Vanos Dailymed
Generic: fluocinonide is used for the treatment of Facial Dermatoses Foot Dermatoses Hand Dermatoses Hypersensitivity Inflammation Leg Dermatoses Pruritus Scalp Dermatoses
Go PRO for all pill images
Rx Only
FOR TOPICAL USE ONLYNOT FOR OPHTHALMIC, ORAL, OR INTRAVAGINAL USE
Description
VANOS (fluocinonide) Cream, 0.1% contains fluocinonide, a synthetic corticosteroid for topical dermatologic use. The corticosteroids constitute a class of primarily synthetic steroids used topically as anti-inflammatory and antipruritic agents. Fluocinonide has the chemical name 6 alpha, 9 alpha-difluoro-11 beta, 21-dihydroxy-16 alpha, 17 alpha-isopropylidenedioxypregna-1, 4-diene-3,20-dione 21-acetate. Its chemical formula is C26H32F2O7 and it has a molecular weight of 494.58.
It has the following chemical structure:
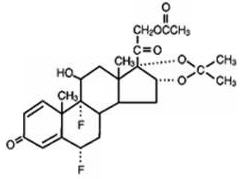
Fluocinonide is an almost odorless white to creamy white crystalline powder. It is practically insoluble in water and slightly soluble in ethanol.
Each gram of VANOS Cream contains 1 mg micronized fluocinonide in a cream base of propylene glycol USP, dimethyl isosorbide, glyceryl stearate (and) PEG-100 stearate, glyceryl monostearate NF, purified water USP, carbopol 980 NF, diisopropanolamine, and citric acid USP.
Clinical Pharmacology
Like other topical corticosteroids, VANOS (fluocinonide) Cream, has anti-inflammatory, antipruritic, and vasoconstrictive properties. The mechanism of the anti-inflammatory activity of topical corticosteroids, in general, is unclear. However, corticosteroids are thought to act by induction of phospholipase A2 inhibitory proteins, collectively called lipocortins. It is postulated that these proteins control the biosynthesis of potent mediators of inflammation such as prostaglandins and leukotrienes by inhibiting the release of their common precursor, arachadonic acid. Arachadonic acid is released from membrane phospholipids by phospholipase A2.
Pharmacokinetics
The extent of percutaneous absorption of topical corticosteroids is determined by many factors including the vehicle and the integrity of the epidermal barrier. Topical corticosteroids can be absorbed from normal intact skin. Inflammation and/or other disease processes in the skin may increase percutaneous absorption.
Vasoconstrictor studies performed with VANOS Cream, 0.1% in healthy subjects indicate that it is in the super-high range of potency as compared with other topical corticosteroids; however, similar blanching scores do not necessarily imply therapeutic equivalence.
Application of VANOS Cream, 0.1% twice daily for 14 days in 18 adult patients with plaque-type psoriasis (10–50% BSA, mean 19.6% BSA) showed demonstrable HPA-axis suppression in 2 patients (with 12% and 25% BSA) where the criterion for HPA-axis suppression is a serum cortisol level of less than or equal to 18 micrograms per deciliter 30 minutes after stimulation with cosyntropin (ACTH1–24) (See PRECAUTIONS: General and Pediatric Use ).
HPA-axis suppression has not been evaluated in psoriasis patients who are less than 18 years of age. HPA-axis suppression has been evaluated in pediatric patients with atopic dermatitis 12 to 18 years of age (See PRECAUTIONS: Pediatric Use ).
Clinical Studies
Two adequate and well-controlled efficacy and safety studies of VANOS Cream have been completed, one in adult patients with plaque-type psoriasis (Table 1), and one in adult patients with atopic dermatitis (Table 2). In each of these studies, patients with between 2% and 10% body surface area involvement at Baseline treated all affected areas either once daily or twice daily with VANOS Cream for 14 consecutive days. The primary measure of efficacy was the proportion of patients whose condition was cleared or almost cleared at the end of treatment. The results of these studies are presented in the tables below as percent and number of patients achieving treatment success at Week 2.
Table 1: Plaque-Type Psoriasis in Adults VANOS Cream, once daily (n=107) Vehicle, once daily (n=54) VANOS Cream, twice daily (n=107) Vehicle, twice daily (n=55) Patients cleared 0 (0) 0 (0) 6 (6%) 0 (0) Patients achieving treatment success Cleared or almost cleared 19 (18%) 4 (7%) 33 (31%) 3 (5%)
Table 2: Atopic Dermatitis in Adults VANOS Cream, once daily (n=109) Vehicle, once daily (n=50) VANOS Cream, twice daily (n=102) Vehicle, twice daily (n=52) Patients cleared 11 (10%) 0 (0) 17 (17%) 0 (0) Patients achieving treatment success Cleared or almost cleared 64 (59%) 6 (12%) 58 (57%) 10 (19%)
No efficacy studies have been conducted to compare VANOS (fluocinonide) Cream, 0.1% with any other topical corticosteroid product, including fluocinonide cream 0.05%.
Indications And Usage
VANOS (fluocinonide) Cream, 0.1%, is a corticosteroid indicated for the relief of the inflammatory and pruritic manifestations of corticosteroid responsive dermatoses in patients 12 years of age or older (See PRECAUTIONS: Pediatric Use ).
Treatment beyond 2 consecutive weeks is not recommended and the total dosage should not exceed 60 g/week because the safety of VANOS Cream for longer than 2 weeks has not been established and because of the potential for the drug to suppress the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis. Therapy should be discontinued when control of the disease is achieved. If no improvement is seen within 2 weeks, reassessment of the diagnosis may be necessary. Do not use more than half of the 120 g tube per week.
Contraindications
VANOS Cream is contraindicated in those patients with a history of hypersensitivity to any of the components of the preparation.
Precautions
General
Systemic absorption of topical corticosteroids can produce reversible hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis suppression with the potential for gluococorticosteroid insufficiency after withdrawal of treatment. Manifestations of Cushing's syndrome, hyperglycemia, and glucosuria can also be produced in some patients by systemic absorption of topical corticosteroids while on treatment. Use of more than one corticosteroid-containing product at the same time may increase total systemic glucocorticoid exposure. In addition, use of VANOS Cream for longer than 2 weeks may also suppress the immune system (see PRECAUTIONS: Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, and Impairment of Fertility ).
Patients applying a topical steroid to a large surface area or to areas under occlusion should be evaluated periodically for evidence of HPA-axis suppression. This may be done by using cosyntropin (ACTH1–24) stimulation testing. Patients should not be treated with VANOS Cream for more than 2 weeks at a time and only small areas should be treated at any time due to the increased risk of HPA-axis suppression.
If HPA-axis suppression is noted, an attempt should be made to withdraw the drug, to reduce the frequency of application, or to substitute a less potent corticosteroid. Recovery of HPA-axis function is generally prompt upon discontinuation of topical corticosteroids. Infrequently, signs and symptoms of glucocorticosteroid insufficiency may occur requiring supplemental systemic corticosteroids. For information on systemic supplementation, see prescribing information for those products.
Application of VANOS Cream, 0.1% twice daily for 14 days in 18 adult patients with plaque-type psoriasis (10–50% BSA, mean 19.6% BSA) and 31 adult patients (17 treated once daily; 14 treated twice daily) with atopic dermatitis (2–10% BSA, mean 5% BSA) showed demonstrable HPA-axis suppression in 2 patients with psoriasis (with 12% and 25% BSA) and 1 patient with atopic dermatitis (treated once daily, 4% BSA) where the criterion for HPA-axis suppression is a serum cortisol level of less than or equal to 18 micrograms per deciliter 30 minutes after stimulation with cosyntropin (ACTH1–24) (See CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY ).
Controlled clinical efficacy studies of VANOS Cream in pediatric patients younger than 17 years of age have not been conducted; (See PRECAUTIONS: Pediatric Use ).
HPA-axis suppression has not been evaluated in psoriasis patients who are less than 18 years of age.
Pediatric patients may be more susceptible to systemic toxicity from equivalent doses due to their larger skin surface to body mass ratios. (See PRECAUTIONS: Pediatric Use ).
If irritation develops, VANOS Cream should be discontinued and appropriate therapy instituted. Allergic contact dermatitis with corticosteroids is usually diagnosed by observing failure to heal rather than noting a clinical exacerbation as with most topical products not containing corticosteroids. Such an observation should be corroborated with appropriate diagnostic patch testing.
If concomitant skin infections are present or develop, an appropriate antifungal or antibacterial agent should be used. If a favorable response does not occur promptly, use of VANOS Cream should be discontinued until the infection has been adequately controlled.
VANOS Cream should not be used in the treatment of rosacea or perioral dermatitis, and should not be used on the face, groin, or axillae.
Information for the Patient
Patients using VANOS Cream should receive the following information and instructions. This information is intended to aid in the safe and effective use of this medication. It is not a disclosure of all possible adverse or unintended effects:
- 1)VANOS Cream is to be used as directed by the physician. It is for external use only. Avoid contact with the eyes. It should not be used on the face, groin, and underarms.
- 2)VANOS Cream should not be used for any disorder other than that for which it was prescribed.
- 3)The treated skin area should not be bandaged or otherwise covered or wrapped, so as to be occlusive unless directed by the physician.
- 4)Patients should report to their physician any signs of local adverse reactions.
- 5)Other corticosteroid-containing products should not be used with VANOS Cream without first talking to the physician.
- 6)As with other corticosteroids, therapy should be discontinued when control is achieved. If no improvement is seen in 2 weeks, the patient should be instructed to contact a physician. The safety of the use of VANOS Cream for longer than 2 weeks has not been established.
- 7)Patients should be informed to not use more than 60 g per week of VANOS Cream. Do not use more than half of the 120 g tube per week.
- 8)Patients should inform their physicians that they are using VANOS Cream if surgery is contemplated.
- 9)Patients should wash their hands after applying medication.
Laboratory Tests
The cosyntropin (ACTH1–24) stimulation test may be helpful in evaluating patients for HPA-axis suppression.
Carcinogenesis, M utagenesis, and Impairment of Fertility
Long-term animal studies have not been performed to evaluate the carcinogenic potential of VANOS Cream because of severe immunosuppression induced in a 13-week dermal rat study. The effects of fluocinonide on fertility have not been evaluated.
Fluocinonide revealed no evidence of mutagenic or clastogenic potential based on the results of two in vitro genotoxicity tests (Ames test and chromosomal aberration assay using human lymphocytes). However, fluocinonide was positive for clastogenic potential when tested in the in vivo mouse micronucleus assay.
Topical (dermal) application of 0.0003%–0.03% fluocinonide cream to rats once daily for 13 weeks resulted in a toxicity profile generally associated with long-term exposure to corticosteroids including decreased skin thickness, adrenal atrophy, and severe immunosuppression. A NOAEL could not be determined in this study. In addition, topical (dermal) application of 0.1% fluocinonide cream plus UVR exposure to hairless mice for 13 weeks and 150–900 mg/kg/day of 0.1% fluocinonide cream to minipigs (a model which more closely approximates human skin) for 13 weeks produced glucocorticoid-related suppression of the HPA axis, with some signs of immunosuppression noted in the dermal minipig study. Although the clinical relevance of the findings in animals to humans is not clear, sustained glucocorticoid-related immune suppression may increase the risk of infection and possibly the risk for carcinogenesis.
Pregnancy Category C
Teratogenic Effects
Corticosteroids have been shown to be teratogenic in laboratory animals when administered systemically at relatively low dosage levels. Some corticosteroids have been shown to be teratogenic after dermal application in laboratory animals.
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Therefore, VANOS Cream should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Nursing Mothers
Systemically administered corticosteroids appear in human milk and could suppress growth, interfere with endogenous corticosteroid production, or cause other untoward effects. It is not known whether topical administration of corticosteroids could result in sufficient systemic absorption to produce detectable quantities in breast milk. Nevertheless, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
Pediatric Use
Safety and efficacy of VANOS Cream in pediatric patients younger than 12 years of age have not been established; therefore use in pediatric patients younger than 12 years of age is not recommended.
HPA-axis suppression was studied in 4 sequential cohorts of pediatric patients with atopic dermatitis covering at least 20% of the body surface area, treated once daily or twice daily with VANOS Cream. The first cohort of 31 patients (mean 36.3% BSA) 12 to < 18 years old; the second cohort included 31 patients (mean 39.0% BSA) 6 to < 12 years old; the third cohort included 30 patients (mean 34.6% BSA) 2 to < 6 years old; the fourth cohort included 31 patients (mean 40.0% BSA) 3 months to < 2 years old. VANOS Cream caused HPA-axis suppression in 1 patient in the twice daily group in Cohort 1, 2 patients in the twice daily group in Cohort 2, and 1 patient in the twice daily group in Cohort 3. Follow-up testing 14 days after treatment discontinuation, available for all 4 suppressed patients, demonstrated a normally responsive HPA-axis. Signs of skin atrophy were present at baseline and severity was not determined making it difficult to assess local skin safety. Therefore, the safety of VANOS Cream in patients younger than 12 years of age has not been demonstrated.
Because of a higher ratio of skin surface area to body mass, pediatric patients are at a greater risk than adults of HPA-axis suppression and Cushing's syndrome when they are treated with topical corticosteroids. They are therefore also at greater risk of adrenal insufficiency during or after withdrawal of treatment. Adverse effects including striae have been reported with inappropriate use of topical corticosteroids in infants and children.
HPA-axis suppression, Cushing's syndrome, linear growth retardation, delayed weight gain, and intracranial hypertension have been reported in children receiving topical corticosteroids. Manifestations of adrenal suppression in children include low plasma cortisol levels and absence of response to cosyntropin (ACTH1–24) stimulation. Manifestations of intracranial hypertension include bulging fontanelles, headaches, and bilateral papilledema.
Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of VANOS Cream did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious.
Adverse Reactions
In clinical trials, a total of 443 adult patients with atopic dermatitis or plaque-type psoriasis were treated once daily or twice daily with VANOS Cream for 2 weeks. The most commonly observed adverse events in these clinical trials were as follows:
Table 3: Most Commonly Observed Adverse Events in Adult Clinical Trials Adverse Event VANOS Cream, once daily (n=216) VANOS Cream, twice daily (n=227) Vehicle Cream, once or twice daily (n=211) Headache 8/216 (3.7%) 9/227 (4.0%) 6/211 (2.8%) Application Site Burning 5/216 (2.3%) 4/227 (1.8%) 14/211 (6.6%) Nasopharyngitis 2/216 (0.9%) 3/227 (1.3%) 3/211 (1.4%) Nasal Congestion 3/216 (1.4%) 1/227 (0.4%) 0 Unspecified Application Site Reaction 1/216 (0.4%) 1/227 (0.4%) 3/211 (1.4%)
No other adverse events were reported by more than 1 subject receiving active treatment. The incidence of all adverse events was similar between the active treatment groups and the vehicle control groups. Safety in patients 12 to 17 years of age was similar to that observed in adults.
The following additional local adverse reactions have been reported with topical corticosteroids, and they may occur more frequently with the use of occlusive dressings and higher potency corticosteroids. These reactions are uled in an approximate decreasing order of occurrence: burning, itching, irritation, dryness, folliculitis, hypertrichosis, acneiform eruptions, hypopigmentation, perioral dermatitis, allergic contact dermatitis, maceration of the skin, secondary infection, skin atrophy, striae, and miliaria.
Systemic absorption of topical corticosteroids has produced hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis suppression manifestations of Cushing's syndrome, hyperglycemia, and glucosuria in some patients.
Overdosage
Topically applied VANOS Cream can be absorbed in sufficient amounts to produce systemic effects (see PRECAUTIONS ).
Dosage And Administration
For psoriasis, apply a thin layer of VANOS Cream once or twice daily to the affected skin areas as directed by a physician. Twice daily application for the treatment of psoriasis has been shown to be more effective in achieving treatment success during 2 weeks of treatment.
For atopic dermatitis, apply a thin layer of VANOS Cream once daily to the affected skin areas as directed by a physician. Once daily application for the treatment of atopic dermatitis has been shown to be as effective as twice daily treatment in achieving treatment success during 2 weeks of treatment (See CLINICAL STUDIES ).
For corticosteroid responsive dermatoses, other than psoriasis or atopic dermatitis, apply a thin layer of VANOS Cream once or twice daily to the affected areas as directed by a physician.
Treatment with VANOS Cream should be limited to 2 consecutive weeks, and no more than 60 g/week should be used. Do not use more than half of the 120 g tube per week.
Therapy should be discontinued when control has been achieved. If no improvement is seen within 2 weeks, reassessment of diagnosis may be necessary.
How Supplied
VANOS (fluocinonide) Cream 0.1% is supplied in tubes as follows:
60 g (NDC 54868-6204-0)
STORAGE AND HANDLING SECTION
Store at controlled room temperature: 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F).
Manufactured for:Medicis, The Dermatology CompanyScottsdale, AZ 85256
Manufactured by:Contract Pharmaceuticals Ltd.Mississauga, OntarioCanada L5N 6L6
Made in Canada
U.S. Patents 6,765,001; 7,217,422; 7,220,424 and Patents PendingVANOS is a registered trademark of Medicis Pharmaceutical Corporation.
Prescribing information as of February 2010.
05100002

Relabeling of "Additional Barcode Label" by: Physicians Total Care, Inc.Tulsa, OK 74146
Principal Display Panel - 60 G Tube Carton
Vanos ® (fluocinonide) cream 0.1%
FOR TOPICAL USE ONLYNOT FOR OPHTHALMIC, ORAL,OR INTRAVAGINAL USE
Rx only
60 g

DISCLAIMER:
"This tool does not provide medical advice, and is for informational and educational purposes only, and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, treatment or diagnosis. Call your doctor to receive medical advice. If you think you may have a medical emergency, please dial 911."
"Do not rely on openFDA to make decisions regarding medical care. While we make every effort to ensure that data is accurate, you should assume all results are unvalidated. We may limit or otherwise restrict your access to the API in line with our Terms of Service."
"This product uses publicly available data from the U.S. National Library of Medicine (NLM), National Institutes of Health, Department of Health and Human Services; NLM is not responsible for the product and does not endorse or recommend this or any other product."
PillSync may earn a commission via links on our site