa (95% CI) Median DFS [years (95% CI)] 6.8 (5.8, NR) 5.6 (3.8, 6.6) 0.03 0.76 (0.59, 0.98) DFS Events 113 (36.6%) 144 (47.1%)   5 Year DFS Rate 59.3% 51.3%  
a P-value based on log-rank test stratified by University of California Los Angeles Integrated Staging System (UISS) prognostic group;
HR based on a Cox proportional hazard model stratified by UISS prognostic group
Abbreviations: BICR=blinded independent central review; CI=confidence interval; DFS=disease-free survival; HR=hazard ratio;
N=number of patients; RCC=renal cell carcinoma.
Table 14. Disease-free Survival by Baseline Disease Characteristics
  Number of Events/ Total n/N Median   DFS [years (95% CI)]          HRa       (95% CI)   Sunitinib Malate Placebo Sunitinib Malate Placebo   T3 Intermediateb 35/115 46/112 NR  (5.2, NR) 6.4 (4.7, NR) 0.82 (0.53, 1.28) T3 Highc 63/165 79/166 6.8 (5.0, NR) 5.3 (2.9, NR) 0.77 (0.55, 1.07) T4/Node Positived 15/29 19/28 3.5 (1.2, NR) 1.7 (0.4, 3.0) 0.62 (0.31, 1.23)
Abbreviations: CI=confidence interval; DFS=disease-free survival; HR=hazard ratio; N=number of patients; n=number of events;
NR=not reached
a HR based on a Cox proportional hazards model
b T3 Intermediate: T3, N0 or NX, M0, any Fuhrman‚Äôs grade, ECOG PS 0 OR T3, N0 or NX, M0, Fuhrman‚Äôs grade 1, ECOG PS ‚Č• 1
c T3 High: T3, N0 or NX, M0, Fuhrman‚Äôs grade ‚Č• 2, ECOG PS ‚Č• 1
d T4/Node Positive: T4, N0 or NX, M0, any Fuhrman’s grade, any ECOG PS OR Any T, N1 to 2, M0, any Fuhrman’s grade, any ECOG PS
Figure 3. Kaplan-Meier Curve of Disease-free Survival as Assessed by BICR (Intent-to-Treat Population)
Abbreviations: BICR=blinded independent central review; CI=confidence interval; N=number of patients.
14.3 Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors
Study 6 (NCT#00428597) was a multi-center, international, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of single-agent sunitinib malate conducted in patients with unresectable pNET. Patients were required to have documented RECIST-defined disease progression within the prior 12 months and were randomized (1:1) to receive either 37.5 mg sunitinib malate (N=86) or placebo (N=85) once daily without a scheduled off-treatment period. The primary objective was to compare PFS in patients receiving sunitinib malate versus patients receiving placebo. Other endpoints included OS, ORR, and safety. Use of somatostatin analogs was allowed in the study.
Demographics were comparable between the sunitinib malate and placebo groups. Additionally, 49% of sunitinib malate patients had nonfunctioning tumors vs 52% of placebo patients, and 92% patients in both arms had liver metastases. A total of 66% of sunitinib malate patients received prior systemic therapy compared with 72% of placebo patients and 35% of sunitinib malate patients had received somatostatin analogs compared with 38% of placebo patients. Patients were treated until disease progression or withdrawal from the study. Upon disease progression or study closure, patients were offered access to sunitinib malate in a separate extension study.
As recommended by the Independent Data Monitoring Committee, the study was terminated prematurely prior to the prespecified interim analysis. This may have led to an overestimate of the magnitude of PFS effect. A clinically significant improvement for sunitinib malate over placebo in PFS was seen by both investigator and independent assessment. A hazard ratio favoring sunitinib malate was observed in all subgroups of baseline characteristics evaluated. OS data were not mature at the time of the analysis. There were 9 deaths in the sunitinib malate arm and 21 deaths in the placebo arm. A statistically significant difference in ORR favoring sunitinib malate over placebo was observed. Efficacy results are summarized in Table 15 and the Kaplan-Meier curve for PFS is in Figure 4.
Table 15. pNET Efficacy Results from Study 6
                    Efficacy Parameter Sunitinib Malate(N=86)  Placebo (N=85) p-value HR (95% CI) Progression-free survival [median, months (95% CI)] 10.2 (7.4, 16.9) 5.4 (3.4, 6.0) 0.000146a 0.427 (0.271, 0.673) Objective response rate [%, (95% CI)] 9.3 (3.2, 15.4) 0 0.0066b NA
Abbreviations: CI=confidence interval; HR=hazard ratio; N=number of patients; NA=not applicable;pNET=pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. a 2-sided unstratified log-rank test. b Fisher’s Exact test.
Figure 4. Kaplan-Meier Curve of PFS in the pNET Study 6
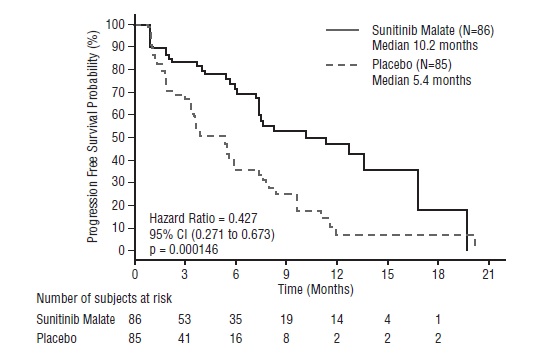
Abbreviations: CI=confidence interval; N=number of patients; PFS=progression-free survival; pNET=pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors.
16 How Supplied/storage And Handling
Sunitinib Malate Capsules, 12.5 mg are supplied as hard gelatin capsule with red opaque cap and red opaque body imprinted ‚ÄėS12.5‚Äô on body with white ink and plain cap, containing yellow to orange granules; available in:
                Bottles of  28 capsules                                                       NDC 59651-464-28                Cartons of 28 Capsules (4 x 7 Unit-Dose)                         NDC 59651-464-29
Sunitinib Malate Capsules, 25 mg are supplied as hard gelatin capsule with olive green opaque cap and red opaque body imprinted ‚ÄėS25‚Äô on body with white ink and plain cap, containing yellow to orange granules; available in:
                Bottles of  28 capsules                                                        NDC 59651-465-28                Cartons of 28 Capsules (4 x 7 Unit-Dose)                          NDC 59651-465-29
Sunitinib Malate Capsules, 37.5 mg are supplied as hard gelatin capsule with light green opaque cap and light green opaque body imprinted ‚ÄėS37.5‚Äô on body with black ink and plain cap, containing yellow to orange granules; available in:
                Bottles of  28 capsules                                                       NDC 59651-466-28                Cartons of 28 Capsules (4 x 7 Unit-Dose)                         NDC 59651-466-29
Sunitinib Malate Capsules, 50 mg are supplied as hard gelatin capsule with olive green opaque cap and olive green opaque body imprinted ‚ÄėS50‚Äô on body with black ink and plain cap, containing yellow to orange granules; available in:
               Bottles of  28 capsules                                                         NDC 59651-467-28               Cartons of 28 Capsules (4 x 7 Unit-Dose)                           NDC 59651-467-29
Store at 20¬įC to 25¬įC (68¬įF to 77¬įF); excursions permitted to 15¬įC to 30¬įC (59¬įF to 86¬įF) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
17 Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide).
Hepatotoxicity
Inform patients of the signs and symptoms of hepatotoxicity. Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider immediately for signs or symptoms of hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Cardiovascular Events
Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider if they develop symptoms of heart failure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
QT Prolongation and Torsade de Pointes
Inform patients of the signs and symptoms of QT prolongation. Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider immediately in the event of syncope, pre-syncopal symptoms, and cardiac palpitations [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Hypertension
Inform patients of the signs and symptoms of hypertension. Advise patients to undergo routine blood pressure monitoring and to contact their health care provider if blood pressure is elevated or if they experience signs or symptoms of hypertension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Hemorrhagic Events
Advise patients that sunitinib malate can cause severe bleeding. Advise patients to immediately contact their healthcare provider for bleeding or symptoms of bleeding [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Gastrointestinal Disorders
Advise patients that gastrointestinal disorders such as diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, and constipation may develop during sunitinib malate treatment and to seek immediate medical attention if they experience persistent or severe abdominal pain because cases of gastrointestinal perforation and fistula have been reported in patients taking sunitinib malate [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5),  Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Dermatologic Effects and Toxicities
Advise patients that depigmentation of the hair or skin may occur during treatment with sunitinib malate due to the drug color (yellow). Other possible dermatologic effects may include dryness, thickness or cracking of skin, buler or rash on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. Severe dermatologic toxicities including Stevens-Johnson syndrome, Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis, erythema multiforme, and necrotizing fasciitis have been reported. Advise patients to immediately inform their healthcare provider if severe dermatologic reactions occur [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9), Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Reversible Posterior Leukoencephalopathy Syndrome
Inform patients of the signs and symptoms of reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome. Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider if they develop symptoms of reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)].
Thyroid Dysfunction
Advise patients that sunitinib malate can cause thyroid dysfunction. Advise patient to contact their healthcare provider if symptoms of abnormal thyroid function occur [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)].
Hypoglycemia
Advise patients that sunitinib malate can cause severe hypoglycemia and may be more severe in patients with diabetes taking antidiabetic medications. Inform patients of the signs, symptoms, and risks associated with hypoglycemia. Advise patients to immediately inform their healthcare provider if severe signs or symptoms of hypoglycemia occur [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12)].
Osteonecrosis of the Jaw
Advise patients regarding good oral hygiene practices and to inform their healthcare provider of any planned dental procedures. Advise patients to immediately contact their healthcare provider for signs or symptoms associated with osteonecrosis of the jaw [see Warnings and Precautions (5.13)].
Impaired Wound Healing
Advise patients that sunitinib malate impairs wound healing. Advise patients to inform their healthcare provider of any planned surgical procedures [see Warnings and Precautions (5.14)].
Concomitant Medications
Advise patients to inform their healthcare providers of all concomitant medications, including over-the-counter medications and dietary supplements [see Drug Interactions (7)].
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential to inform their healthcare provider of a known or suspected pregnancy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.15), Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment and for 4 weeks after receiving the last dose of sunitinib malate [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
Advise males with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment and for 7 weeks after receiving the last dose of sunitinib malate [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
Lactation
Advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with sunitinib malate and for at least 4 weeks after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
Infertility
Advise patients that sunitinib malate may impair male and female fertility [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3),  Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
Missed Dose
Advise patients that miss a dose of sunitinib malate by less than 12 hours to take the missed dose right away. Advise patients that miss a dose of sunitinib malate by more than 12 hours to take the next scheduled dose at its regular time. Dispense with Medication Guide available at:  www.aurobindousa.com/medication-guides
Distributed by: Aurobindo Pharma USA, Inc. 279 Princeton-Hightstown Road East Windsor, NJ 08520
Manufactured by: Eugia Pharma Specialities Limited Hyderabad - 500032
India Dispense with Medication Guide available at: www.aurobindousa.com/medication-guides
MEDICATION GUIDE Sunitinib Malate Capsules (soo ni‚Äô ti nib mal‚Äô ate) What is the most important information I should know about sunitinib malate capsules? Sunitinib malate capsules can cause serious side effects including: ¬†Your healthcare provider should do blood tests to check your liver function before you start taking and during treatment with sunitinib malate capsules. Your healthcare provider may temporarily stop, reduce your dose, or permanently stop treatment with sunitinib malate capsules if you develop liver problems.¬†See ‚ÄúWhat are the possible side effects of sunitinib malate capsules?‚ÄĚ for more information about side effects.
- Severe liver problems, that can lead to death. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you develop any of the following signs and symptoms of liver problems during treatment with sunitinib malate capsules:
- itching
- yellow eyes or skin
- dark urine
- pain or discomfort in the right upper stomach area
What are sunitinib malate capsules?  Sunitinib malate capsule is a prescription medicine used to treat:   It is not known if sunitinib malate capsules are safe and effective in children.
- a rare cancer of the stomach, bowel, or esophagus called gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) and when:
- you have taken the medicine imatinib mesylate and it did not stop the cancer from growing, or
- you cannot take imatinib mesylate.
- advanced kidney cancer (advanced renal cell carcinoma or RCC).
- adults with kidney cancer that has not spread (localized), and who are at high risk of RCC coming back again after having kidney surgery.
- a type of pancreatic cancer called pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (pNET), that has progressed and cannot be treated with surgery.
Before taking sunitinib malate capsules tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:       Females who are able to become pregnant:
- have any heart problems
- have high blood pressure
- have thyroid problems
- have a history of low blood sugar or diabetes
- have kidney function problems (other than cancer)
- have liver problems
- have any bleeding problem
- plan to have surgery or have had a recent surgery. You should stop taking sunitinib malate capsules at least 3 weeks before planned surgery. See ‚ÄúWhat are the possible side effects of sunitinib malate capsules?‚ÄĚ
- have seizures
- have or have had pain in the mouth, teeth or jaw, swelling or sores inside the mouth, numbness or a feeling of heaviness in the jaw, or loosening of a tooth
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. Sunitinib malate capsules can harm your unborn baby.
Tell your healthcare provider right away if you become pregnant or think you are pregnant during treatment with sunitinib malate capsules.    Males with female partners who are able to become pregnant should use effective birth control (contraception) during treatment and for 7 weeks after your last dose of sunitinib malate capsules.     Sunitinib malate capsules may cause fertility problems in males and females. Tell your healthcare provider if this is a concern for you. 
- Your healthcare provider should do a pregnancy test before you start treatment with sunitinib malate capsules.
- You should use effective birth control (contraception) during treatment and for at least 4 weeks after your last dose of sunitinib malate capsules.
 Tell all of your healthcare providers and dentists that you are taking sunitinib malate capsules. They should talk to the healthcare provider who prescribed sunitinib malate capsules for you, before you have any surgery, or medical or dental procedure.  Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription medicines and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. Using sunitinib malate capsules with certain other medicines can cause serious side effects. You may have an increased risk of severe jawbone problems (osteonecrosis) if you take sunitinib malate capsules and a bisphosphonate medicine. Especially tell your healthcare provider if you are taking or have taken an osteoporosis medicine. Know the medicines you take. Keep a ul of them to show your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medicine.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. Do not breastfeed during treatment with sunitinib malate capsules and for at least 4 weeks (1 month) after the last dose.
How should I take sunitinib malate capsules?
- Take sunitinib malate capsules exactly the way your healthcare provider tells you.
- Take sunitinib malate capsules 1 time each day with or without food.
- If you take sunitinib malate capsules for GIST or RCC, you will usually take your medicine for 4 weeks (28 days) and then stop for 2 weeks (14 days). This is 1 cycle of treatment. You will repeat this cycle for as long as your healthcare provider tells you to.
- If you take sunitinib malate capsules for pNET, take it 1 time each day until your healthcare provider tells you to stop.
- Do not drink grapefruit juice or eat grapefruit during your treatment with sunitinib malate capsules. They may cause you to have too much sunitinib malate capsules in your body.
- Your healthcare provider may do blood tests before each cycle of treatment to check you for side effects.
- If you miss a dose of sunitinib malate capsules by less than 12 hours, take the missed dose right away. If you miss a dose of sunitinib malate capsules by more than 12 hours, just take your next dose at your regular time. Do not make up the missed dose. Tell your healthcare provider about any missed dose.
- Call your healthcare provider right away, if you take too much sunitinib malate capsules.
What are possible side effects of sunitinib malate capsules? Sunitinib malate capsules may cause serious side effects, including:  
- See ‚ÄúWhat is the most important information I should know about sunitinib malate capsules?‚ÄĚ
- Heart problems. Heart problems may include heart failure, heart attack and heart muscle problems (cardiomyopathy) that can lead to death. Tell your healthcare provider if you feel very tired, are short of breath, or have swollen feet and ankles.
- Abnormal heart rhythm changes. Changes in the electrical activity of your heart called QT prolongation can cause irregular heart beats that can be life threatening. Your healthcare provider may do electrocardiograms and blood tests (electrolytes) to watch for these problems during your treatment with sunitinib malate capsules. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you feel dizzy, faint, or have abnormal heartbeats during your treatment with sunitinib malate capsules
 Your healthcare provider may prescribe medicine for you to treat high blood pressure, if needed.  
- you feel faint or lightheaded, or you pass out
- dizziness
- feel your heart beat is irregular or fast
- High blood pressure. High blood pressure is common with sunitinib malate capsules and may sometimes be severe. Follow your healthcare provider’s instructions about having your blood pressure checked regularly. Call your healthcare provider if your blood pressure is high, or if you have any of the following signs or symptoms of high blood pressure:
- severe headache
- lightheadedness
- dizziness
- change in vision
 
- Bleeding problems. Bleeding is common with sunitinib malate capsules, but sunitinib malate capsules can also cause severe bleeding problems that can lead to death. Your healthcare provider will monitor you for bleeding and may do blood tests if needed. Call your healthcare provider right away if you have any of these symptoms or a serious bleeding problem during treatment with sunitinib malate capsules, including:
- painful, swollen stomach (abdomen)
- vomiting blood
- coughing up blood
- black, sticky stools
- bloody urine
- headache
- change in your mental status
 
- Serious stomach and intestinal problems, that can sometimes lead to death. Some people have had tears in their stomach or intestine (perforation), or have developed an abnormal opening between the stomach and intestine (fistula). Get medical help right away if you get stomach-area (abdominal) pain that does not go away or is severe during treatment with sunitinib malate capsules.
 
- Tumor lysis syndrome (TLS). TLS is caused by the fast breakdown of cancer cells and may lead to death. TLS can cause kidney failure and the need for dialysis treatment, abnormal heart rhythm, seizure, and sometimes death. Your healthcare provider may do blood tests to check you for TLS.
 
- Abnormal changes in the brain (Reversible Posterior Leukoencephalopathy Syndrome [RPLS]). RPLS can cause a collection of symptoms including headache, confusion, and vision loss. Some people who have taken sunitinib malate capsules have developed RPLS that can lead to death.
 
- Thrombotic microangiopathy (TMA) including thrombotic thrombocytopenia purpura (TTP) and hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS). TMA is a condition that involves injury to the smallest blood vessels, and blood clots that can happen while taking sunitinib malate capsules. TMA is accompanied by a decrease in red cells and cells that are involved with clotting. TMA may harm your body’s organs such as the brain and kidneys, and can sometimes lead to death.
 
- Protein in your urine. Some people who have taken sunitinib malate capsules have developed protein in their urine, and in some cases, kidney problems that can lead to death. Your healthcare provider will check you for this problem.
 If you have any signs or symptoms of severe skin reactions, stop taking sunitinib malate capsules and call your healthcare provider or get medical help right away. 
- Serious skin and mouth reactions. Treatment with sunitinib malate capsules has caused severe skin reactions that can lead to death, including:
- severe rash with bulers or peeling of the skin.
- painful sores or ulcers on the skin, lips or inside the mouth.
- tissue damage (necrotizing fasciitis).
 
- Thyroid problems. Your healthcare provider may do tests to check your thyroid function during sunitinib malate capsules treatment. Tell your healthcare provider if you have any of the following signs and symptoms during your treatment with sunitinib malate capsules:
- tiredness that gets worse and does not go away
- loss of appetite
- problems with heat
- feeling nervous or agitated, tremors
- sweating
- nausea or vomiting
- diarrhea
- fast heat rate
- weight gain or weight loss
- feeling depressed
- irregular menstrual periods or no menstrual periods
- headache
- hair los
- Low blood sugar (hypoglycemia). Low blood sugar can happen with sunitinib malate capsules, and may cause you to become unconscious, or you may need to be hospitalized. Low blood sugar with sunitinib malate capsules may be worse in people who have diabetes and take antidiabetic medicines. Your healthcare provider should check your blood sugar levels regularly during treatment with sunitinib malate capsules and may need to adjust the dose of your antidiabetic medicines. Call your healthcare provider right away if you have any of the following signs or symptoms of low blood sugar during your treatment with sunitinib malate capsules:
- Headache
- drowsiness
- weakness
- dizziness
- confusion
- irritability
- hunger
- fast heart beat
- sweating
- feeling jitter
- Jawbone problems (osteonecrosis). Severe jawbone problems have happened in some people who take sunitinib malate capsules. Certain risk factors such as taking a bisphosphonate medicine or having dental disease may increase your risk of getting osteonecrosis. Your healthcare provider may tell you to see your dentist before you start taking sunitinib malate capsules. Your healthcare provider may tell you to avoid dental procedures, if possible, during your treatment with sunitinib malate capsules, especially if you are receiving a bisphosphonate medicine into a vein (intravenous). Tell your healthcare provider if you plan to have any dental procedures before or during treatment with sunitinib malate capsules.
- You should stop taking sunitinib malate capsules at least 3 weeks before planned dental procedures.
- Your healthcare provider should tell you when you may start taking sunitinib malate capsules again after dental procedures.
Your healthcare provider may temporarily stop, reduce your dose, or permanently stop treatment with sunitinib malate capsules if you develop serious side effects.  Common side effects of sunitinib malate capsules include: 
- Wound healing problems. Wound healing problems have happened in some people who take sunitinib malate capsules. Tell your healthcare provider if you plan to have any surgery before or during treatment with sunitinib malate capsules.
- You should stop taking sunitinib malate capsules at least 3 weeks before planned surgery.
- Your healthcare provider should tell you when you may start taking sunitinib malate capsules again after surgery.
The medicine in sunitinib malate capsules is yellow, and it may make your skin look yellow. Your skin and hair may get lighter in color. Sunitinib malate capsules may also cause other skin problems including: dryness, thickness or cracking of the skin. These are not all of the possible side effects of sunitinib malate capsules. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at1-800-FDA-1088.
- tiredness
- weakness
- diarrhea
- pain, swelling or sores inside of your mouth
- nausea
- loss of appetite
- indigestion
- vomiting
- stomach-area (abdominal) pain
- bulers or rash on the palms of your hands and soles of your feet
- high blood pressure
- taste changes
- low platelet counts
How do I store sunitinib malate capsules? Keep sunitinib malate capsules and all medicines out of the reach of children.
- Store sunitinib malate capsules at room temperature, between 68¬įF to 77¬įF (20¬įC to 25¬įC).
General information about the safe and effective use of sunitinib malate capsules. Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those uled in a Medication Guide. Do not use sunitinib malate capsules for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give sunitinib malate capsules to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. They may harm them. You can ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for information about sunitinib malate capsules that is written for health professionals. What are the ingredients in sunitinib malate capsules? Active ingredient: sunitinib malate Inactive ingredients: croscarmellose sodium, magnesium stearate, mannitol, and povidone. Red opaque gelatin capsule shells: gelatin, iron oxide red, and titanium dioxide. Olive green opaque gelatin capsule shells: FD&C Blue 2, gelatin, iron oxide red, iron oxide yellow, and titanium dioxide. Light green opaque gelatin capsule shells: FD&C Blue 2, gelatin, iron oxide yellow, and titanium dioxide. White printing ink: potassium hydroxide, propylene glycol, shellac, and titanium dioxide. Black printing ink: black iron oxide, potassium hydroxide, propylene glycol, and shellac. Distributed by: Aurobindo Pharma USA, Inc. 279 Princeton-Hightstown RoadEast Windsor, NJ 08520 Manufactured by: Eugia Pharma Specialities Limited Hyderabad - 500032India For more information call Aurobindo Pharma USA, Inc. at 1-866-850-2876.
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Revised: November 2023
Package Label-principal Display Panel - 12.5 Mg (28 Capsules Bottle)
NDC 59651-464-28   Sunitinib Malate Capsules 12.5 mg*   PHARMACIST: Dispense the Medication Guide provided separately to each patient.
Rx only                             28 Capsules AUROBINDO
Package Label-principal Display Panel -12.5 Mg 28 Capsules (4 X 7 Unit-dose)
NDC 59651-464-29 Rx only   Sunitinib Malate Capsules 12.5 mg*   PHARMACIST: Dispense the Medication Guide provided separately to each patient.
AUROBINDO                    28 Capsules (4 x 7 Unit-Dose)
Package Label-principal Display Panel - 25 Mg (28 Capsules Bottle)
NDC 59651-465-28   Sunitinib Malate Capsules 25 mg*   PHARMACIST: Dispense the Medication Guide provided separately to each patient.
Rx only                             28 Capsules AUROBINDO
Package Label-principal Display Panel - 25 Mg 28 Capsules (4 X 7 Unit-dose)
NDC 59651-465-29 Rx only   Sunitinib Malate Capsules 2 5 mg*   PHARMACIST: Dispense the Medication Guide provided separately to each patient.
AUROBINDO                    28 Capsules (4 x 7 Unit-Dose)
Package Label-principal Display Panel - 37.5 Mg (28 Capsules Bottle)
NDC 59651-466-28   Sunitinib Malate Capsules 37.5 mg*   PHARMACIST: Dispense the Medication Guide provided separately to each patient.
Rx only                             28 Capsules AUROBINDO
Package Label-principal Display Panel - 37.5 Mg 28 Capsules (4 X 7 Unit-dose)
NDC 59651-466-29 Rx only   Sunitinib Malate Capsules 37.5 mg*   PHARMACIST: Dispense the Medication Guide provided separately to each patient.
AUROBINDO                    28 Capsules (4 x 7 Unit-Dose)
Package Label-principal Display Panel - 50 Mg (28 Capsules Bottle)
NDC 59651-467-28   Sunitinib Malate Capsules 50 mg*   PHARMACIST: Dispense the Medication Guide provided separately to each patient.
Rx only                             28 Capsules AUROBINDO
Package Label-principal Display Panel - 50 Mg 28 Capsules (4 X 7 Unit-dose)
NDC 59651-467-29 Rx only   Sunitinib Malate Capsules 50 mg*   PHARMACIST: Dispense the Medication Guide provided separately to each patient.
AUROBINDO                   28 Capsules (4 x 7 Unit-Dose)
DISCLAIMER:
"This tool does not provide medical advice, and is for informational and educational purposes only, and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, treatment or diagnosis. Call your doctor to receive medical advice. If you think you may have a medical emergency, please dial 911."
"Do not rely on openFDA to make decisions regarding medical care. While we make every effort to ensure that data is accurate, you should assume all results are unvalidated. We may limit or otherwise restrict your access to the API in line with our Terms of Service."
"This product uses publicly available data from the U.S. National Library of Medicine (NLM), National Institutes of Health, Department of Health and Human Services; NLM is not responsible for the product and does not endorse or recommend this or any other product."
PillSync may earn a commission via links on our site


